* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
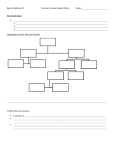
Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Organization of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system The Nervous System Nervous System: Consists of all the nerve cells. **It is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication system. Central Nervous System (CNS): the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body. Organization of the nervous system 4 The central nervous system Brain Spinal cord A collection of neurons and supportive tissue running from the base of the brain down the center of the back Protected by spinal column Central Nervous System – The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Organization of the nervous system The Nerves • Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. • They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System • There are two divisions of the peripheral nervous system: – the somatic, or voluntary portion – the autonomic, or involuntary portion Somatic Nervous System: The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles (voluntary). Autonomic Nervous System: Part of the PNS that controls the glands and other muscles (involuntary). Organization of the nervous system Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • The autonomic portion of the peripheral nervous system governs involuntary, visceral functions…such as heart and breathing rate, blood pressure, etc. • It is divided into two systems: – Sympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. – Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its energy. Organization of the nervous system The Sympathetic Nervous System • Mobilizes the body’s resources for emergencies and creates the fight-orflight response. • “Arouses” Organization of the nervous system The Parasympathetic Nervous System • Activates processes that conserve bodily resources… slowing heart rate, reducing blood pressure, etc. • “Calms” (rest and digest) Recap See “Fight or Flight” in action in this short cartoon: http://cmhc.utexas.edu/stressreces s/Level_One/fof.html Review • In everyday situations the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system work together to keep you in a steady internal rate. • What happens if these are out of wack? –. Journal • How does information flow through your nervous system as you pick up a fork? Summarize this process.