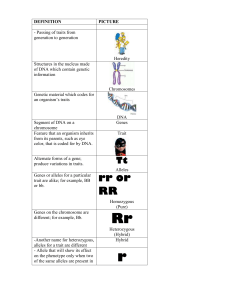
Allele: One of the variant forms of the DNA sequence at a particular
... eye color. One form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than the other form (the recessive one). Some alleles may have no direct affect (silent) but may tag genes or other nearby alleles that are causative or contribute to a genetic characteristic, such as a disease or disease sus ...
... eye color. One form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than the other form (the recessive one). Some alleles may have no direct affect (silent) but may tag genes or other nearby alleles that are causative or contribute to a genetic characteristic, such as a disease or disease sus ...
definition - Humble ISD
... chromosome Feature that an organism inherits from its parents, such as eye color, that is coded for by DNA. Alternate forms of a gene; produce variations in traits. ...
... chromosome Feature that an organism inherits from its parents, such as eye color, that is coded for by DNA. Alternate forms of a gene; produce variations in traits. ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
... 1. What is a plant that has two dominant genes or two recessive genes called? 2. The “rungs” of the DNA ladder are made up of __________. 3. What is heredity? 4. How are sex cells different from other human cells? 5. What is the name of the process for the way cells divide in asexual reproduction? 6 ...
11.3 Other Patterns of Inheritance
... • Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive • In complete dominance, neither allele is dominant • The heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes • The heterozygous genotype yields a mixed phenotype ...
... • Some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive • In complete dominance, neither allele is dominant • The heterozygous phenotype lies somewhere between the two homozygous phenotypes • The heterozygous genotype yields a mixed phenotype ...
Chapter 10.2
... _________: sequence of DNA that can be bound by a _____________ ___________ Located __________ of nucleotide bases away from __________ Loop in DNA may bring ________ and its attached transcription factor (________) into _______ with the transcription factors and RNA polymerase at the ...
... _________: sequence of DNA that can be bound by a _____________ ___________ Located __________ of nucleotide bases away from __________ Loop in DNA may bring ________ and its attached transcription factor (________) into _______ with the transcription factors and RNA polymerase at the ...
Chromosomes & Inheritance
... • Missing protein (dystrophin) • Hemophilia • Absence of protein for blood clotting ...
... • Missing protein (dystrophin) • Hemophilia • Absence of protein for blood clotting ...
Document
... Genotype- The genetic makeup, as distinguished from the physical appearance, of an organism or a group of organisms. Phenotype- The expression of a specific trait, such as stature or blood type, based on genetic and environmental influences. Homozygote- An organism that has the same alleles as a par ...
... Genotype- The genetic makeup, as distinguished from the physical appearance, of an organism or a group of organisms. Phenotype- The expression of a specific trait, such as stature or blood type, based on genetic and environmental influences. Homozygote- An organism that has the same alleles as a par ...
Animal Development and Homeotic Genes
... 2. When the embryo is developing, there are proteins concentrated at different places. These proteins (transcription factors) turn on specific __________________ __________________ needed for the next stage of development. ...
... 2. When the embryo is developing, there are proteins concentrated at different places. These proteins (transcription factors) turn on specific __________________ __________________ needed for the next stage of development. ...
DNA, Mutations, Chromosomes, and Reproduction Review
... Chromosome Theory of Inheritance • Sutton discovered that sex cells contain half the number of chromosomes as body cells. • One set of alleles comes from the male parent; the second set comes from the female parent • Chromosome theory of inheritance – Genes are carried from parents to their offspri ...
... Chromosome Theory of Inheritance • Sutton discovered that sex cells contain half the number of chromosomes as body cells. • One set of alleles comes from the male parent; the second set comes from the female parent • Chromosome theory of inheritance – Genes are carried from parents to their offspri ...
Tumour-Suppressor Genes
... – 0 in which there is complete absence of chain production. This is common in the Mediterranean. – + in which there is a partial block in chain synthesis. At least three different mutant genes are involved: +1 – 10% of normal chain synthesis occurs +2 – 50% of normal chain synthesis occu ...
... – 0 in which there is complete absence of chain production. This is common in the Mediterranean. – + in which there is a partial block in chain synthesis. At least three different mutant genes are involved: +1 – 10% of normal chain synthesis occurs +2 – 50% of normal chain synthesis occu ...
Pair-Rule Gene
... embryonic development in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. In normal unmutated Drosophila, each segment produces bristles called denticles in a band arranged on the side of the segment closer to the head. They found five genes – Even-skipped, Hairy, Odd-skipped, Paired and Runt – where mutation ...
... embryonic development in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. In normal unmutated Drosophila, each segment produces bristles called denticles in a band arranged on the side of the segment closer to the head. They found five genes – Even-skipped, Hairy, Odd-skipped, Paired and Runt – where mutation ...
Genes and Cell Division
... nuclei create a bulge or bud, when the bud is completely grown it breaks off – Yeast reproduce this way ...
... nuclei create a bulge or bud, when the bud is completely grown it breaks off – Yeast reproduce this way ...
Review L14 Gene to Protein L15 Gene Reg
... 13. What happens to the polypeptide chain after it is synthesized? 14. How do proteins that should be made in the ER get to the ER? 15. Make a list of all the different types of RNA and their functions. 16. What is a mutation? 17. What is a point mutation? 18. Distinguish between the following types ...
... 13. What happens to the polypeptide chain after it is synthesized? 14. How do proteins that should be made in the ER get to the ER? 15. Make a list of all the different types of RNA and their functions. 16. What is a mutation? 17. What is a point mutation? 18. Distinguish between the following types ...
Working with enriched gene sets in R
... available from Bioconductor – MetaData for commercial arrays – AnnBuilder for homemade – Unigene name, code, symbol, entrez gene, GO terms, KEGG pathways, Pubmed ids... ...
... available from Bioconductor – MetaData for commercial arrays – AnnBuilder for homemade – Unigene name, code, symbol, entrez gene, GO terms, KEGG pathways, Pubmed ids... ...
Chapter 8c
... Only form of gene exchange in which donor survives Mediated by plasmids Can code for traits that give bacteria advantage ...
... Only form of gene exchange in which donor survives Mediated by plasmids Can code for traits that give bacteria advantage ...
AP Biology Chapter 18, 19, 27 Study Guide Chapter 18: Regulation
... AP Biology Chapter 18, 19, 27 Study Guide Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Draw and label an operon. Explain the function of the operator, regulatory gene, inducer, repressor, and corepressor. ...
... AP Biology Chapter 18, 19, 27 Study Guide Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Draw and label an operon. Explain the function of the operator, regulatory gene, inducer, repressor, and corepressor. ...
separate PDF document
... gene controls the development of a specific characteristic of the living organism (such as eye color). Each gene has its own position (or "locus") on its chromosome. Some genes have one or more variants that together comprise a group, one variant of which can occur at the gene's locus. An allele ref ...
... gene controls the development of a specific characteristic of the living organism (such as eye color). Each gene has its own position (or "locus") on its chromosome. Some genes have one or more variants that together comprise a group, one variant of which can occur at the gene's locus. An allele ref ...
Gene Regulation - yayscienceclass
... Four of the many different types of human cells: They all share the same genome. What makes them different? ...
... Four of the many different types of human cells: They all share the same genome. What makes them different? ...
The Nucleus, Chromosomes and Genes
... Effects of mutation A) If the mutation is in a normal body cell Cell death or a change in its functioning. In the worst cases the change in function leads to cancer. This is when a cell start to undergo uncontrollable division to create a tumour. B) If the mutation is in a sperm or egg cell All the ...
... Effects of mutation A) If the mutation is in a normal body cell Cell death or a change in its functioning. In the worst cases the change in function leads to cancer. This is when a cell start to undergo uncontrollable division to create a tumour. B) If the mutation is in a sperm or egg cell All the ...
a10 Genetics Non-Mendel
... Non- Mendelian Genetics and Chromosomal Inheritance 1. Define the nature and give an example of incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, pleiotropy, epistasis, and polygenic inheritance. Which type of inheritance involves the suppression of one locus over another? Which type involves mor ...
... Non- Mendelian Genetics and Chromosomal Inheritance 1. Define the nature and give an example of incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, pleiotropy, epistasis, and polygenic inheritance. Which type of inheritance involves the suppression of one locus over another? Which type involves mor ...
rec07
... • Splicing: the removal of the introns. • Performed by complexes called spliceosomes, containing both proteins and snRNA. • The snRNA recognizes the splice sites through RNA-RNA base-pairing • Recognition must be precise: a 1nt error can shift the reading frame making nonsense of its message. • Many ...
... • Splicing: the removal of the introns. • Performed by complexes called spliceosomes, containing both proteins and snRNA. • The snRNA recognizes the splice sites through RNA-RNA base-pairing • Recognition must be precise: a 1nt error can shift the reading frame making nonsense of its message. • Many ...