Genetics Vocabulary
... Inherited trait — A characteristic that makes one person different from another. Eye color and height are traits. For every inherited trait, you have two genes, one from each parent. ...
... Inherited trait — A characteristic that makes one person different from another. Eye color and height are traits. For every inherited trait, you have two genes, one from each parent. ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of ________. ...
... The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of ________. ...
Sex-linked genes, genes located on one of the sex chromosomes (X
... red-green colorblindness. Hemophilia is the failure (lack of genetic code) to produce certain substance needed for proper blood-clotting, so a hemophiliac’s blood doesn’t clot, and (s)he could bleed to death from an injury that a normal person might not even notice. ...
... red-green colorblindness. Hemophilia is the failure (lack of genetic code) to produce certain substance needed for proper blood-clotting, so a hemophiliac’s blood doesn’t clot, and (s)he could bleed to death from an injury that a normal person might not even notice. ...
Ingenious Genes Curriculum Links for AQA GCSE Combined
... All the genes present in an individual organism interact with the environment in which the organism grows and develops its observable appearance and character. These characteristics are its phenotype. The variation in the characteristics of individuals of the same kind may be due to differences in: ...
... All the genes present in an individual organism interact with the environment in which the organism grows and develops its observable appearance and character. These characteristics are its phenotype. The variation in the characteristics of individuals of the same kind may be due to differences in: ...
Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q
... What do we call the mathematical chance that an event will occur? ...
... What do we call the mathematical chance that an event will occur? ...
Genes and genomes
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
... of A, T, C, and G. These unique combinations code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
Crossbreeding terminology
... characteristics of the parent breeds. Dominant an allele that masks the expression of another. F1 First generation following the crossing of two breeds, and refers to Filial 1 . For example, the progeny of a cross between a Limousin and an Angus would be referred to as the F1. Gene a portion of the ...
... characteristics of the parent breeds. Dominant an allele that masks the expression of another. F1 First generation following the crossing of two breeds, and refers to Filial 1 . For example, the progeny of a cross between a Limousin and an Angus would be referred to as the F1. Gene a portion of the ...
PG1007 Lecture 7 Anterior-Posterior Patterning, HOX Genes and
... Consider the fact that overall external symmetry of the body is not matched in the visceral organs How can this be? The answer in part may be due to cilia and the asymmetric accumulation of nodal protein secreted from the primitive node Mutations in key cilial motor proteins produce situs inversus a ...
... Consider the fact that overall external symmetry of the body is not matched in the visceral organs How can this be? The answer in part may be due to cilia and the asymmetric accumulation of nodal protein secreted from the primitive node Mutations in key cilial motor proteins produce situs inversus a ...
The human genome: gene structure and function
... processed pseudogenes • are pseudogenes that have been formed, not by mutation, but by a process called retrotransposition, and reverse transcription , and finally integration of such DNA copies back into the genome. • Because such pseudogenes are created by retrotransposition of a DNA copy of proc ...
... processed pseudogenes • are pseudogenes that have been formed, not by mutation, but by a process called retrotransposition, and reverse transcription , and finally integration of such DNA copies back into the genome. • Because such pseudogenes are created by retrotransposition of a DNA copy of proc ...
Review of Genetics Genes Punnett Square Example Incidence of
... did not have them. The woman in this couple has no freckles. What percentage of the children will have freckles? ...
... did not have them. The woman in this couple has no freckles. What percentage of the children will have freckles? ...
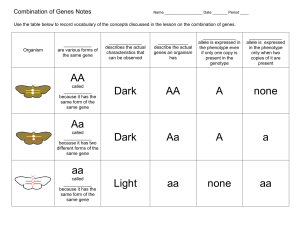
Combination of Genes Notes
... Identify the parent alleles. _________________ Which parent’s alleles are homozygous? ______________________ Identify the heterozygous alleles? _____________________ What percent of Rusty and Carrie’s offspring will have Brown eyes? ______________ Explain how you determined the percent on the previo ...
... Identify the parent alleles. _________________ Which parent’s alleles are homozygous? ______________________ Identify the heterozygous alleles? _____________________ What percent of Rusty and Carrie’s offspring will have Brown eyes? ______________ Explain how you determined the percent on the previo ...
Developmental Biology 8/e - Florida International University
... 9.28 Expression and regulatory interactions among gap genes products High levels of Bicoid and Hunchback induce the expression of giant, while Kruppel transcript appears over the region where Hunchback begins to decline. ...
... 9.28 Expression and regulatory interactions among gap genes products High levels of Bicoid and Hunchback induce the expression of giant, while Kruppel transcript appears over the region where Hunchback begins to decline. ...
A single characteristic may be influenced by many genes
... Females have counterpart on second X chromosome ...
... Females have counterpart on second X chromosome ...
Genes
... heredity. Each gene is a segment of double-stranded DNA that holds the recipe for making a specific molecule, usually a protein. ...
... heredity. Each gene is a segment of double-stranded DNA that holds the recipe for making a specific molecule, usually a protein. ...
People Pieces
... mutations, that cause certain diseases or medical problems. One goal of the Human Genome Project is to learn the correct sequence for each gene, which mutations cause which problems, and how to correct the mutations in order to solve the problems. The genomes of other organisms are also being studie ...
... mutations, that cause certain diseases or medical problems. One goal of the Human Genome Project is to learn the correct sequence for each gene, which mutations cause which problems, and how to correct the mutations in order to solve the problems. The genomes of other organisms are also being studie ...
Can environmental factors acting on an organism cause inherited
... One of the well known epigenetic signal is DNA methylation which tags cytosine with a methyl group. It is generally associated with silencing gene expression because active genes are usually unmethylated. Another important epigenetic mechanism is chromatin remodelling. Chromatins are densely packed ...
... One of the well known epigenetic signal is DNA methylation which tags cytosine with a methyl group. It is generally associated with silencing gene expression because active genes are usually unmethylated. Another important epigenetic mechanism is chromatin remodelling. Chromatins are densely packed ...
Prenatal development
... Dominant: Needs only one copy of the gene for the trait to be expressed (and can be from either parent). Recessive: Needs two copies of the gene for the trait to be expressed (one from mother, and one from father). ii. Co-dominant genes Co-dominant genes: When two genes are of equal dominance, they ...
... Dominant: Needs only one copy of the gene for the trait to be expressed (and can be from either parent). Recessive: Needs two copies of the gene for the trait to be expressed (one from mother, and one from father). ii. Co-dominant genes Co-dominant genes: When two genes are of equal dominance, they ...
Consortium for Educational Communication Summary
... factors involved one each contributed by male and female parents during reproduction. The law of independent assortment states that the distribution of alleles to gametes during meiosis is random. If one particular allele goes to one gamete, it has no influence on the likelihood of any other allele ...
... factors involved one each contributed by male and female parents during reproduction. The law of independent assortment states that the distribution of alleles to gametes during meiosis is random. If one particular allele goes to one gamete, it has no influence on the likelihood of any other allele ...
Epigenetics Questions Jessica Lewis C Block How does methylation
... 3. How does cocaine affect epigenetic control of gene expression? Cocaine affects epigenetic control of gene expression by unwinding histones, this changes means that genes are more susceptible to being expressed, because the genes are not as tightly coiled and inaccessible as before. If an animal r ...
... 3. How does cocaine affect epigenetic control of gene expression? Cocaine affects epigenetic control of gene expression by unwinding histones, this changes means that genes are more susceptible to being expressed, because the genes are not as tightly coiled and inaccessible as before. If an animal r ...
Notes Guide
... 6. Hybrid- __________________ of parents with __________________ traits 7. Homozygous - _______________pairs of genes for a _______________ trait are the _______________ 8. Heterozygous - _______________ pairs of genes are _______________ 9. Genotype – the _______________ makeup of an organism (ie. ...
... 6. Hybrid- __________________ of parents with __________________ traits 7. Homozygous - _______________pairs of genes for a _______________ trait are the _______________ 8. Heterozygous - _______________ pairs of genes are _______________ 9. Genotype – the _______________ makeup of an organism (ie. ...
Genes, Chromosomes and DNA
... _________ is found in the _________ of each of the body's billions of cells. Every human cell (with the exception of mature red blood cells, which have no nucleus) contains the same _________. Each cell has 46 molecules of doublestranded DNA. Each molecule of DNA is made up of 50 to 250 million base ...
... _________ is found in the _________ of each of the body's billions of cells. Every human cell (with the exception of mature red blood cells, which have no nucleus) contains the same _________. Each cell has 46 molecules of doublestranded DNA. Each molecule of DNA is made up of 50 to 250 million base ...