AP Biology - Naber Biology
... during which linked genes become unlinked. What do geneticists call the offspring that show these new combinations? ...
... during which linked genes become unlinked. What do geneticists call the offspring that show these new combinations? ...
rights reserved. AP Biology Living System and Genetic Information
... They then allowed the bacteriophages to infect samples of E. coli bacteria. After 10 minutes, the bacteria were agitated in a blender to shake any materials loose from the surface of the host. Using a centrifuge, they separated the samples into a pellet of bacteria and their contents, and a liquid m ...
... They then allowed the bacteriophages to infect samples of E. coli bacteria. After 10 minutes, the bacteria were agitated in a blender to shake any materials loose from the surface of the host. Using a centrifuge, they separated the samples into a pellet of bacteria and their contents, and a liquid m ...
Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) Scents Colours
... Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) ...
... Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) ...
THE STUDY OF HERITABLE CHANGES IN GENE FUNCTION THAT
... of Rett syndrome, which primarily affects brain development. Severity probably depends upon which X chromosome is inactivated. ...
... of Rett syndrome, which primarily affects brain development. Severity probably depends upon which X chromosome is inactivated. ...
Lecture 4 – Gene Expression Control and Regulation
... X Chromosome Inactivation X chromosome inactivation • In cells of female mammals, either the maternal or paternal X chromosome is randomly condensed (Barr body) and is inactive • Occurs in an early embryonic stage, so that all descendents of that particular cell have the same inactive X chromosom ...
... X Chromosome Inactivation X chromosome inactivation • In cells of female mammals, either the maternal or paternal X chromosome is randomly condensed (Barr body) and is inactive • Occurs in an early embryonic stage, so that all descendents of that particular cell have the same inactive X chromosom ...
Document
... or are controlled by more than 1 gene. Polygenic Inheritance (Multiple genes): When several genes (not just one) affect a trait. Example: eye color is controlled by several genes. Multiple alleles: When there are more than 2 alleles for a trait. Example: Blood types A, B or AB or O. ...
... or are controlled by more than 1 gene. Polygenic Inheritance (Multiple genes): When several genes (not just one) affect a trait. Example: eye color is controlled by several genes. Multiple alleles: When there are more than 2 alleles for a trait. Example: Blood types A, B or AB or O. ...
13.4 Gene Regulation and Expression
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Prokaryotes do not need to transcribe all of their genes at the same time. They can conserve energy and resources by regulating their activities, producing only those genes necessary for the cell to function. In prokaryotes, DNA-binding proteins regulate genes by controll ...
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Prokaryotes do not need to transcribe all of their genes at the same time. They can conserve energy and resources by regulating their activities, producing only those genes necessary for the cell to function. In prokaryotes, DNA-binding proteins regulate genes by controll ...
Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
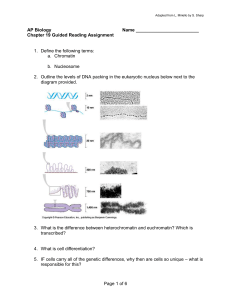
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
Genetic basis of adaptation and speciation
... 3. Epistatic interactions between alleles in Mc1r and Agouti 4. Mutations in 60 genes affect pigmentation in laboratory mouse (Hoekstra et al. 2006) ...
... 3. Epistatic interactions between alleles in Mc1r and Agouti 4. Mutations in 60 genes affect pigmentation in laboratory mouse (Hoekstra et al. 2006) ...
Abstract - Anil Jegga - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital
... Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH-45229 The combinatorial interaction of sequence specific trans-acting factors with localized genomic cis-elements is the principal underlying mechanism for regulating tissue specific and developmental gene expression. Recent computational ...
... Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH-45229 The combinatorial interaction of sequence specific trans-acting factors with localized genomic cis-elements is the principal underlying mechanism for regulating tissue specific and developmental gene expression. Recent computational ...
Ch 15 Gudied Reading
... case of E. coli regulating tryptophan synthesis, is it positive or negative inhibition? ...
... case of E. coli regulating tryptophan synthesis, is it positive or negative inhibition? ...
May 4, 2004 B4730/5730 Plant Physiological Ecology
... traits • Two copies of alleles determines traits ...
... traits • Two copies of alleles determines traits ...
Ghost in Your Genes Response
... 6. An experiment to test how environment affects the epigenome used rats raised by lowlicking mothers and high-licking mothers. How did the scientist ensure it wasn’t genetics that dictated how the offspring responded to stress? ...
... 6. An experiment to test how environment affects the epigenome used rats raised by lowlicking mothers and high-licking mothers. How did the scientist ensure it wasn’t genetics that dictated how the offspring responded to stress? ...
21.1 Mitochondria and Chloroplasts Are Eukaryotic
... • The study of evolution through the analysis of development • Some genes in distantly related organisms can shape similar developmental pathways, but they may exert quite different effects. • Many major evolutionary adaptations are through changes in the expression of genes that encode proteins tha ...
... • The study of evolution through the analysis of development • Some genes in distantly related organisms can shape similar developmental pathways, but they may exert quite different effects. • Many major evolutionary adaptations are through changes in the expression of genes that encode proteins tha ...
Document
... machinery that turns on genes. It includes the TATA-binding factor, which binds to the TATA box, located at -35 of many eukaryotic promoters. Riboswitches are small molecules which stabilize one of two alternate stemloop conformations found in the leaders (5’UTRs) of some eukaryotic transcripts. In ...
... machinery that turns on genes. It includes the TATA-binding factor, which binds to the TATA box, located at -35 of many eukaryotic promoters. Riboswitches are small molecules which stabilize one of two alternate stemloop conformations found in the leaders (5’UTRs) of some eukaryotic transcripts. In ...
Chapters 13-20 "Fill in the Blank"
... __________________. Mendel worked with peas & studied many of their traits. He then used some rules of genetics to make predictions about the numbers of offspring of various genotypes in the next generation. For example, if Mendel crossed these 2 pea parents, AaBbcc x aaBbCc, then he would expect 11 ...
... __________________. Mendel worked with peas & studied many of their traits. He then used some rules of genetics to make predictions about the numbers of offspring of various genotypes in the next generation. For example, if Mendel crossed these 2 pea parents, AaBbcc x aaBbCc, then he would expect 11 ...
History of Genetics
... structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from two different species in vitro, then transform it into ...
... structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from two different species in vitro, then transform it into ...
History of Genetics - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from two different species in vitro, then transform it into ...
... structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from two different species in vitro, then transform it into ...
Pair rule genes also encode TFs
... Clones = Genetically identical individuals Two Kinds of Animal Cloning Reproductive Cloning: Remove nucleus from egg cell. Replace it with nucleus from somatic cell (e.g., skin cell). Stimulate cell to divide (like a fertilized egg). Implant embryo into surrogate mother. Therapeutic Cloning (Nuclea ...
... Clones = Genetically identical individuals Two Kinds of Animal Cloning Reproductive Cloning: Remove nucleus from egg cell. Replace it with nucleus from somatic cell (e.g., skin cell). Stimulate cell to divide (like a fertilized egg). Implant embryo into surrogate mother. Therapeutic Cloning (Nuclea ...
Protein - UDKeystone
... • Definition: more than two alleles • (more than 2 alleles exist in a population not an individual) Ex: rabbit’s coat color Ex: human’s blood type ...
... • Definition: more than two alleles • (more than 2 alleles exist in a population not an individual) Ex: rabbit’s coat color Ex: human’s blood type ...
Answers to Biological Inquiry Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What are two reasons why the groups of species shown in (a) have variation in their total amount of DNA? ANSWER: One reason is that more complex species tend to have more genes. A second reason is that species vary with regard to the amount of repetitive DNA that is foun ...
... BIOLOGICAL INQUIRY QUESTION: What are two reasons why the groups of species shown in (a) have variation in their total amount of DNA? ANSWER: One reason is that more complex species tend to have more genes. A second reason is that species vary with regard to the amount of repetitive DNA that is foun ...