Political
... Their basic argument at that time was that the US had to reconceptualize American foreign policy in light of the end of the Cold War and changing relative importance of states within the international system ...
... Their basic argument at that time was that the US had to reconceptualize American foreign policy in light of the end of the Cold War and changing relative importance of states within the international system ...
APUSH Period 7 review powerpoint
... ○ First New Deal ○ Second New Deal ● World War II ○ Foreign Policy ...
... ○ First New Deal ○ Second New Deal ● World War II ○ Foreign Policy ...
Public Policy: Mexico
... • In order to keep their company going, PEMEX has borrowed an excess of money and is now $42.5 billion in debt. • With the record breaking oil prices starting in 2005, resulting partially from the Iraqi war, PEMEX has seen a rise in revenue. ...
... • In order to keep their company going, PEMEX has borrowed an excess of money and is now $42.5 billion in debt. • With the record breaking oil prices starting in 2005, resulting partially from the Iraqi war, PEMEX has seen a rise in revenue. ...
High-level Regional Policy Dialogue on
... protection is necessary for the softening the most serious consequences of market and financial shocks to limit long-term consequences. - Support the investments into agricultural infrastructure. It is necessary to the governments of the countries, as well as the international organizations and to d ...
... protection is necessary for the softening the most serious consequences of market and financial shocks to limit long-term consequences. - Support the investments into agricultural infrastructure. It is necessary to the governments of the countries, as well as the international organizations and to d ...
First Term ppr, Pol sc. XII - Ans Key
... Review of Rio Summit SAARC countries should adopt common position on major global environmental issues. In thinking about the consequences of globalization, it is necessary to keep in mind that the same set of policies does not lead to the same results everywhere. While globalization has led to simi ...
... Review of Rio Summit SAARC countries should adopt common position on major global environmental issues. In thinking about the consequences of globalization, it is necessary to keep in mind that the same set of policies does not lead to the same results everywhere. While globalization has led to simi ...
HIBT – Economics of Business Environment – Notes Lecture 10
... huge amount of trade within our stock markets, the short-term money markets and the bond markets. UK trade with other countries continues to take a high and rising percentage of our total national output. Clearly, the globalisation process impacts significantly on the British economy with benefits a ...
... huge amount of trade within our stock markets, the short-term money markets and the bond markets. UK trade with other countries continues to take a high and rising percentage of our total national output. Clearly, the globalisation process impacts significantly on the British economy with benefits a ...
South Korea - WordPress.com
... the United Nations policies when delineating need and while deployed. Currently UN peacekeepers have an approximate fatality rate of 1.7% which South Korea applauds. However, South Korea, as a country like so many others has a rich culture, as such we are aware of the cultural impact on countries cu ...
... the United Nations policies when delineating need and while deployed. Currently UN peacekeepers have an approximate fatality rate of 1.7% which South Korea applauds. However, South Korea, as a country like so many others has a rich culture, as such we are aware of the cultural impact on countries cu ...
(July 2003 est.) Capital
... production focused on military not consumer needs Centrally planned production goals not related to customer demand Enterprises lied regularly to report desired outputs ...
... production focused on military not consumer needs Centrally planned production goals not related to customer demand Enterprises lied regularly to report desired outputs ...
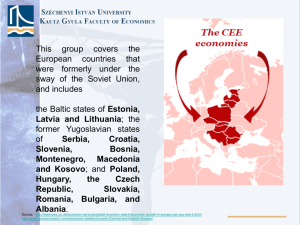
1. dia
... 1, The smaller economies of the Baltic States were most severely affected by the crisis (annual GDP fell by 15% in 2009), but they are also now bouncing back most strongly. 3.5-4% GDP growth per annum over the next 5 years. (ES,LA,LI – 2.99; 4.16; 3.04 - 2013) ...
... 1, The smaller economies of the Baltic States were most severely affected by the crisis (annual GDP fell by 15% in 2009), but they are also now bouncing back most strongly. 3.5-4% GDP growth per annum over the next 5 years. (ES,LA,LI – 2.99; 4.16; 3.04 - 2013) ...
10.9 Lecture – Wars in Korea and Vietnam
... B. Southeast Asia was a resource rich area controlled by the French. 1. The development of nationalist independent movements began. 2. Ho Chi Minh a. Spent several years in France during World War I. b. He helped form the Communist Party in France c. In 1930, after training in Moscow, he returned to ...
... B. Southeast Asia was a resource rich area controlled by the French. 1. The development of nationalist independent movements began. 2. Ho Chi Minh a. Spent several years in France during World War I. b. He helped form the Communist Party in France c. In 1930, after training in Moscow, he returned to ...
Domestic Policy and Policymaking
... Economic development policies deal with the related issue of how to deal with economic growth and change. Economic development programs are intended to protect and promote the growth of the economy. A. Historically, the national government has always been concerned with international trade, and toda ...
... Economic development policies deal with the related issue of how to deal with economic growth and change. Economic development programs are intended to protect and promote the growth of the economy. A. Historically, the national government has always been concerned with international trade, and toda ...
1. Intertwined World Economy
... • Despite the increasingly intertwined world economy, the United States is still relatively more insulated from the global economy than other nations. In 2004, the U.S. economy was about $11.7 trillion and imports about 80% more as it exports. ...
... • Despite the increasingly intertwined world economy, the United States is still relatively more insulated from the global economy than other nations. In 2004, the U.S. economy was about $11.7 trillion and imports about 80% more as it exports. ...
Economic Systems: Capitalists vs. Communists
... stagnation. In order to foster renewed economic growth and development, firms, industry, and the state must develop extensive sociopolitical accumulation innovation. A world economic divide was taking place between high-skilled flexible production, such as biotechnical, electronic, and information p ...
... stagnation. In order to foster renewed economic growth and development, firms, industry, and the state must develop extensive sociopolitical accumulation innovation. A world economic divide was taking place between high-skilled flexible production, such as biotechnical, electronic, and information p ...
DOC - Europa.eu
... Yet, we have to recall that public debt in the EU has risen from around 60% of GDP before the crisis to around 90% of GDP. And it is widely acknowledged, based on serious academic research, that when public debt levels rise above 90% they tend to have a negative impact on economic dynamism, which tr ...
... Yet, we have to recall that public debt in the EU has risen from around 60% of GDP before the crisis to around 90% of GDP. And it is widely acknowledged, based on serious academic research, that when public debt levels rise above 90% they tend to have a negative impact on economic dynamism, which tr ...
The history of globalisation
... The most recent wave of globalisation, which started in 1980, was spurred by a combination of advances in transport and communications technologies and by large developing countries who sought foreign investment by opening up to international trade. This is actually the third wave of a phenomenon th ...
... The most recent wave of globalisation, which started in 1980, was spurred by a combination of advances in transport and communications technologies and by large developing countries who sought foreign investment by opening up to international trade. This is actually the third wave of a phenomenon th ...
F13_POLS-2100_TextbookNotes
... Why regulate trade? - To generate state revenue - To foster local industry - To protect local jobs - To keep wealth in the country ...
... Why regulate trade? - To generate state revenue - To foster local industry - To protect local jobs - To keep wealth in the country ...
IMFC Statement by Helen Clark, Administrator of the United Nations
... a strong growth rebound appears unlikely in these countries as commodity prices are projected to remain well below pre-2014 levels. Conflict and drought are also severely impacting prospects in parts of the continent. Aggregate growth in the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) is projected to remain we ...
... a strong growth rebound appears unlikely in these countries as commodity prices are projected to remain well below pre-2014 levels. Conflict and drought are also severely impacting prospects in parts of the continent. Aggregate growth in the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) is projected to remain we ...
Ask not what Capitalism can do for you
... Venture Captains and Venture Capital Power by birth and co-optation vs. Leadership in discovery and creative destruction (entrepreneurship…) ...
... Venture Captains and Venture Capital Power by birth and co-optation vs. Leadership in discovery and creative destruction (entrepreneurship…) ...
Economic co-operation, globalisation, chemicals and OPCW
... Benefits of integrating similar (small) economies: • Larger markets – trade, production scale ,efficiency • More competition and investments • More efficient use of resources – specialisation, technology exchange • Increased international bargaining power ...
... Benefits of integrating similar (small) economies: • Larger markets – trade, production scale ,efficiency • More competition and investments • More efficient use of resources – specialisation, technology exchange • Increased international bargaining power ...
GGl_ESCAP_Beijing_21
... >> depends on the policy context >> in a comprehensive framework they can be hierarchically linked Green growth-related country initiatives • Green growth roadmaps or related comprehensive programmes - supported by comprehensive programmes and investment , fully mainstreamed – Republic of Korea Chin ...
... >> depends on the policy context >> in a comprehensive framework they can be hierarchically linked Green growth-related country initiatives • Green growth roadmaps or related comprehensive programmes - supported by comprehensive programmes and investment , fully mainstreamed – Republic of Korea Chin ...