Global European economic model
... All EU countries have three social common characteristics: social citizenship which has the equity principle, not in terms of income but in terms of equality before the law, political, economic and social rights, and protection gap against market; no individual have a higher position. Giving up the ...
... All EU countries have three social common characteristics: social citizenship which has the equity principle, not in terms of income but in terms of equality before the law, political, economic and social rights, and protection gap against market; no individual have a higher position. Giving up the ...
International Monetary Fund
... Fund policies were anti-developmental. The deflationary effects of IMF programmes quickly led to losses of output and employment in economies where incomes were low and unemployment was high. Fourthly is the accusation that harsh policy conditions were self-defeating where a vicious circle develop ...
... Fund policies were anti-developmental. The deflationary effects of IMF programmes quickly led to losses of output and employment in economies where incomes were low and unemployment was high. Fourthly is the accusation that harsh policy conditions were self-defeating where a vicious circle develop ...
From Economic Cooperation to Collective Security
... various national developmental efforts of member-states, for accelerating and achieving the goals of self-reliance and sustainable development in the sub-region. At the global level, its formation was encouraged, in fact significantly boosted, by the bourgeoning emphasis placed on economic integrati ...
... various national developmental efforts of member-states, for accelerating and achieving the goals of self-reliance and sustainable development in the sub-region. At the global level, its formation was encouraged, in fact significantly boosted, by the bourgeoning emphasis placed on economic integrati ...
RESTRICTEDCode - World Trade Organization
... Declaration which contains all the elements needed to achieve the main objective of liberalization, i.e. reducing poverty levels and thereby improving the quality of life for our peoples. For those of us who work for the State, those events call for unequivocal decisions to be taken on aspects of co ...
... Declaration which contains all the elements needed to achieve the main objective of liberalization, i.e. reducing poverty levels and thereby improving the quality of life for our peoples. For those of us who work for the State, those events call for unequivocal decisions to be taken on aspects of co ...
CANTI-CORRUPTION CRUSADE AND POVERTY ALLEVIATION IN
... 15. Accordingly, we urge the government to rekindle its machinery for policy implementation so that the national economy can be diversified and insulated from the vagaries of the global economy. The various programmes for the overhaul of the nation’s weak infrastructural base should be pursued with ...
... 15. Accordingly, we urge the government to rekindle its machinery for policy implementation so that the national economy can be diversified and insulated from the vagaries of the global economy. The various programmes for the overhaul of the nation’s weak infrastructural base should be pursued with ...
Chapter 2
... United States but do not grant equal access to U.S. products in their countries. 2. To ease trade restrictions, the OTCA focused on correcting perceived injustice in trade practices. 3. It dealt with trade deficits, protectionism, and the overall fairness of our trading partners. The bill covers thr ...
... United States but do not grant equal access to U.S. products in their countries. 2. To ease trade restrictions, the OTCA focused on correcting perceived injustice in trade practices. 3. It dealt with trade deficits, protectionism, and the overall fairness of our trading partners. The bill covers thr ...
Marketing in a Developing Country
... • Marketing is an economy’s arbitrator between productive capacity and consumer demand • The marketing process is the critical element in ...
... • Marketing is an economy’s arbitrator between productive capacity and consumer demand • The marketing process is the critical element in ...
World Economic Outlook Update Contractionary Forces Receding
... While policies still have much work to do in dealing with the crisis, there will also be a need to increasingly shift from providing short-term support to laying the foundations for a return to strong medium-run growth. This will depend crucially on fostering stronger potential output growth, partic ...
... While policies still have much work to do in dealing with the crisis, there will also be a need to increasingly shift from providing short-term support to laying the foundations for a return to strong medium-run growth. This will depend crucially on fostering stronger potential output growth, partic ...
Richest Countries
... travelers, who discover that they can buy more, or less, of the same goods in different countries when converting their money using the prevailing exchange rates. To measure the real size of the world’s economy and to compare costs of living across countries, we need to adjust for differences in pu ...
... travelers, who discover that they can buy more, or less, of the same goods in different countries when converting their money using the prevailing exchange rates. To measure the real size of the world’s economy and to compare costs of living across countries, we need to adjust for differences in pu ...
APEC: The sordid saga of East Asian nations
... open and bringing economies together. These 21 member states, today, account for more than half of the global economic output. The founding members, Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and the United States had no ...
... open and bringing economies together. These 21 member states, today, account for more than half of the global economic output. The founding members, Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and the United States had no ...
Effects of the War 19.4
... However after the end of the war also spelled the end of wartime economic opportunities for both groups. The post war recession created a competitive job market. Also race riots began in the cities in one city the white rioters burned down 35 African American city blocks to the ground. ...
... However after the end of the war also spelled the end of wartime economic opportunities for both groups. The post war recession created a competitive job market. Also race riots began in the cities in one city the white rioters burned down 35 African American city blocks to the ground. ...
Theoretical Perspectives Page 2
... provides a framework for understanding how and why people change as they grow older. (Berger, 2010) There are four developmental theoretical concepts. Psychoanalytic, Cognitive, Systems, and Behavioral. Behaviorism came about in the early twentieth century when it was argued that for psychology to b ...
... provides a framework for understanding how and why people change as they grow older. (Berger, 2010) There are four developmental theoretical concepts. Psychoanalytic, Cognitive, Systems, and Behavioral. Behaviorism came about in the early twentieth century when it was argued that for psychology to b ...
Chapter Six
... Major differences exist in cultures, languages, attitudes, and demands. Attempts to devise treaties give a false sense of common identity. Most countries still have greater trading links outside this area. Within the area, distances between places are long. ...
... Major differences exist in cultures, languages, attitudes, and demands. Attempts to devise treaties give a false sense of common identity. Most countries still have greater trading links outside this area. Within the area, distances between places are long. ...
Ch 04
... Forms of Competitive Advantage (cont’d) National Competitive Advantage Conditions favoring heavy involvement in international business: 1. Factor conditions—labor, capital, entrepreneurs, physical resources, and information resources 2. Demand conditions—a large domestic consumer base that prom ...
... Forms of Competitive Advantage (cont’d) National Competitive Advantage Conditions favoring heavy involvement in international business: 1. Factor conditions—labor, capital, entrepreneurs, physical resources, and information resources 2. Demand conditions—a large domestic consumer base that prom ...
PowerPoint
... Policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services, and capital within the internal market and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries, and regional development. ...
... Policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services, and capital within the internal market and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries, and regional development. ...
outline chapter 29
... i) 1975 US supported gov fell to Communist (Khmer Rouge) ii) Genocide of over 1,000,000 iii) Pres. Ford attack on Cambodian naval base that had captured the US merchant ship Mayaguez (1) Freed 39 crewmen, 38 mariners died b) Future of Southeast Asia i) Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia helped Asian ...
... i) 1975 US supported gov fell to Communist (Khmer Rouge) ii) Genocide of over 1,000,000 iii) Pres. Ford attack on Cambodian naval base that had captured the US merchant ship Mayaguez (1) Freed 39 crewmen, 38 mariners died b) Future of Southeast Asia i) Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia helped Asian ...
An introduction to globalization
... What is their alternative? A naive view of the state? What does it take to achieve the desired end? ...
... What is their alternative? A naive view of the state? What does it take to achieve the desired end? ...
Internal Market
... It has contributed to a 30% increase in trade in manufactured goods in the EU since 1992, thus increasing the selection of goods available and increasing competition. It has made the EU more internationally competitive. For example EU export to countries outside the EU increased from 6.9% of the EU ...
... It has contributed to a 30% increase in trade in manufactured goods in the EU since 1992, thus increasing the selection of goods available and increasing competition. It has made the EU more internationally competitive. For example EU export to countries outside the EU increased from 6.9% of the EU ...
Economic Bancrupcy of Communism in Bulgaria
... reserve seemed as the only available option 1962-63 Bulgaria had to sell almost its entire gold reserve of 5.9 metric tons of gold Operation brought $ 45 m. and the outstanding debt was agreed to be paid in kind with additional export of: 100,000 tons of sugar; 1,000 tons of zinc; 3,000 tons of fr ...
... reserve seemed as the only available option 1962-63 Bulgaria had to sell almost its entire gold reserve of 5.9 metric tons of gold Operation brought $ 45 m. and the outstanding debt was agreed to be paid in kind with additional export of: 100,000 tons of sugar; 1,000 tons of zinc; 3,000 tons of fr ...
Foreign and Defense Policy
... 13. ______ Which of the following is NOT a member of the military-industrial complex? a. the military establishment d. United Nations b. House of Representatives e. industries that manufacture weapons systems c. US Senators 14. ______ A government that offers protectionism in its global trade emphas ...
... 13. ______ Which of the following is NOT a member of the military-industrial complex? a. the military establishment d. United Nations b. House of Representatives e. industries that manufacture weapons systems c. US Senators 14. ______ A government that offers protectionism in its global trade emphas ...
- Session 1: Introduction to IPE - Session 2: Transnational economic
... economically and unipolar militarily? (eg can we live with the US?) Can an international system which is a product of US hegemony, and more broadly of western hegemony, be made to serve the interests of developing countries? (eg whose interests?!) Are regionalism and multilateralism contradictor ...
... economically and unipolar militarily? (eg can we live with the US?) Can an international system which is a product of US hegemony, and more broadly of western hegemony, be made to serve the interests of developing countries? (eg whose interests?!) Are regionalism and multilateralism contradictor ...
History A level 2015: Democracy and Nazism: Germany (1918–1945)
... History A level 2015: Democracy and Nazism: Germany (1918–1945) This option provides for the study in depth of a period of German history during which a newly developed democratic form of government gave way to a dictatorial Nazi regime. It explores political concepts such as 'right' and 'left', nat ...
... History A level 2015: Democracy and Nazism: Germany (1918–1945) This option provides for the study in depth of a period of German history during which a newly developed democratic form of government gave way to a dictatorial Nazi regime. It explores political concepts such as 'right' and 'left', nat ...
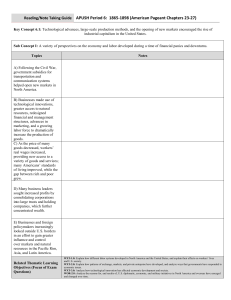
Reading/note taking guide
... greater access to natural resources, redesigned financial and management structures, advances in marketing, and a growing labor force to dramatically increase the production of goods. C) As the price of many goods decreased, workers’ real wages increased, providing new access to a variety of goods a ...
... greater access to natural resources, redesigned financial and management structures, advances in marketing, and a growing labor force to dramatically increase the production of goods. C) As the price of many goods decreased, workers’ real wages increased, providing new access to a variety of goods a ...
Unit 7 Jeopardy
... Which of these is usually true in nations with a market economy? • Businesses that are inefficient risk going out of business. • Most farms are owned and operated by the government. • Workers are restricted by the government from changing jobs. • Consumers have little choice in the types of goods t ...
... Which of these is usually true in nations with a market economy? • Businesses that are inefficient risk going out of business. • Most farms are owned and operated by the government. • Workers are restricted by the government from changing jobs. • Consumers have little choice in the types of goods t ...