Chapter 4 Ancient Greece 1 ppt
... the sun and stars to find their way at sea, religion- before conquering them. • Myceneans were successful in trade but took pride in their deeds in battle. Their most famous victory is the Trojan War, led by King Agamemnon. ...
... the sun and stars to find their way at sea, religion- before conquering them. • Myceneans were successful in trade but took pride in their deeds in battle. Their most famous victory is the Trojan War, led by King Agamemnon. ...
File
... for the glory of Sparta. The greatest honor a Spartan could earn was dying in battle. The greatest humiliation was to return from a defeat alive. Some Spartans even committed suicide instead of returning home after a defeat. Sparta’s patron (protector) goddess was Athena, whom they worshipped for he ...
... for the glory of Sparta. The greatest honor a Spartan could earn was dying in battle. The greatest humiliation was to return from a defeat alive. Some Spartans even committed suicide instead of returning home after a defeat. Sparta’s patron (protector) goddess was Athena, whom they worshipped for he ...
About test, questions something you knew you did not do well on
... habituate them to a single garment the whole year through, thinking that so they would be better prepared to withstand the variations of heat and cold.” ...
... habituate them to a single garment the whole year through, thinking that so they would be better prepared to withstand the variations of heat and cold.” ...
Chapter 8: The Ancient Greeks
... economy where people lived simple lives of hard work and physical activity. It had a standing army led by two kings who were part of a governing council. ...
... economy where people lived simple lives of hard work and physical activity. It had a standing army led by two kings who were part of a governing council. ...
Greek Unit Test Review
... A. The leader of Athens who brought about the Golden Age of Athens and made the Delian League B. The beautiful woman who had a war fought over her. C. A goddess who Athens was named after D. The famous Greek thinker who asked others to think for themselves and question their beliefs. He was killed f ...
... A. The leader of Athens who brought about the Golden Age of Athens and made the Delian League B. The beautiful woman who had a war fought over her. C. A goddess who Athens was named after D. The famous Greek thinker who asked others to think for themselves and question their beliefs. He was killed f ...
Lesson
... emotionally and physically. Mothers told their sons, “Bring back this shield yourself or be brought back on it.” (Spartans carried dead warriors home on their shields.) Education for girls in Sparta focused on making them strong. They had athletic training and learned to defend themselves. The empha ...
... emotionally and physically. Mothers told their sons, “Bring back this shield yourself or be brought back on it.” (Spartans carried dead warriors home on their shields.) Education for girls in Sparta focused on making them strong. They had athletic training and learned to defend themselves. The empha ...
Chapter 7 Section 2
... slaves owned by the city-state of Sparta. – _________________________ were treated very harshly by Spartans because there was fear of a revolt. Spartans also turned their city into an armed camp for this reason. Growing Up in Sparta • The life of every Spartan was in the hands of the _______________ ...
... slaves owned by the city-state of Sparta. – _________________________ were treated very harshly by Spartans because there was fear of a revolt. Spartans also turned their city into an armed camp for this reason. Growing Up in Sparta • The life of every Spartan was in the hands of the _______________ ...
Chapter 5 Section 1-4 True/False Indicate whether the statement is
... a. to gain control of Greece’s vast natural resources b. to exact revenge for the Athenians’ victory at Marathon c. to kidnap Helen, the beautiful queen of Athens d. to punish Athens for aiding the Ionians in their revolt against Persian rule Macedonia was able to take control of all of Greece in th ...
... a. to gain control of Greece’s vast natural resources b. to exact revenge for the Athenians’ victory at Marathon c. to kidnap Helen, the beautiful queen of Athens d. to punish Athens for aiding the Ionians in their revolt against Persian rule Macedonia was able to take control of all of Greece in th ...
Athens vs. Sparta, Pro Sparta
... and most other polis, at war. This allowed us to conquer lots of land for military camps. The Spartan warriors were brave and stood strong in war, playing a key role in many Persian Wars. A part of Athens’ defeat was because of our strategies. We formed a blockade at the Athenian port for trade. It ...
... and most other polis, at war. This allowed us to conquer lots of land for military camps. The Spartan warriors were brave and stood strong in war, playing a key role in many Persian Wars. A part of Athens’ defeat was because of our strategies. We formed a blockade at the Athenian port for trade. It ...
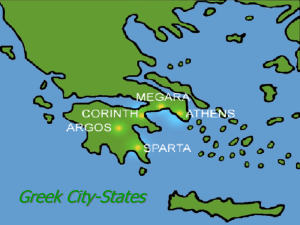
The Greek City-States
... lifetime in the army. Their training was brutal. They were given little food or clothing and were expected to survive by stealing whatever they needed. ...
... lifetime in the army. Their training was brutal. They were given little food or clothing and were expected to survive by stealing whatever they needed. ...
Warring City-States.key
... During the Dorian period, Greek civilization experienced decline. However, two things changed life in Greece. First, Dorians and Mycenaeans alike began to identify less with the culture of their ancestors and more with the local area where they lived. Second, by the end of this period, the method of ...
... During the Dorian period, Greek civilization experienced decline. However, two things changed life in Greece. First, Dorians and Mycenaeans alike began to identify less with the culture of their ancestors and more with the local area where they lived. Second, by the end of this period, the method of ...
Honor Code
... iii) The ___________ was a fierce formation of soldiers side-by-side holding a shield and a spear. c) Tyrants Seize Power i) Powerful individuals, called tyrants, gained control of the government by appealing to the _______ and the ________________ for support. ii) Some city-states passed rule from ...
... iii) The ___________ was a fierce formation of soldiers side-by-side holding a shield and a spear. c) Tyrants Seize Power i) Powerful individuals, called tyrants, gained control of the government by appealing to the _______ and the ________________ for support. ii) Some city-states passed rule from ...
Classical Greece The High Point of Greek civilization is the time
... failed. The ruler of the Persian Empire at the time was Darius. He planned to seek revenge against the Greeks, specifically Athens. In 490 BC the Persians landed an army at the city of Marathon, only 26 miles from Athens. The Athenians and their allies were clearly outnumbered but continued to attac ...
... failed. The ruler of the Persian Empire at the time was Darius. He planned to seek revenge against the Greeks, specifically Athens. In 490 BC the Persians landed an army at the city of Marathon, only 26 miles from Athens. The Athenians and their allies were clearly outnumbered but continued to attac ...
Greek Unit Test Review
... A. The leader of Athens who brought about the Golden Age of Athens and made the Delian League B. The beautiful woman who had a war fought over her. C. A goddess who Athens was named after D. The famous Greek thinker who asked others to think for themselves and question their beliefs. He was killed f ...
... A. The leader of Athens who brought about the Golden Age of Athens and made the Delian League B. The beautiful woman who had a war fought over her. C. A goddess who Athens was named after D. The famous Greek thinker who asked others to think for themselves and question their beliefs. He was killed f ...
Guided Notes Answers
... After defeat of Persians, Athens took over leadership of entire Greek world. 478 B.C. Athenians formed defensive alliance against Persians known as Delian League, that liberated all Greek states in the Aegean from Persian control. The leader in Athens from 461 to 429 B.C. who helped create democracy ...
... After defeat of Persians, Athens took over leadership of entire Greek world. 478 B.C. Athenians formed defensive alliance against Persians known as Delian League, that liberated all Greek states in the Aegean from Persian control. The leader in Athens from 461 to 429 B.C. who helped create democracy ...
Accommodated GCS
... Aristocrats were nobles who took over the government and lead the army. o Only aristocrats could become citizens. o They were members of the Assembly, which passed laws and decided questions on war and peace. Helots, or slaves, did the farming. Perioeci, or merchants and artisans, lived in Spa ...
... Aristocrats were nobles who took over the government and lead the army. o Only aristocrats could become citizens. o They were members of the Assembly, which passed laws and decided questions on war and peace. Helots, or slaves, did the farming. Perioeci, or merchants and artisans, lived in Spa ...
File
... – 1. Monarchy- Kings control the power – 2. Aristocracy – Rich Nobles provided protection – 3. Tyranny- Single rulers took control • Tyrants who worked for reform: Draco: 621 B.C. Improved law code but was STRICT – (Death for stealing cabbage) – origination of the term “Draconian” Solon: 594 B.C. Fo ...
... – 1. Monarchy- Kings control the power – 2. Aristocracy – Rich Nobles provided protection – 3. Tyranny- Single rulers took control • Tyrants who worked for reform: Draco: 621 B.C. Improved law code but was STRICT – (Death for stealing cabbage) – origination of the term “Draconian” Solon: 594 B.C. Fo ...
Greek City-States Politics and Society Characteristics of City
... Around 800 BCE the polis (poleis) begin to form Allowed people to diversify in occupations The towns become walled cities Each city-state had a guardian deity ...
... Around 800 BCE the polis (poleis) begin to form Allowed people to diversify in occupations The towns become walled cities Each city-state had a guardian deity ...
Greek City
... • Boys were educated quite differently. • Until age 6 or 7, boys were taught at home by their mothers. • From 7-14, boys attended a day school outside the home, memorizing Homeric poetry, learning to play the lyre, drama, public speaking, reading, writing, and math. • After, they went to a four year ...
... • Boys were educated quite differently. • Until age 6 or 7, boys were taught at home by their mothers. • From 7-14, boys attended a day school outside the home, memorizing Homeric poetry, learning to play the lyre, drama, public speaking, reading, writing, and math. • After, they went to a four year ...
Guided Notes - Alvinisd.net
... Sophists were traveling teachers who sold their services to the young men of Greece, and believed it was beyond the reach of the human mind to understand the universe. They believed it was more important for individuals to improve themselves, and they also believed that there was no absolute rig ...
... Sophists were traveling teachers who sold their services to the young men of Greece, and believed it was beyond the reach of the human mind to understand the universe. They believed it was more important for individuals to improve themselves, and they also believed that there was no absolute rig ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.