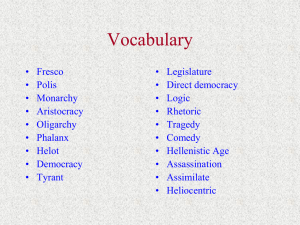
The Glory of Greek Civilization
... conflict with the people who lived in the city-state of Troy Between 1200-1180 B.C. two Trojan wars were fought ...
... conflict with the people who lived in the city-state of Troy Between 1200-1180 B.C. two Trojan wars were fought ...
File
... The Ephors may have kept order while the kings were leading armies in battle. Council of Elders (Gerousia) The law-making body of Sparta. Was only open to people over 60 years old. They prepared laws for the assembly of citizens to vote on. ...
... The Ephors may have kept order while the kings were leading armies in battle. Council of Elders (Gerousia) The law-making body of Sparta. Was only open to people over 60 years old. They prepared laws for the assembly of citizens to vote on. ...
A unique legacy: 2500 ago Greeks began on rock bound peninsula
... Road to democracy took years going through tyrants and many revolts. Athens went through years of aristocrats and tyrants until 508 B.C.E. reforms were made leading to almost a full democracy: Athenian assembly (Ekklesia); Council of 500 whose job was to propose laws and advise the assembly members ...
... Road to democracy took years going through tyrants and many revolts. Athens went through years of aristocrats and tyrants until 508 B.C.E. reforms were made leading to almost a full democracy: Athenian assembly (Ekklesia); Council of 500 whose job was to propose laws and advise the assembly members ...
Impact of Geography on Greece
... Greeks would be safe behind a “wooden wall” – Athenian General Themistocles believed “wooden wall” meant fleet of ships & that they needed to challenge the Persians at sea – Greek army had to set up a distraction on land to build this fleet at sea – Greeks chose Thermopylae as place for distraction ...
... Greeks would be safe behind a “wooden wall” – Athenian General Themistocles believed “wooden wall” meant fleet of ships & that they needed to challenge the Persians at sea – Greek army had to set up a distraction on land to build this fleet at sea – Greeks chose Thermopylae as place for distraction ...
Hellenic History
... b. Mothones c. Harmosts d. Neodamodes 16. What aristocrat was the uncle of Plato and most extreme of the Thirty Tyrants? a. Dracontides b. Thrasybulus c. Theramenes d. Critias 17. What Phocian king was the only person to defeat Philip II of Macedon in battle, doing so twice due to his possession of ...
... b. Mothones c. Harmosts d. Neodamodes 16. What aristocrat was the uncle of Plato and most extreme of the Thirty Tyrants? a. Dracontides b. Thrasybulus c. Theramenes d. Critias 17. What Phocian king was the only person to defeat Philip II of Macedon in battle, doing so twice due to his possession of ...
History
... _____ Leonides was the one who betrayed the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopolyae _____ Xerxes thought that the Greeks would fight against his superior numbers _____ Xerxes thought that freedom was a disadvantage to the Greeks _____ Xerxes thought that a single master is what makes men courageous ...
... _____ Leonides was the one who betrayed the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopolyae _____ Xerxes thought that the Greeks would fight against his superior numbers _____ Xerxes thought that freedom was a disadvantage to the Greeks _____ Xerxes thought that a single master is what makes men courageous ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Alexandria an ancient Hellenistic city in
... sank the Persian navy in the strait of Salamis with underwater battering rams ...
... sank the Persian navy in the strait of Salamis with underwater battering rams ...
GREECE
... • War between Athens and Sparta – Sparta and allies dominate the land – Athens and allies dominate the sea • Spartans surround Athens hoping for an open battle – Athens avoids any battles on land – Knowing they can’t compete in open battle, they hide behind their city walls, relying on supplies from ...
... • War between Athens and Sparta – Sparta and allies dominate the land – Athens and allies dominate the sea • Spartans surround Athens hoping for an open battle – Athens avoids any battles on land – Knowing they can’t compete in open battle, they hide behind their city walls, relying on supplies from ...
The Rise of Greek Cities
... Farmers in Sparta were slaves More slaves than other city-states with 7-1 ratio ...
... Farmers in Sparta were slaves More slaves than other city-states with 7-1 ratio ...
File
... Geography & Climate of Greece The Greek climate was another important environment influence on the development of Greek civilization. Greece had a varied climate. Temperatures range from 48 degrees in the winter to 80 in the summer. Moderate temperatures supported outdoor life. People spent much of ...
... Geography & Climate of Greece The Greek climate was another important environment influence on the development of Greek civilization. Greece had a varied climate. Temperatures range from 48 degrees in the winter to 80 in the summer. Moderate temperatures supported outdoor life. People spent much of ...
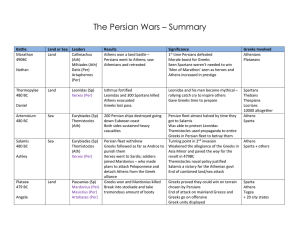
The Persian Wars – Summary Battle Land or Sea Leaders Results
... Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory for the Athenian govt End of combined land/s ...
... Themistocles used propaganda to entire Greeks in Persian fleet to betray them Turning point in 2nd invasion Weakened the allegiance of the Greeks in Asia Minor and paved the way for the revolt in 479BC Themistocles naval policy justified Salamis a victory for the Athenian govt End of combined land/s ...
Warring City
... Spartan girls also led hardy lives. Although they did not receive military training, they ran, wrestled, and played sports. Like the boys, they also learned to put service to Sparta above even love of family. As adults, women managed the family estates while their husbands served the polis. Although ...
... Spartan girls also led hardy lives. Although they did not receive military training, they ran, wrestled, and played sports. Like the boys, they also learned to put service to Sparta above even love of family. As adults, women managed the family estates while their husbands served the polis. Although ...
The Greeks
... huge slave population called helots • All boys and girls educated- women considered equals • Military education • Farming economy • Closed society- very paranoid- did not like outsiders • No wall around city ...
... huge slave population called helots • All boys and girls educated- women considered equals • Military education • Farming economy • Closed society- very paranoid- did not like outsiders • No wall around city ...
Ancient Greece (3 of 4) - Bonner Social Studies
... The Greek goal is to not to defeat the Persian army, but to crush their navy The Greeks decide to try and stall the Persian army by defending the only road into southern Greece. Led by the Spartans, a force of under 5,000 would try to hold back nearly 200,000 Persians Using the terrain to their adv ...
... The Greek goal is to not to defeat the Persian army, but to crush their navy The Greeks decide to try and stall the Persian army by defending the only road into southern Greece. Led by the Spartans, a force of under 5,000 would try to hold back nearly 200,000 Persians Using the terrain to their adv ...
Cla 3930, sec
... place called _Isles of the Blessed__. In the Odyssey, Bk.11, Odysseus goes to the Underworld and talks w/dead Greek heros, esp. the hero named __Achilles___ -who describes Hades as a dreary place. The god of Healing named __Asklepios___ had a famed spa at Epidauros. Herodotos says priests told him t ...
... place called _Isles of the Blessed__. In the Odyssey, Bk.11, Odysseus goes to the Underworld and talks w/dead Greek heros, esp. the hero named __Achilles___ -who describes Hades as a dreary place. The god of Healing named __Asklepios___ had a famed spa at Epidauros. Herodotos says priests told him t ...
World History
... 12. Who got Citizenship in Athens 13. Athenian Education for boys 14. Athenian Education for girls 15. Peloponnesus 16. Sparta 17. Messenians/Helots & their impact on Spartan culture 18. Sparta’s government & what all parts did (Assembly, Council of Elders, 5 elected officials, 2 kings) 19. Spartan ...
... 12. Who got Citizenship in Athens 13. Athenian Education for boys 14. Athenian Education for girls 15. Peloponnesus 16. Sparta 17. Messenians/Helots & their impact on Spartan culture 18. Sparta’s government & what all parts did (Assembly, Council of Elders, 5 elected officials, 2 kings) 19. Spartan ...
Heather Balogh, 8th - Crestwood Local Schools
... destroyed Attica's fields, but the Athenians sat behind their walls. Because of jam-packed quarters, however, a plague broke out which killed many people. Athens surrendered to Sparta in 404 BC. Persian Wars - from 546 BC through 479 BC Greece was at war with Persia. Darius sent an army towards Gree ...
... destroyed Attica's fields, but the Athenians sat behind their walls. Because of jam-packed quarters, however, a plague broke out which killed many people. Athens surrendered to Sparta in 404 BC. Persian Wars - from 546 BC through 479 BC Greece was at war with Persia. Darius sent an army towards Gree ...
The Greek World
... * Battle of Plataea * Alliance of Greek soldiers defeated Persian Army * Ended the Persian Wars ...
... * Battle of Plataea * Alliance of Greek soldiers defeated Persian Army * Ended the Persian Wars ...
Athens and Sparta Video Questions ANSWERS
... The Spartans won the war after they defeated the Athenian navy and then proceeded to a land invasion of Athens (after Athens had been weakened by a plague). The Spartans were able to build such a strong navy because they received money from the Persians, who did not like Athens’ growing power. Choic ...
... The Spartans won the war after they defeated the Athenian navy and then proceeded to a land invasion of Athens (after Athens had been weakened by a plague). The Spartans were able to build such a strong navy because they received money from the Persians, who did not like Athens’ growing power. Choic ...
WHICh5Sec3SpartaAthens-2016 - Alabama School of Fine Arts
... • This made it truly possibly for poor citizens to participate fully. ...
... • This made it truly possibly for poor citizens to participate fully. ...
sol 5d wars and pericles
... • Pericles had Athens rebuilt after destruction in the Persian Wars; the Parthenon is an example of this reconstruction. • After the Persian Wars, Greece formed an alliance known as the Delian League, headed by Athens • Known for the Funeral Oration to commemorate those who died fighting Sparta in t ...
... • Pericles had Athens rebuilt after destruction in the Persian Wars; the Parthenon is an example of this reconstruction. • After the Persian Wars, Greece formed an alliance known as the Delian League, headed by Athens • Known for the Funeral Oration to commemorate those who died fighting Sparta in t ...
6th grade Chapter 7 review
... Under Pericles Athens became the economic and cultural center of Greece and enjoyed its “Golden Age” Athenians used a direct democracy where all citizens could participate which worked because of Athens small number of citizens. Pericles was Athens most important general and his wise rule guided Ath ...
... Under Pericles Athens became the economic and cultural center of Greece and enjoyed its “Golden Age” Athenians used a direct democracy where all citizens could participate which worked because of Athens small number of citizens. Pericles was Athens most important general and his wise rule guided Ath ...
SOL 5d Wars and Pericles
... • Pericles had Athens rebuilt after destruction in the Persian Wars; the Parthenon is an example of this reconstruction. • After the Persian Wars, Greece formed an alliance known as the Delian League, headed by Athens • Known for the Funeral Oration to commemorate those who died fighting Sparta in t ...
... • Pericles had Athens rebuilt after destruction in the Persian Wars; the Parthenon is an example of this reconstruction. • After the Persian Wars, Greece formed an alliance known as the Delian League, headed by Athens • Known for the Funeral Oration to commemorate those who died fighting Sparta in t ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.