Greece vocab and notes - Warren County Schools
... 3.) Themistocles-Athenian general in charge of sea. Wanted to cut off food supply to Persian Army. Fought at the Salamis straight. Greek ships were smaller and could turn around quicker and rammed Persian ships. Greeks won the battle on the water *****Persian Army march to Athens (everyone gone) Per ...
... 3.) Themistocles-Athenian general in charge of sea. Wanted to cut off food supply to Persian Army. Fought at the Salamis straight. Greek ships were smaller and could turn around quicker and rammed Persian ships. Greeks won the battle on the water *****Persian Army march to Athens (everyone gone) Per ...
Life in Two City-States: Athens and Sparta
... citizens. All Athenian-born men over the age of 18 were considered Athenian citizens. Women and slaves were not permitted citizenship. Every citizen could take part in the city’s government. A group called the Council of 500 met every day. Each year, the names of all citizens 30 years of age or olde ...
... citizens. All Athenian-born men over the age of 18 were considered Athenian citizens. Women and slaves were not permitted citizenship. Every citizen could take part in the city’s government. A group called the Council of 500 met every day. Each year, the names of all citizens 30 years of age or olde ...
Ancient Greece Section 2: The Greek City
... Acropolis: a fortified area at the top of a hill in a Greek city-state (page 115) Agora: an open area below the acropolis where people would assemble and where the market was located (page 115) Hoplites: heavily armed infantry soldiers (page 116) Phalanx: a rectangular formation used by hoplites to ...
... Acropolis: a fortified area at the top of a hill in a Greek city-state (page 115) Agora: an open area below the acropolis where people would assemble and where the market was located (page 115) Hoplites: heavily armed infantry soldiers (page 116) Phalanx: a rectangular formation used by hoplites to ...
Chapter 8- Ancient Greeks
... 3.Which of the following statements best explains why direct democracy worked in ancient Athens? a. The council controlled the work of the assembly. b. People were paid to take part in government. c. The city-state’s population was small. d. Free people could vote and hold office. 4.Who benefited mo ...
... 3.Which of the following statements best explains why direct democracy worked in ancient Athens? a. The council controlled the work of the assembly. b. People were paid to take part in government. c. The city-state’s population was small. d. Free people could vote and hold office. 4.Who benefited mo ...
Ancient Greece: Day 2
... • Persian Empire controlled Middle East and Greek colonies on Asia Minor – Colonies Revolted(with aid of Athens), Persian king (Darius) determined to punish Athens ...
... • Persian Empire controlled Middle East and Greek colonies on Asia Minor – Colonies Revolted(with aid of Athens), Persian king (Darius) determined to punish Athens ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR SPARTA AND ATHENS: BE ABLE TO WRITE
... girls in Sparta learned to fist fight, wrestle and handle weapons! The Spartans had a powerful army, defeated many other armies. Athens, named after the goddess Athena, on the other hand, was not a war-like society like Sparta. Athens and Sparta were considered enemies. Unlike Sparta, Athens was mor ...
... girls in Sparta learned to fist fight, wrestle and handle weapons! The Spartans had a powerful army, defeated many other armies. Athens, named after the goddess Athena, on the other hand, was not a war-like society like Sparta. Athens and Sparta were considered enemies. Unlike Sparta, Athens was mor ...
Document
... power than women in other Greek city-states. They were expected to remain fit to bear and raise healthy children. They expected their husbands and sons to be brave in battle, to win or be killed. D. Two kings who led the Spartan army headed the Spartan oligarchy. Five men known as ephors were respon ...
... power than women in other Greek city-states. They were expected to remain fit to bear and raise healthy children. They expected their husbands and sons to be brave in battle, to win or be killed. D. Two kings who led the Spartan army headed the Spartan oligarchy. Five men known as ephors were respon ...
Classical Greece Notes
... Sparta and Athens Sparta Conquered their neighbors, the Laconians & the Messenians These people became known as helots (Greek word for “capture”) Became a military state to ensure control over the helots From childhood boys are trained to be soldiers Spartan = “highly self-disciplined” men ...
... Sparta and Athens Sparta Conquered their neighbors, the Laconians & the Messenians These people became known as helots (Greek word for “capture”) Became a military state to ensure control over the helots From childhood boys are trained to be soldiers Spartan = “highly self-disciplined” men ...
Persians and Greeks PowerPoint
... Delian League—the other city-states paid Athens to maintain their navy • Which made Athens rich and powerful • The Parthenon and other great buildings • The great plays, the great sculptures • Socrates, Plato and Aristotle—more on them ...
... Delian League—the other city-states paid Athens to maintain their navy • Which made Athens rich and powerful • The Parthenon and other great buildings • The great plays, the great sculptures • Socrates, Plato and Aristotle—more on them ...
Persian War
... 10 Years later Xerxes, successor of Darius, assembled an enormous invasion to crush your Athenian city. All of Greece was worried at this point because of how massive Xerxes’ army had become. It was debated if they should even come to your aide when the invasion hit. The great Spartan warriors, alw ...
... 10 Years later Xerxes, successor of Darius, assembled an enormous invasion to crush your Athenian city. All of Greece was worried at this point because of how massive Xerxes’ army had become. It was debated if they should even come to your aide when the invasion hit. The great Spartan warriors, alw ...
Impact of Geography on Greece - Momin2015-2016
... Philosophers Socrates, Plato, & Aristotle questioned assumptions & the use of logic to find answers to questions ...
... Philosophers Socrates, Plato, & Aristotle questioned assumptions & the use of logic to find answers to questions ...
Sparta and Athens RESEARCH
... of the population. Though they often held important positions such as teachers and nurses. The Women’s principle role in Ancient Athens was in the home. They held no rights in the Athenian democracy. Sparta: Spartan society was broken up into three main classes: Spartiates – the military leade ...
... of the population. Though they often held important positions such as teachers and nurses. The Women’s principle role in Ancient Athens was in the home. They held no rights in the Athenian democracy. Sparta: Spartan society was broken up into three main classes: Spartiates – the military leade ...
Greece and Persia
... to Athens. • Their hope was to cut off the Persian fleet, and it worked. Seeing the Athenians on top of their walls, ready for another battle, they retreated. • Legend says Pheidippides ran before the army and shouted “nenikēkamen!” (we won!) before dying of exhaustion. • His story inspired the mode ...
... to Athens. • Their hope was to cut off the Persian fleet, and it worked. Seeing the Athenians on top of their walls, ready for another battle, they retreated. • Legend says Pheidippides ran before the army and shouted “nenikēkamen!” (we won!) before dying of exhaustion. • His story inspired the mode ...
The Geography and Early Cultures of Ancient Greece
... • Women, foreigners, and slaves had no political rights – Promoting commercial/business life • Getting people to trade products/ideas • A city-state is known as a polis – Polis: city and surrounding countryside • Ex—Washington DC and its suburbs – Agora: city center—like business district – Acropoli ...
... • Women, foreigners, and slaves had no political rights – Promoting commercial/business life • Getting people to trade products/ideas • A city-state is known as a polis – Polis: city and surrounding countryside • Ex—Washington DC and its suburbs – Agora: city center—like business district – Acropoli ...
Sophocles (496-406 B
... Sophocles (496-406 B.C.) 90 years! Family From distinguished Athenian family Father = Sophillus – wealth from slave-manufactured weaponry Boyhood Education the usual poetry & gymnastics Music (Lampros = teacher) – lead boys’ chorus to celebrate Athenian victory over Persians (480 B.C.) Actor – ...
... Sophocles (496-406 B.C.) 90 years! Family From distinguished Athenian family Father = Sophillus – wealth from slave-manufactured weaponry Boyhood Education the usual poetry & gymnastics Music (Lampros = teacher) – lead boys’ chorus to celebrate Athenian victory over Persians (480 B.C.) Actor – ...
Spartan Hegemony
... these as of old should belong to the Athenians. But whatever of the two parties does not except the peace, upon them I shall make war, in company with those who desire this arrangement, both by land and by sea, with ships and with money” (Xenophon, Hellenica, 5.1.31). 387/6 The King’s Peace/Peace of ...
... these as of old should belong to the Athenians. But whatever of the two parties does not except the peace, upon them I shall make war, in company with those who desire this arrangement, both by land and by sea, with ships and with money” (Xenophon, Hellenica, 5.1.31). 387/6 The King’s Peace/Peace of ...
Name
... 22___ Leonides was the one who betrayed the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopolyae 23___ Xerxes thought that the Greeks would flee when confronted with his superior numbers 24___ Xerxes thought that freedom was a disadvantage for the Greeks 25___ Xerxes thought that a single master is what makes men c ...
... 22___ Leonides was the one who betrayed the Greeks at the Battle of Thermopolyae 23___ Xerxes thought that the Greeks would flee when confronted with his superior numbers 24___ Xerxes thought that freedom was a disadvantage for the Greeks 25___ Xerxes thought that a single master is what makes men c ...
Plataea
... supposed to have taken place at the same time, accounting for at least 25,000 men (mostly Athenians but also many Spartans) on the Asian front, which means the Greek coalition could have numbered around 80,000 men. Other historians have rejected the idea that there were any light troops at all, only ...
... supposed to have taken place at the same time, accounting for at least 25,000 men (mostly Athenians but also many Spartans) on the Asian front, which means the Greek coalition could have numbered around 80,000 men. Other historians have rejected the idea that there were any light troops at all, only ...
peloponnesian War read-aloud sheet
... was a military society. Men spent most of their lives training for and fighting in wars. Their lives were noted for simplicity and hardship. Spartan government was dominated by the military. Athens and Sparta had joined to defeat an invading Persian army in 480–479 BCE. Located on the coast, Athens ...
... was a military society. Men spent most of their lives training for and fighting in wars. Their lives were noted for simplicity and hardship. Spartan government was dominated by the military. Athens and Sparta had joined to defeat an invading Persian army in 480–479 BCE. Located on the coast, Athens ...
The Greeks
... After 5 years of fighting, Ionians were defeated but the Persian King Darius was not satisfied and wanted to punish the Greeks for helping the Ionians In 490 B.C. Darius sent armies to Greece. They landed about 26 miles northeast of Athens in a plain called Marathon. ...
... After 5 years of fighting, Ionians were defeated but the Persian King Darius was not satisfied and wanted to punish the Greeks for helping the Ionians In 490 B.C. Darius sent armies to Greece. They landed about 26 miles northeast of Athens in a plain called Marathon. ...
ANCIENT GREECE-Revised2012
... • War between Athens and Sparta – Sparta and allies dominate the land – Athens and allies dominate the sea • Spartans surround Athens hoping for an open battle – Athens avoids any battles on land – Knowing they can’t compete in open battle, they hide behind their city walls, relying on supplies from ...
... • War between Athens and Sparta – Sparta and allies dominate the land – Athens and allies dominate the sea • Spartans surround Athens hoping for an open battle – Athens avoids any battles on land – Knowing they can’t compete in open battle, they hide behind their city walls, relying on supplies from ...
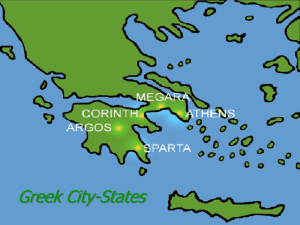
Greek City - States
... and hardship to become a superior Spartan soldier and citizen! • Sparta's government was an oligarchy. The people were ruled by a small group of warriors. The Spartans spoke Greek, wrote Greek, thought of themselves as Greeks, but they were very different from the other Greek city-states, and proud ...
... and hardship to become a superior Spartan soldier and citizen! • Sparta's government was an oligarchy. The people were ruled by a small group of warriors. The Spartans spoke Greek, wrote Greek, thought of themselves as Greeks, but they were very different from the other Greek city-states, and proud ...
HIST%20225%20L18%20Pelo%20War%202
... apprehended by men thrust into such a place was spared them. For some seventy days they thus lived all together, after which all, except the Athenians and any Siceliots or Italians who had joined in the expedition, were sold. The total number of prisoners taken it would be difficult to state exactly ...
... apprehended by men thrust into such a place was spared them. For some seventy days they thus lived all together, after which all, except the Athenians and any Siceliots or Italians who had joined in the expedition, were sold. The total number of prisoners taken it would be difficult to state exactly ...
File - Mrs. Ward World History
... role in society The women were also taught to value service to Sparta above family; they would often say to sons and husbands before they went off to war: “Come back WITH your shield… or ON it.” ...
... role in society The women were also taught to value service to Sparta above family; they would often say to sons and husbands before they went off to war: “Come back WITH your shield… or ON it.” ...
City States of Greece
... role in society The women were also taught to value service to Sparta above family; they would often say to sons and husbands before they went off to war: “Come back WITH your shield… or ON it.” ...
... role in society The women were also taught to value service to Sparta above family; they would often say to sons and husbands before they went off to war: “Come back WITH your shield… or ON it.” ...
Spartan army
The Spartan army stood at the centre of the Spartan state, whose male and female citizens were trained in the discipline and honor of the warrior society. Subject to military drill from early manhood, the Spartans were one of the most feared military forces in the Greek world. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – it was commonly accepted that, ""one Spartan was worth several men of any other state."" According to Thucydides, the famous moment of Spartan surrender at the island of Sphacteria off of Pylos was highly unexpected. He said that ""it was the common perception at the time that Spartans would never lay down their weapons for any reason, be it hunger, or danger.""The iconic army was first coined by the Spartan legislator Lycurgus. In his famous quote of Sparta having a ""wall of men, instead of bricks"", he proposed to create a military-focused lifestyle reformation in the Spartan society in accordance to proper virtues such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. A Spartan man's involvement with the army began in infancy when he was inspected by the Gerousia. If the baby was found to be weak or deformed he was left at Mount Taygetus to die, since the world of the Spartans was no place for those who could not already fend for themselves. It should be noted, however, that the practice of discarding children at birth took place in Athens as well. Those deemed strong were then put in the agoge at the age of seven. Under the agoge the young boys or Spartiates were kept under intense and rigorous military training. Their education focused primarily on cunning, sports and war tactics, but also included poetry, music, academics, and sometimes politics. Those who passed the agoge by the age of 30 were given full Spartan citizenship.The term ""spartan"" became synonymous with multiple meanings such as: fearlessness, harsh and cruel life, bland and lacking creativity, or simplicity by design.