How is DNA packed in the nucleus?
... chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G). The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. ...
... chemical nucleotide bases (A, C, T, and G). The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. ...
Advanced Biology Vocabulary
... An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
... An individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species. ...
karyotypes - TeacherWeb
... cells during meiosis. This can result in an abnormal number of chromosomes. If a sperm with an extra chromosome fertilizes an egg with a normal chromosome number, the resulting zygote will have 3 copies of one chromosome. This is called _________. If a sperm that is missing a chromosome fertilizes a ...
... cells during meiosis. This can result in an abnormal number of chromosomes. If a sperm with an extra chromosome fertilizes an egg with a normal chromosome number, the resulting zygote will have 3 copies of one chromosome. This is called _________. If a sperm that is missing a chromosome fertilizes a ...
Mutation Notes What is a MUTATION? Any change made to the DNA
... Mutation Notes What is a MUTATION? Any change made to the DNA Do all mutation cause a change in a trait? Not always, it depends on location of mutation and type Mutations can be inherited from parent to child or acquired due to environmental damage or mistakes in replication Mutations happen regular ...
... Mutation Notes What is a MUTATION? Any change made to the DNA Do all mutation cause a change in a trait? Not always, it depends on location of mutation and type Mutations can be inherited from parent to child or acquired due to environmental damage or mistakes in replication Mutations happen regular ...
HumanGenetics
... Occurs when either homologues fail to separate during anaphase I of meiosis, or sister chromatids fail to separate during anaphase II. The result is that one gamete has 2 copies of one chromosome and the other has no copy of that chromosome. (The other chromosomes are distributed normally.) If eithe ...
... Occurs when either homologues fail to separate during anaphase I of meiosis, or sister chromatids fail to separate during anaphase II. The result is that one gamete has 2 copies of one chromosome and the other has no copy of that chromosome. (The other chromosomes are distributed normally.) If eithe ...
3U 1.7a Midpoint Review
... What are the three basic concepts of cell theory? What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 3.1 Principles of Cell division Why do cells divide? What are the benefits of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? 3.2 The Cell Cycle What is the importance of int ...
... What are the three basic concepts of cell theory? What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 3.1 Principles of Cell division Why do cells divide? What are the benefits of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? 3.2 The Cell Cycle What is the importance of int ...
What is the difference between Autotrophs and heterotrophs?
... b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome ...
... b. independent segregation of genes during the formation of gametes c. result of the cytoplasm not dividing evenly d. chromosome that is not a sex chromosome e. two different alleles for the same trait f. two identical alleles for a particular trait g. gene located on the X or Y chromosome ...
Chromosome Mapping The following data were collected from
... Chromosome Mapping The following data were collected from repeated matings of fruit flies (D. melanogaster). The data record the frequency, to 0.1 percent, of the recombinant characteristics for seven genes located on the same side of the centromere on chromosome 3. The veinlet gene is located one m ...
... Chromosome Mapping The following data were collected from repeated matings of fruit flies (D. melanogaster). The data record the frequency, to 0.1 percent, of the recombinant characteristics for seven genes located on the same side of the centromere on chromosome 3. The veinlet gene is located one m ...
Mutation in Mitosis and Meiosis
... Mutations can be: positive – have a good effect on the organism negative – be detrimental or fatal neutral – have no effect (repetition of triplet code) If a mutation occurs in a gamete or during meiosis, the mutation is passed on to the offspring. Mutations during DNA replication 1. base pair subst ...
... Mutations can be: positive – have a good effect on the organism negative – be detrimental or fatal neutral – have no effect (repetition of triplet code) If a mutation occurs in a gamete or during meiosis, the mutation is passed on to the offspring. Mutations during DNA replication 1. base pair subst ...
Expressing_CENH3_Orthologs
... The centromere is the locus on the chromosome where the kinetochore, which will be bound by the spindle microtubules, assembles. There are three broadly defined types of centromere DNA sequences : ...
... The centromere is the locus on the chromosome where the kinetochore, which will be bound by the spindle microtubules, assembles. There are three broadly defined types of centromere DNA sequences : ...
Looking at karyotypes
... 5. Describe how the Klinefelter’s karyotype is different. Klinefelter’s syndrome produces a sterile male with female features and small testes. 6. Explain why a person with Klinefelter’s syndrome is male, not female, even though they have two X chromosomes. 7. Half of all miscarriages are due to chr ...
... 5. Describe how the Klinefelter’s karyotype is different. Klinefelter’s syndrome produces a sterile male with female features and small testes. 6. Explain why a person with Klinefelter’s syndrome is male, not female, even though they have two X chromosomes. 7. Half of all miscarriages are due to chr ...
chapter 6 vocabulary card sort
... form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring ...
... form of asexual reproduction that produces identical offspring ...
Biology Mitosis / Meiosis 2012 – 2013 #3
... A. Deletion = part of the chromosome is broken off and lost B. Duplication = part of the chromosome breaks off and attaches to its homologous chromosome C. Inversion = part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards D. Translocation = part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a Non-ho ...
... A. Deletion = part of the chromosome is broken off and lost B. Duplication = part of the chromosome breaks off and attaches to its homologous chromosome C. Inversion = part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards D. Translocation = part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a Non-ho ...
Bio 130 * Quiz March 23
... can bind to spindle microtubules B. the centromere region of a metaphase chromosome at which the DNA can bind with spindle proteins C. the array of vesicles that will form between two dividing nuclei and give rise to the metaphase plate D. the ring of actin microfilaments that will cause the appeara ...
... can bind to spindle microtubules B. the centromere region of a metaphase chromosome at which the DNA can bind with spindle proteins C. the array of vesicles that will form between two dividing nuclei and give rise to the metaphase plate D. the ring of actin microfilaments that will cause the appeara ...
Genetic Disorders
... don’t separate from each other then the gametes could end up with the wrong number of chromosomes If the egg has a wrong # of chromosomes and it gets fertilized, the zygote and every single cell after it begins to divide will have the wrong # of chromosomes ...
... don’t separate from each other then the gametes could end up with the wrong number of chromosomes If the egg has a wrong # of chromosomes and it gets fertilized, the zygote and every single cell after it begins to divide will have the wrong # of chromosomes ...
BioSc 231 2001 Exam4
... _____ A female Drosophila supposedly heterozygous for two recessive mutations cn and lz that are on the same arm of the X chromosome (cn lz/+ +) surprisingly expresses both these genes. The male progeny of the female will be A. all wild type B. all cn lz C. 1/2 cn lz and 1/2 wild type D. cn + E. + l ...
... _____ A female Drosophila supposedly heterozygous for two recessive mutations cn and lz that are on the same arm of the X chromosome (cn lz/+ +) surprisingly expresses both these genes. The male progeny of the female will be A. all wild type B. all cn lz C. 1/2 cn lz and 1/2 wild type D. cn + E. + l ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
... DNA is located in the chromosomes present in the nucleus of the cell. The DNA of an individual is the same in every one of his or her cells (but is not present in red blood cells because these cells have no nuclei) and different from everyone else’s other than identical twins. The DNA molecule resem ...
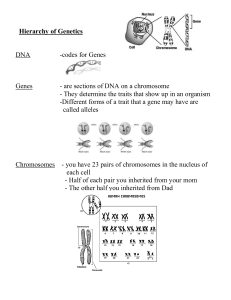
Hierarchy of Genetics
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
... - are sections of DNA on a chromosome - They determine the traits that show up in an organism -Different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles ...
Chromosomes, Chromatids, Loci, and Alleles
... impossible to see. Then, at some point in the cell’s life cycle, the cell will start to prepare for cell division through either mitosis (somatic cells) or meiosis (sex cells). The DNA will first replicate in the synthesis phase of the cell life cycle to produce two identical copies of the chromosom ...
... impossible to see. Then, at some point in the cell’s life cycle, the cell will start to prepare for cell division through either mitosis (somatic cells) or meiosis (sex cells). The DNA will first replicate in the synthesis phase of the cell life cycle to produce two identical copies of the chromosom ...
Mitosis and Meiosis Power Point
... Reproduction To make more of its own kind: A) asexual – 1 parent, identical offspring B) sexual – 2 parents, NOT identical offspring ...
... Reproduction To make more of its own kind: A) asexual – 1 parent, identical offspring B) sexual – 2 parents, NOT identical offspring ...
IB Biology--Chromosome Review Activity
... https://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/search?text=telomeres&sort_by=search_api_releva nce&redirect=1 to complete the following questions : 1. Since the DNA of prokaryotes lacks histones it is termed _____________________. 2. How does eukaryote and prokaryote DNA compare? ...
... https://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/search?text=telomeres&sort_by=search_api_releva nce&redirect=1 to complete the following questions : 1. Since the DNA of prokaryotes lacks histones it is termed _____________________. 2. How does eukaryote and prokaryote DNA compare? ...
Karotype Chromosomal Abnormalities
... A picture of chromosomes used to detect chromosomal abnormalities. Autosomal (somatic): Pairs 1-22 Sex: Pair 23 ...
... A picture of chromosomes used to detect chromosomal abnormalities. Autosomal (somatic): Pairs 1-22 Sex: Pair 23 ...