Energy Transformations - Science with Mrs. Sinning
... • Energy that comes from splitting (fission) or combining (fusion) the nuclei ...
... • Energy that comes from splitting (fission) or combining (fusion) the nuclei ...
Name Date Energy in One Form or Another ENERGY
... There are several energy conversion devices on the demonstration table. Your job is to analyze each, and write down all of the energy conversions involved in the operation of the device. Use the abbreviations from above and follow the example (1) below. 1. Mass oscillating on a spring ELPE --> KE -- ...
... There are several energy conversion devices on the demonstration table. Your job is to analyze each, and write down all of the energy conversions involved in the operation of the device. Use the abbreviations from above and follow the example (1) below. 1. Mass oscillating on a spring ELPE --> KE -- ...
Energy Forms - Greenwood County School District 52
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
Mechanical energy
... Electrical energy light, thermal energy, sound Chemical energy kinetic energy to move a car, ...
... Electrical energy light, thermal energy, sound Chemical energy kinetic energy to move a car, ...
Work, Power, and Machines
... States of Energy • Kinetic Energy – energy of motion – a moving object has the ability to do work • this depends on the object’s mass and ...
... States of Energy • Kinetic Energy – energy of motion – a moving object has the ability to do work • this depends on the object’s mass and ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Problems
... 1) What is the gravitational constant on Earth? 2) What is the Potential Energy of a 10 N (pay attention to the unit, Newtons, here) book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 meters high? 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcas ...
... 1) What is the gravitational constant on Earth? 2) What is the Potential Energy of a 10 N (pay attention to the unit, Newtons, here) book that is placed on a shelf that is 2.5 meters high? 3) Determine the amount of potential energy of a 5 N book that is moved to three different shelves on a bookcas ...
Chemical Energy
... 1. Attracting – To draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull. 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoes a chemical reaction. 3. Electr ...
... 1. Attracting – To draw by a physical force causing or tending to cause to approach, adhere, or unite; pull. 2. Chemical Energy – Energy which is stored within the bonds of atoms and molecules of a a. substance. Released when they are broken and the substance undergoes a chemical reaction. 3. Electr ...
Physics Chapter 5 Vocabulary Section 1 Energy: the ability to do
... Fossil fuels: nonrenewable energy resources that form in the Earth’s crust over millions of years from the buried remains of once-‐living organisms. ...
... Fossil fuels: nonrenewable energy resources that form in the Earth’s crust over millions of years from the buried remains of once-‐living organisms. ...
Week 3 CCA Review
... 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. They are found on the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Metalloids are semiconductors, which means they can conduct electricity at high temperatures. 4. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can ...
... 3. Metalloids are elements that have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. They are found on the stair step line on the Periodic Table. Metalloids are semiconductors, which means they can conduct electricity at high temperatures. 4. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can ...
Energy Vocabulary
... electrical energy: energy that comes from an electric current conductor: material that allows heat to move through it easily ...
... electrical energy: energy that comes from an electric current conductor: material that allows heat to move through it easily ...
Energy - Maples Elementary School
... A Roller Coaster As it slows to a stop at the top of a hill, it has potential energy because of where it is. It has the potential to move because it is above the ground and has somewhere to go. ...
... A Roller Coaster As it slows to a stop at the top of a hill, it has potential energy because of where it is. It has the potential to move because it is above the ground and has somewhere to go. ...
Environmental Systems
... • Joule: basic unit of energy (J) • Energy and Power a. energy-ability to do work power-rate at which work is done therefore, energy = power X time power = energy / time ...
... • Joule: basic unit of energy (J) • Energy and Power a. energy-ability to do work power-rate at which work is done therefore, energy = power X time power = energy / time ...
Name: Period:______ Date:______ Infinite Potential Forms of
... 7. What is electrical energy? It is kinetic energy that results from movement of charges. 8. How is sound energy transferred? Sound energy is transferred by vibrations passed along through the air. 9. How fast do electromagnetic waves travel? Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light. 10. W ...
... 7. What is electrical energy? It is kinetic energy that results from movement of charges. 8. How is sound energy transferred? Sound energy is transferred by vibrations passed along through the air. 9. How fast do electromagnetic waves travel? Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light. 10. W ...
Energy study guide worksheet
... above, is not as high as the first. (Hint: Think about the energy transformations that occurred during the ride. Was 100% of the gravitational potential transformed into kinetic energy?) ...
... above, is not as high as the first. (Hint: Think about the energy transformations that occurred during the ride. Was 100% of the gravitational potential transformed into kinetic energy?) ...
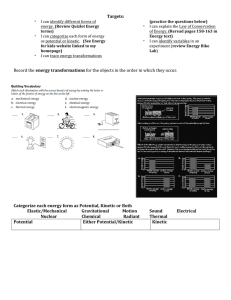
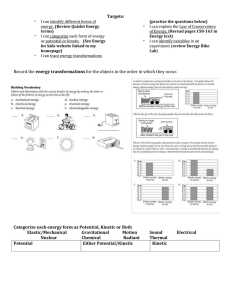
Targets: * I can identify different forms of energy. (Review Quizlet
... as potential or kinetic. (See Energy for kids website linked to my homepage) I can trace energy transformations ...
... as potential or kinetic. (See Energy for kids website linked to my homepage) I can trace energy transformations ...
Kinetic Energy
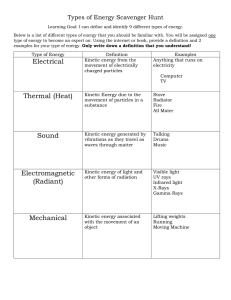
... Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 examples for your type of energy. Only write down a definition that you understand! ...
... Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 examples for your type of energy. Only write down a definition that you understand! ...
Chapter 9 Test Study Guide - Motion and Energy
... 26. A car traveling at 75.5 Km/h encounters an emergency and comes to a complete stop. How much time will it take for the car to stop if it accelerates at -6.4 Km/h/s? ...
... 26. A car traveling at 75.5 Km/h encounters an emergency and comes to a complete stop. How much time will it take for the car to stop if it accelerates at -6.4 Km/h/s? ...
Chapter-9-Energy-notes
... The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of a force against gravity and against friction. The equation for work is ______________ The unit of work is Newton-meters or Nm is called ...
... The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of a force against gravity and against friction. The equation for work is ______________ The unit of work is Newton-meters or Nm is called ...
SOL PS 6
... vibrations of electrically charged particles. • Transfers energy without a medium. • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of the particles. • Depends on the number of particles as well as the temperature . ...
... vibrations of electrically charged particles. • Transfers energy without a medium. • All of the kinetic energy due to random motion of the particles. • Depends on the number of particles as well as the temperature . ...
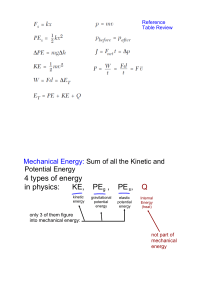
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
... Kinetic Energy: K = ½ mv2 For each of the following energy problems, use the problem solving strategy. Include sketches, your system, and bar charts in your answers. 5.2 Regular Problem If you drop a 0.3 kg baseball from a window 20 m above the ground, how fast will the ball be moving the instant ...
... Kinetic Energy: K = ½ mv2 For each of the following energy problems, use the problem solving strategy. Include sketches, your system, and bar charts in your answers. 5.2 Regular Problem If you drop a 0.3 kg baseball from a window 20 m above the ground, how fast will the ball be moving the instant ...
Regenerative brake

A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form which can be either used immediately or stored until needed. This contrasts with conventional braking systems, where the excess kinetic energy is converted to heat by friction in the brakes and therefore wasted. In addition to improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle, regeneration can also greatly extend the life of the braking system as its parts do not wear as quickly.