Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... a good example.... You cannot easily store excess electricity generating capacity.... Pump the water back up the hill ...
... a good example.... You cannot easily store excess electricity generating capacity.... Pump the water back up the hill ...
Heat and Energy
... Identify the physical state of a substance as a solid, liquid, or gas. Describe the changes of state between solids, liquids, and gases; calculate the energy involved. ...
... Identify the physical state of a substance as a solid, liquid, or gas. Describe the changes of state between solids, liquids, and gases; calculate the energy involved. ...
Tutorial 4 - UniMAP Portal
... 8. A metal ball of mass 10g was attached to the lower side of a vertical spring. Calculate the spring constant, k if attaching the metal ball makes the spring stretch downwards by 1.2cm. An external force pulls the metal ball further down by 2.0cm and releases it. How much energy does this external ...
... 8. A metal ball of mass 10g was attached to the lower side of a vertical spring. Calculate the spring constant, k if attaching the metal ball makes the spring stretch downwards by 1.2cm. An external force pulls the metal ball further down by 2.0cm and releases it. How much energy does this external ...
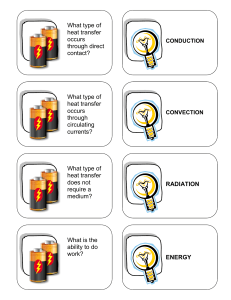
What type of heat transfer occurs through circulating currents? What
... What is the area surrounding a magnet that can attract or repel objects? ...
... What is the area surrounding a magnet that can attract or repel objects? ...
Types of Energy Powerpoint
... Examples are Wind (turns windmill) Hydropower- going over dam Ball flying through air You walking ...
... Examples are Wind (turns windmill) Hydropower- going over dam Ball flying through air You walking ...
Conservation of Energy
... Conservation of Energy • Energy will always be energy, no matter what form it is in • Energy can be transferred from one type of energy to another • Potential Energy to Kinetic Energy • Kinetic Energy to Heat Energy • Heat Energy to Light Energy etc….. Any examples? ...
... Conservation of Energy • Energy will always be energy, no matter what form it is in • Energy can be transferred from one type of energy to another • Potential Energy to Kinetic Energy • Kinetic Energy to Heat Energy • Heat Energy to Light Energy etc….. Any examples? ...
Energy Notes
... Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temperature of a substance. Chemical Energy - Energy stored in chemical bonds. Electromagnetic Energy - Energy which can travel ...
... Potential Energy - Energy an object has because of its postion or shape. Kinetic Energy - Energy an object has because it is moving. Heat Energy - The energy related to the temperature of a substance. Chemical Energy - Energy stored in chemical bonds. Electromagnetic Energy - Energy which can travel ...
Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Do Now
... Which of the following explains the total amount of kinetic What is the rolling motion of boiling water an example of? energy contained in the particles of a substance? a. Conduction a. Temperature b. Convection b. Heat c. Radiation c. Thermal energy d. Insulation d. Kinetic energy Label the parts o ...
... Which of the following explains the total amount of kinetic What is the rolling motion of boiling water an example of? energy contained in the particles of a substance? a. Conduction a. Temperature b. Convection b. Heat c. Radiation c. Thermal energy d. Insulation d. Kinetic energy Label the parts o ...
Transformations of Energy Notes
... The matter that a wave travels through is called a medium. For example, the medium through which a wave travels in the ocean is the water. The crest is the top of the wave The trough is the bottom of the wave The wavelength is the distance from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next wave Amp ...
... The matter that a wave travels through is called a medium. For example, the medium through which a wave travels in the ocean is the water. The crest is the top of the wave The trough is the bottom of the wave The wavelength is the distance from the crest of one wave to the crest of the next wave Amp ...
File
... 3. A small 50-kilogram canoe is floating downriver at a speed of 4 m/s. What is the canoe’s kinetic energy? 4. A 12-kg sled is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. At what speed will the sled have twice as much kinetic energy? 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give thre ...
... 3. A small 50-kilogram canoe is floating downriver at a speed of 4 m/s. What is the canoe’s kinetic energy? 4. A 12-kg sled is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. At what speed will the sled have twice as much kinetic energy? 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give thre ...
What is Energy?
... atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! ...
... atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! ...
What is Energy?
... Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position – gravitational potential energy. ...
... Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position – gravitational potential energy. ...
Energy - Griffin School District
... Bill Nye Video: Energy (complete this on a separate sheet of paper) ...
... Bill Nye Video: Energy (complete this on a separate sheet of paper) ...
Sample outline for Cornell Notes
... KE = ½ x Mass x (Velocity)2 Example; Bowling ball has greater KE than golf ball moving at same speed II. Potential Energy 4) PE is stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object A. Gravitational Potential Energy 5) GPE is energy related to an objects height ...
... KE = ½ x Mass x (Velocity)2 Example; Bowling ball has greater KE than golf ball moving at same speed II. Potential Energy 4) PE is stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object A. Gravitational Potential Energy 5) GPE is energy related to an objects height ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
Chapter 9 Vocabulary Energy – the ability to do work Kinetic energy
... Gravitational potential energy – energy due to an object’s position above the Earth’s surface. Mechanical energy - total energy of motion and position of an object Energy Conversion - a change from one form of energy into another; any form of energy can be converted into another form Law of Conserva ...
... Gravitational potential energy – energy due to an object’s position above the Earth’s surface. Mechanical energy - total energy of motion and position of an object Energy Conversion - a change from one form of energy into another; any form of energy can be converted into another form Law of Conserva ...
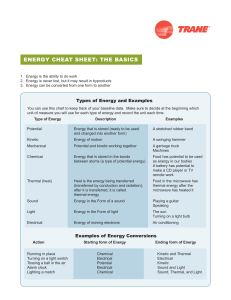
energy CheAt Sheet: the bASiCS
... 1. Energy is the ability to do work 2. Energy is never lost, but it may result in byproducts 3. Energy can be converted from one form to another ...
... 1. Energy is the ability to do work 2. Energy is never lost, but it may result in byproducts 3. Energy can be converted from one form to another ...
2nd 6 Weeks - Forms of Energy, Circuits and Force
... Light energy – radiant energy that our eyes can see from the visible part of the electromagnetic ...
... Light energy – radiant energy that our eyes can see from the visible part of the electromagnetic ...
Chapter 12: Work and Energy
... 2. Explain how energy is different from work. 3. Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy. 4. What form or forms of energy apply to each of the following? (a) a Frisbee flying through the air (b) a hot cup of soup (c) a wound clock spring (d) sunlight (e) a boulder sitting at the ...
... 2. Explain how energy is different from work. 3. Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy. 4. What form or forms of energy apply to each of the following? (a) a Frisbee flying through the air (b) a hot cup of soup (c) a wound clock spring (d) sunlight (e) a boulder sitting at the ...
Regenerative brake

A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form which can be either used immediately or stored until needed. This contrasts with conventional braking systems, where the excess kinetic energy is converted to heat by friction in the brakes and therefore wasted. In addition to improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle, regeneration can also greatly extend the life of the braking system as its parts do not wear as quickly.