Advanced Version
... d. Plan and carry out investigations on the effects of heat transfer on molecular motion as it relates to the collision of atoms (conduction), through space (radiation), or in currents in a liquid or a gas (convection). ...
... d. Plan and carry out investigations on the effects of heat transfer on molecular motion as it relates to the collision of atoms (conduction), through space (radiation), or in currents in a liquid or a gas (convection). ...
the law of conservation of energy
... A car launched up the hill at a given speed will never go higher than a certain point. A car rolling downhill will only reach a certain speed. Why? The answer is that nature keeps an exact balance of energy: the law of conservation of energy Speed uses one form of energy and height uses another. Thi ...
... A car launched up the hill at a given speed will never go higher than a certain point. A car rolling downhill will only reach a certain speed. Why? The answer is that nature keeps an exact balance of energy: the law of conservation of energy Speed uses one form of energy and height uses another. Thi ...
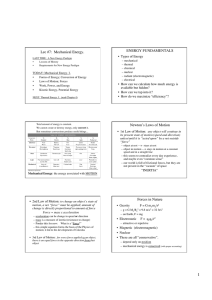
Mechanical & Thermal Energy Energy
... The sum of all kinetic energies of all the particles comprising an object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
... The sum of all kinetic energies of all the particles comprising an object is thermal energy. (most matter expands as its thermal energy increases) The faster molecules are moving, the more thermal energy they have; which is why balls go farther in warm weather than cold. ...
File
... Forms of Energy The form of the energy is the way that the ability to do something is produced in an object. For example, an object which can affect other objects because of its movement is said to have kinetic energy. (Kinetic is a word from Greek which means movement) An object which can affect o ...
... Forms of Energy The form of the energy is the way that the ability to do something is produced in an object. For example, an object which can affect other objects because of its movement is said to have kinetic energy. (Kinetic is a word from Greek which means movement) An object which can affect o ...
Energy and energy resources
... Chemical- Energy can be stored in the bonds between atoms, when you break these bonds to rearrange the atoms you can release the energy. Digesting food releases chemical energy ( possible in the dark lifesavers activity) ...
... Chemical- Energy can be stored in the bonds between atoms, when you break these bonds to rearrange the atoms you can release the energy. Digesting food releases chemical energy ( possible in the dark lifesavers activity) ...
Energy Notes - Student
... 2. A toddler pushes a 5kg car horizontally across the floor with a constant force. If the car starts from rest and after 0.60 meters, the car is travelling at a speed of 1.5m/s, with what force did he push it? ...
... 2. A toddler pushes a 5kg car horizontally across the floor with a constant force. If the car starts from rest and after 0.60 meters, the car is travelling at a speed of 1.5m/s, with what force did he push it? ...
Conceptual Questions Chap. 13
... Suppose you are sitting in a car and a 20–kV power line drops across the car. Should you stay in the car or get out? The power line potential is 20 kV compared to the potential of the ground. You should stay inside the car. If you step outside, a 20 kV potential difference could exist between you an ...
... Suppose you are sitting in a car and a 20–kV power line drops across the car. Should you stay in the car or get out? The power line potential is 20 kV compared to the potential of the ground. You should stay inside the car. If you step outside, a 20 kV potential difference could exist between you an ...
Work, Power, and Energy Webquest
... department store to the second. The second floor is located 5-meters above the first floor. The average passenger's mass is 60 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time. ...
... department store to the second. The second floor is located 5-meters above the first floor. The average passenger's mass is 60 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of passengers in this amount of time. ...
Chapter 5 – Work and Energy Study Guide
... 1. Potential energy is the stored energy of an object due to the object’s position or condition a. Gravitational potential energy: the stored energy of an object due to its position PEg = mgh b. Elastic potential energy: the stored energy in any compressed or stretched object PEelastic = ½ kx2 (k = ...
... 1. Potential energy is the stored energy of an object due to the object’s position or condition a. Gravitational potential energy: the stored energy of an object due to its position PEg = mgh b. Elastic potential energy: the stored energy in any compressed or stretched object PEelastic = ½ kx2 (k = ...
Transparancies for Energy & Momentum Section
... • Work = Force F ×Distance s, units of Joules[J] – More precisely W=F.x – F,x Vectors so W=F x cos • e.g. raise a 10kg weight 2m • F=mg=10*9.8 N, • W=Fx=98*2=196 Nm=196J ...
... • Work = Force F ×Distance s, units of Joules[J] – More precisely W=F.x – F,x Vectors so W=F x cos • e.g. raise a 10kg weight 2m • F=mg=10*9.8 N, • W=Fx=98*2=196 Nm=196J ...
Work and Energy PPT - Aurora City Schools
... The Principle of Conservation of Energy Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed, i.e. the total energy of a system is constant Energy is measured in joules and it is a scalar quantity ...
... The Principle of Conservation of Energy Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created nor destroyed, i.e. the total energy of a system is constant Energy is measured in joules and it is a scalar quantity ...
Document
... A metal spoon becomes warm when placed in a cup of hot tea. This is an example of A. convection. B. radiation. C. conduction. ...
... A metal spoon becomes warm when placed in a cup of hot tea. This is an example of A. convection. B. radiation. C. conduction. ...
Sci_ch9_Lesson_3_notes
... hill, pencil on the edge of your desk Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. Examples: roller coaster moving along the track, ball rolling across the ground. Types of kinetic energy include electricity, light, sound, heat, and motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object ...
... hill, pencil on the edge of your desk Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. Examples: roller coaster moving along the track, ball rolling across the ground. Types of kinetic energy include electricity, light, sound, heat, and motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object ...
Chapter 5 Test
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
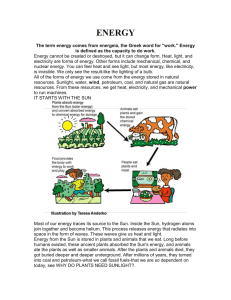
ENERGY
... The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can feel he ...
... The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can feel he ...
Answers
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? _gases_____ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _kinetic_ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? _gases_____ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _kinetic_ ...
Physical Science Worksheet: Energy Short Answer 1. The kinetic
... a height of 500 m then he stopped and floated in the air at that height. Suddenly, a piece of Kryptonite rope came out of nowhere and wrapped around Superman. The Kryptonite rope took Superman’s powers and he fell to the ground. At what Velocity did he hit the ground? Which of the following is not u ...
... a height of 500 m then he stopped and floated in the air at that height. Suddenly, a piece of Kryptonite rope came out of nowhere and wrapped around Superman. The Kryptonite rope took Superman’s powers and he fell to the ground. At what Velocity did he hit the ground? Which of the following is not u ...
Weekly Overview - School District 27J
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
Energy Transformations- Homework
... energy from one form to another. An energy transformation is a change of one type of energy into another type of energy. For example, the energy in your body comes from the food you eat. Your body transforms chemical energy from food into another kind of chemical energy—a molecule called ATP. Your b ...
... energy from one form to another. An energy transformation is a change of one type of energy into another type of energy. For example, the energy in your body comes from the food you eat. Your body transforms chemical energy from food into another kind of chemical energy—a molecule called ATP. Your b ...
I hypothesize a correlation between irradiation of the
... escape energy in the ionosphere can give two possible consequences: the first possibility is a continuous drift of electron from the Earth ionosphere (with a ever greater escape energy that reduces the drift, and it seem unlikely over a long period), the second possibility is an oscillation of the e ...
... escape energy in the ionosphere can give two possible consequences: the first possibility is a continuous drift of electron from the Earth ionosphere (with a ever greater escape energy that reduces the drift, and it seem unlikely over a long period), the second possibility is an oscillation of the e ...
Mr. Kelley`s 8th Grade Science – February
... Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
... Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
Energy Transformation Demos
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy (electricity) using a ...
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy (electricity) using a ...
Chemical Energy
... When would the car have the greatest and the least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic ene ...
... When would the car have the greatest and the least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic ene ...
Regenerative brake

A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form which can be either used immediately or stored until needed. This contrasts with conventional braking systems, where the excess kinetic energy is converted to heat by friction in the brakes and therefore wasted. In addition to improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle, regeneration can also greatly extend the life of the braking system as its parts do not wear as quickly.