* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conceptual Questions Chap. 13
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Vehicle-to-grid wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
UltraBattery wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Supercapacitor wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
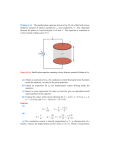
Conceptual Questions Chap. 16 1. Suppose you are sitting in a car and a 20–kV power line drops across the car. Should you stay in the car or get out? The power line potential is 20 kV compared to the potential of the ground. You should stay inside the car. If you step outside, a 20 kV potential difference could exist between you and the ground, causing a large charge to flow through you and likely resulting in injury. 2. Distinguish between electric potential and electrical potential energy. Electric potential is a measure of the electrical potential energy per unit charge. Electrical potential energy is a measure of the potential energy of a system consisting of a charge in an electric field. 3. Why is it dangerous to touch the terminals of a high-voltage capacitor even after the voltage source that charged the capacitor is disconnected from it? What can be done to make the capacitor safe to handle after the voltage source has been removed? The plates of a capacitor often remained charged long after the voltage source is removed. Touching the terminals grounds the capacitor (under normal circumstances) and large amounts of charge can pass through you. Instead, the capacitor can be “short-circuited” with a conductor having an insulating handle. 4. What happens to the energy stored in a capacitor if a dielectric is inserted into the capacitor while it is connected to a battery? What if the battery has been disconnected? In the first case, the stored energy increases. In the second case, the stored energy decreases.




![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)