How to Calculate Kinetic Energy
... 5.2 Regular Problem If you drop a 0.3 kg baseball from a window 20 m above the ground, how fast will the ball be moving the instant before it hits the ground? 5.3 Practice If a stretched slingshot has 100 J of elastic potential energy, how fast will a 0.5 kg softball be moving right after the laun ...
... 5.2 Regular Problem If you drop a 0.3 kg baseball from a window 20 m above the ground, how fast will the ball be moving the instant before it hits the ground? 5.3 Practice If a stretched slingshot has 100 J of elastic potential energy, how fast will a 0.5 kg softball be moving right after the laun ...
Energy - ability of an object to do work
... Kinetic energy – the actual movement of an object Mechanical – when potential and kinetic energy are put to an object Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a path in which electrons move Conductor – materials that allow electrons, sound, or heat to move ...
... Kinetic energy – the actual movement of an object Mechanical – when potential and kinetic energy are put to an object Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a path in which electrons move Conductor – materials that allow electrons, sound, or heat to move ...
Chapter 10 Energy PowerPoint
... that energy is lowered. Concentrated energy (like gasoline) used to do work becomes energy that is spread out throughout the universe. Energy concerns are based on the quality, not the quantity of energy. The concept of the “heat death” of the universe addresses the eventuality that at some point in ...
... that energy is lowered. Concentrated energy (like gasoline) used to do work becomes energy that is spread out throughout the universe. Energy concerns are based on the quality, not the quantity of energy. The concept of the “heat death” of the universe addresses the eventuality that at some point in ...
Forms of Energy - Ms. Morgan's Science Spot
... For example: A car with the mass of 200 kilograms moving at 2 meters per second would have this kinetic energy: KE= (1/2)200 x 4 KE= 400 Joules ...
... For example: A car with the mass of 200 kilograms moving at 2 meters per second would have this kinetic energy: KE= (1/2)200 x 4 KE= 400 Joules ...
Forms of Energy Review
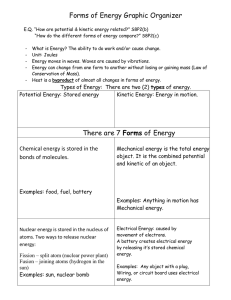
... converts electrical energy into light (electromagnetic) energy and heat (thermal) energy ...
... converts electrical energy into light (electromagnetic) energy and heat (thermal) energy ...
Energy - TeacherWeb
... Types of Chemical Systems • An open system is a system in which both matter and energy are free to enter and leave the system (ex: barbecue) • A closed system is a system in which energy can enter and leave the system, but matter cannot (ex: glow stick) • An isolated system is an ideal system in wh ...
... Types of Chemical Systems • An open system is a system in which both matter and energy are free to enter and leave the system (ex: barbecue) • A closed system is a system in which energy can enter and leave the system, but matter cannot (ex: glow stick) • An isolated system is an ideal system in wh ...
SPH 4C - mackenziekim
... 22. Which are the most efficient types of light bulb in the home today? Which are the least efficient? 23. a) Where is most of your electricity used in the home? b) How can you as an individual reduce how much energy you use / waste in your home? 24. In energy conservation, no energy is actually “lo ...
... 22. Which are the most efficient types of light bulb in the home today? Which are the least efficient? 23. a) Where is most of your electricity used in the home? b) How can you as an individual reduce how much energy you use / waste in your home? 24. In energy conservation, no energy is actually “lo ...
Light Energy - DiMaggio
... Electrical Energy • Electrical Energy is the energy stored in electrons(electricity) • Electrical energy can be thought of as potential energy that is waiting to be used. The potential energy is changed into kinetic energy when you plug in an electrical appliance and use it. Examples: ...
... Electrical Energy • Electrical Energy is the energy stored in electrons(electricity) • Electrical energy can be thought of as potential energy that is waiting to be used. The potential energy is changed into kinetic energy when you plug in an electrical appliance and use it. Examples: ...
Chemical energy is stored in some substances
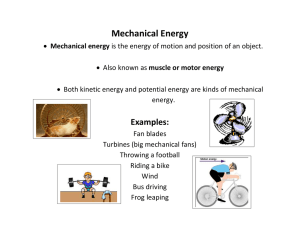
... are two types of mechanical energy: kinetic energy and potential energy. ...
... are two types of mechanical energy: kinetic energy and potential energy. ...
Types and Forms of Energy
... ball or turn the pedals of a bicycle. • Other examples include water flowing in a stream, tires rolling down a road and sound waves from your iPod. ...
... ball or turn the pedals of a bicycle. • Other examples include water flowing in a stream, tires rolling down a road and sound waves from your iPod. ...
Chapter 9 Test Study Guide - Motion and Energy
... Answer Bank – Answers may be used more than once and may need to be combined to answer a question ...
... Answer Bank – Answers may be used more than once and may need to be combined to answer a question ...
Different forms of energy
... particles in a substance. All matter is made up of atoms ( particles) that move faster when they heat up. The faster the particles move, higher the temperature. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ...
... particles in a substance. All matter is made up of atoms ( particles) that move faster when they heat up. The faster the particles move, higher the temperature. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects ...
Forms of Energy
... Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
... Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
Name_______________________________ Energy, Heat, and
... 1. Energy has different forms. The two basic kinds of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the force that causes an object to move. Power is the rate at which the work is done. Potential energy is the stored energy of an object based on its positi ...
... 1. Energy has different forms. The two basic kinds of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. Energy is the ability to do work. Work is the force that causes an object to move. Power is the rate at which the work is done. Potential energy is the stored energy of an object based on its positi ...
Name: Date: Chapter 8-Lesson 3-5: Energy Transformations and
... temperaturea measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance Fahrenheit scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees Celsius scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees Kelvin scaleThe tem ...
... temperaturea measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance Fahrenheit scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees Celsius scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees Kelvin scaleThe tem ...
Energy Transformation Poster Rubric
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
Resource Page Work, Power, and Energy
... depends on how fast or slow the object vibrates. SC.4.P.10.4 - Describe how moving water and air are sources of energy and can be used to move things. SC.5.P.10.1 - Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. SC.5.P.10.2 - ...
... depends on how fast or slow the object vibrates. SC.4.P.10.4 - Describe how moving water and air are sources of energy and can be used to move things. SC.5.P.10.1 - Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. SC.5.P.10.2 - ...
Name
... 8. Complete the table by following the instructions below. a. Fill in the definitions at the top of the table for potential and kinetic energy. b. Read the different types of energy that fall into each category. List the forms of energy that fall under potential energy. DO NOT WRITE ANY MORE THAN T ...
... 8. Complete the table by following the instructions below. a. Fill in the definitions at the top of the table for potential and kinetic energy. b. Read the different types of energy that fall into each category. List the forms of energy that fall under potential energy. DO NOT WRITE ANY MORE THAN T ...
Energy Test Study Guide
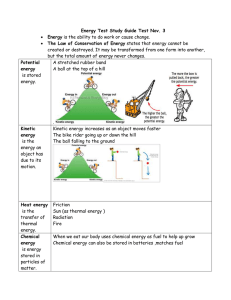
... created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at the top of a hill ...
... created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy never changes. A stretched rubber band A ball at the top of a hill ...
Chapter 5 Test
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
... 1) Objects that have been lifted against the force of _______________ have stored or potential energy. 2) A compressed spring also stores its __________ 3) Automobiles store _______________ energy in their gasoline tanks. C. Gravitational Potential Energy ...
Section 3 What is energy? Energy “Ability to do work” Anything that
... Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant energy Energy from the Sun warms the planet provides energy t ...
... Formation and breaking of bonds Match releases energy as light and heat Kinetic energy The energy of an object due to its motion Depends on mass and speed Equation KE(J)=1/2 x mass(kg)x speed2(m/s)2 KE=1/2mv2 Radiant energy Energy from the Sun warms the planet provides energy t ...
Energy Vocabulary I
... thermal energy elastic energy insulation potential energy efficiency light gravitational potential energy conduction insulator electrical energy calories Law of Conservation of Energy energy transformation Fill in the blank with the correct term ...
... thermal energy elastic energy insulation potential energy efficiency light gravitational potential energy conduction insulator electrical energy calories Law of Conservation of Energy energy transformation Fill in the blank with the correct term ...
World energy consumption
World energy consumption refers to the total energy used by all of human civilization. Typically measured per year, it involves all energy harnessed from every energy source applied towards humanity's endeavors across every single industrial and technological sector, across every country. Being the power source metric of civilization, World Energy Consumption has deep implications for humanity's social-economic-political sphere.Institutions such as the International Energy Agency (IEA), the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), and the European Environment Agency record and publish energy data periodically. Improved data and understanding of World Energy Consumption may reveal systemic trends and patterns, which could help frame current energy issues and encourage movement towards collectively useful solutions.In 2012, the IEA estimated that the world energy consumption was 155,505 terawatt-hour (TWh), or 5.598 × 1020 joules. This works out to 17.7 TW, or a bit less than the estimated 20 TW produced by radioactive decay on earth. From 2000–2012 coal was the source of energy with the largest growth. The use of oil and natural gas also had considerable growth, followed by hydro power and renewable energy. Renewable energy grew at a rate faster than any other time in history during this period, which can possibly be explained by an increase in international investment in renewable energy. The demand for nuclear energy decreased, possibly due to the accidents at Chernobyl and Three Mile Island.In 2011, expenditures on energy totaled over 6 trillion USD, or about 10% of the world gross domestic product (GDP). Europe spends close to one quarter of the world energy expenditures, Americans close to 20%, and Japan 6%.