energy! - Saint Mary Catholic School
... height above the ground PE = mgh m = mass g = acceleration due to gravity h = height ...
... height above the ground PE = mgh m = mass g = acceleration due to gravity h = height ...
What Is Energy? Questions
... diagram that shows how energy from the sun is used by producers. It also shows how this energy is transferred to consumers in an ecosystem. There is energy all around us. What do we use it for? We use it to keep warm. We use it to power our vehicles. Did you ever stop to think of where this energy c ...
... diagram that shows how energy from the sun is used by producers. It also shows how this energy is transferred to consumers in an ecosystem. There is energy all around us. What do we use it for? We use it to keep warm. We use it to power our vehicles. Did you ever stop to think of where this energy c ...
ENERGY
... Sub categories of Potential Energy Gravitational potential energy – The energy an object has because it is off of the earth’s surface (you in your seat) Chemical Energy – Energy stored in elements/compounds that will be released during a chemical reaction (batteries, food) Electromagnetic Energy - ...
... Sub categories of Potential Energy Gravitational potential energy – The energy an object has because it is off of the earth’s surface (you in your seat) Chemical Energy – Energy stored in elements/compounds that will be released during a chemical reaction (batteries, food) Electromagnetic Energy - ...
Form Of - eduScapes
... tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are made of even smaller particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons. Applying a force can make some of the electrons move. Radiant Energy is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. ...
... tiny particles called atoms. Atoms are made of even smaller particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons. Applying a force can make some of the electrons move. Radiant Energy is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... Energy possessed by an object due to its motion or position (the objects combined potential and kinetic energy) ME=PE+KE ...
... Energy possessed by an object due to its motion or position (the objects combined potential and kinetic energy) ME=PE+KE ...
Energy Resources
... potential energy in tides to generate electricity + reliable as always two tides a day - Costs a lot to build a local dam, could cause flooding ...
... potential energy in tides to generate electricity + reliable as always two tides a day - Costs a lot to build a local dam, could cause flooding ...
Energy - SchoolRack
... things) about using these resources? What are the cons (bad things) about using these resources? ...
... things) about using these resources? What are the cons (bad things) about using these resources? ...
Types of Energy
... substances from one place to another. • Examples: wind (air particles), transportation ...
... substances from one place to another. • Examples: wind (air particles), transportation ...
5.1 Energy Changes in Chemical and Nuclear Reactions
... • Thermal energy is the total quantity of kinetic and potential energy in a substance • This depends on how fast its particles are moving • When a substance absorbs thermal energy, its particles move at a greater speed and it warms up ...
... • Thermal energy is the total quantity of kinetic and potential energy in a substance • This depends on how fast its particles are moving • When a substance absorbs thermal energy, its particles move at a greater speed and it warms up ...
Energy Study Guide
... Energy of sound waves moving through a substance like air or water Electromagnetic radiation (like light waves, microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, etc.) that move in wave forms Internal energy of a substance caused by its atoms and molecules moving and vibrating within the substance ...
... Energy of sound waves moving through a substance like air or water Electromagnetic radiation (like light waves, microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, etc.) that move in wave forms Internal energy of a substance caused by its atoms and molecules moving and vibrating within the substance ...
Energy, Forms of Energy and Sound Travels - Stars
... Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy can never be made or destroyed but it can change forms Example: A car transforms the gas stored into movement. This is an example of energy transformation. ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy can never be made or destroyed but it can change forms Example: A car transforms the gas stored into movement. This is an example of energy transformation. ...
WELCOME TO PHYSICS 1103
... •How can gravitational potential energy be used to do work with a water wheel? •What is the efficiency of multiple energy conversion processes? ...
... •How can gravitational potential energy be used to do work with a water wheel? •What is the efficiency of multiple energy conversion processes? ...
Forms of Energy and its Changes - Notes
... _____________________ Energy are forms of energy in motion _____________________ Energy are forms of energy that are stored Mechanical Energy Mechanical energy is due to the position and motion of the object. It can be in either potential or kinetic form. Mechanical energy = _________________ Therma ...
... _____________________ Energy are forms of energy in motion _____________________ Energy are forms of energy that are stored Mechanical Energy Mechanical energy is due to the position and motion of the object. It can be in either potential or kinetic form. Mechanical energy = _________________ Therma ...
CURRICULUM MAPPING EXAMPLES Grade : 9 Physical Science
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
Curriculum Mapping Samples
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
Review
... 14. If the dad lifted the child in half the time, how would the new power compare to the original? What about if he lifted the child in twice the amount of time? (Hint: say if the power increases or decreases and also by how much!) ...
... 14. If the dad lifted the child in half the time, how would the new power compare to the original? What about if he lifted the child in twice the amount of time? (Hint: say if the power increases or decreases and also by how much!) ...
notes
... Energy can not be created or destroyed but must be transferred and transformed from one form to another. ...
... Energy can not be created or destroyed but must be transferred and transformed from one form to another. ...
File
... more of the following functions: • transferring a force from one place to another, • changing the direction of a force, • increasing the magnitude of a force, or • increasing the distance or speed of a force. ...
... more of the following functions: • transferring a force from one place to another, • changing the direction of a force, • increasing the magnitude of a force, or • increasing the distance or speed of a force. ...
General
... This equation relates what two things (mass and energy) Einstein’s equation explains what two types of reactions (Fission and Fusion) In a frictionless environment the kinetic energy of a falling object will be _________ to the potential energy at the beginning of the fall. (Equal) The process of en ...
... This equation relates what two things (mass and energy) Einstein’s equation explains what two types of reactions (Fission and Fusion) In a frictionless environment the kinetic energy of a falling object will be _________ to the potential energy at the beginning of the fall. (Equal) The process of en ...
Forms of Energy
... Major Forms of Energy Thermal Energy- (Heat Energy) Total kinetic energy contained in all the particles of a substance. Mechanical Energy- Energy an object has because of its motion or position. Chemical Energy- The energy stored in chemical ...
... Major Forms of Energy Thermal Energy- (Heat Energy) Total kinetic energy contained in all the particles of a substance. Mechanical Energy- Energy an object has because of its motion or position. Chemical Energy- The energy stored in chemical ...
Energy - SCHOOLinSITES
... • KE= 1/2mv2 • The kinetic energy of a moving object is equal to the work required to bring it to that speed from rest, or the work the object can do while being brought to rest. • Fd= 1/2mv2 ...
... • KE= 1/2mv2 • The kinetic energy of a moving object is equal to the work required to bring it to that speed from rest, or the work the object can do while being brought to rest. • Fd= 1/2mv2 ...
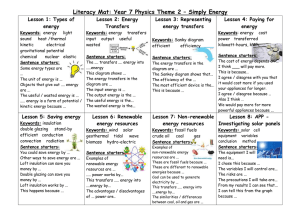
Theme 2 Simply Energ..
... Proper nouns need capital letters. These are unique people, places or things e.g. there are many cities so ‘city’ doesn’t take a capital letter. However there is only one London, therefore it takes a capital letter. Remember don’t mix up ‘was’ and ‘were.’ For example ‘I was (singular)’ and ‘We wer ...
... Proper nouns need capital letters. These are unique people, places or things e.g. there are many cities so ‘city’ doesn’t take a capital letter. However there is only one London, therefore it takes a capital letter. Remember don’t mix up ‘was’ and ‘were.’ For example ‘I was (singular)’ and ‘We wer ...
energy - Denton ISD
... 2. Newton= Nuclear • Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. The energy that holds the nucleus Example: Breaking together. down Uranium ...
... 2. Newton= Nuclear • Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. The energy that holds the nucleus Example: Breaking together. down Uranium ...
World energy consumption
World energy consumption refers to the total energy used by all of human civilization. Typically measured per year, it involves all energy harnessed from every energy source applied towards humanity's endeavors across every single industrial and technological sector, across every country. Being the power source metric of civilization, World Energy Consumption has deep implications for humanity's social-economic-political sphere.Institutions such as the International Energy Agency (IEA), the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), and the European Environment Agency record and publish energy data periodically. Improved data and understanding of World Energy Consumption may reveal systemic trends and patterns, which could help frame current energy issues and encourage movement towards collectively useful solutions.In 2012, the IEA estimated that the world energy consumption was 155,505 terawatt-hour (TWh), or 5.598 × 1020 joules. This works out to 17.7 TW, or a bit less than the estimated 20 TW produced by radioactive decay on earth. From 2000–2012 coal was the source of energy with the largest growth. The use of oil and natural gas also had considerable growth, followed by hydro power and renewable energy. Renewable energy grew at a rate faster than any other time in history during this period, which can possibly be explained by an increase in international investment in renewable energy. The demand for nuclear energy decreased, possibly due to the accidents at Chernobyl and Three Mile Island.In 2011, expenditures on energy totaled over 6 trillion USD, or about 10% of the world gross domestic product (GDP). Europe spends close to one quarter of the world energy expenditures, Americans close to 20%, and Japan 6%.