Thermochemistry ch 16 energy diagrams phase
... • How many Joules are in a bowl of breakfast cereal and milk which contain 340 Calories? ...
... • How many Joules are in a bowl of breakfast cereal and milk which contain 340 Calories? ...
Name: KEY Class Period: GTT (7th) – SCIENCE OF TECHNOLOGY
... Name: KEY Class Period: GTT (7th) – SCIENCE OF TECHNOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW ...
... Name: KEY Class Period: GTT (7th) – SCIENCE OF TECHNOLOGY FINAL EXAM REVIEW ...
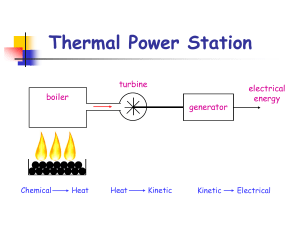
Thermal Power Station
... Nuclear power stations operate similarly to thermal power stations, but instead of burning fossil fuels to produce heat, a nuclear reaction takes place inside a reactor. ...
... Nuclear power stations operate similarly to thermal power stations, but instead of burning fossil fuels to produce heat, a nuclear reaction takes place inside a reactor. ...
Matter and Energy
... along with neutrons, but is also stable by itself and contains a second identity as a hydrogen ion. The proton has a +1 charge, that balances it out with the electron which has a -1 charge. There are a total of three quarks two up, and one down, these quarks are bound together by a strong force. ...
... along with neutrons, but is also stable by itself and contains a second identity as a hydrogen ion. The proton has a +1 charge, that balances it out with the electron which has a -1 charge. There are a total of three quarks two up, and one down, these quarks are bound together by a strong force. ...
Matter and Energy mike jacob
... along with neutrons, but is also stable by itself and contains a second identity as a hydrogen ion. The proton has a +1 charge, that balances it out with the electron which has a -1 charge. There are a total of three quarks two up, and one down, these quarks are bound together by a strong force. ...
... along with neutrons, but is also stable by itself and contains a second identity as a hydrogen ion. The proton has a +1 charge, that balances it out with the electron which has a -1 charge. There are a total of three quarks two up, and one down, these quarks are bound together by a strong force. ...
Energy Review Worksheet - KEY
... 4. What causes kinetic energy to increase? Speed and mass 5. What causes potential energy to increase? Height and mass 6. What is the law of conservation of energy? Energy cannot be created or destroyed only transferred from one thing to another. 7. What is the difference between an energy transform ...
... 4. What causes kinetic energy to increase? Speed and mass 5. What causes potential energy to increase? Height and mass 6. What is the law of conservation of energy? Energy cannot be created or destroyed only transferred from one thing to another. 7. What is the difference between an energy transform ...
Work, Power and Energy
... is equal to the work done on a system. • Change in Ke = work • This is the work energy theorem. • Ex. If a 2kg object moves at 3m/s, what is its kinetic energy? • This is the amount of work that has been done by the object. ...
... is equal to the work done on a system. • Change in Ke = work • This is the work energy theorem. • Ex. If a 2kg object moves at 3m/s, what is its kinetic energy? • This is the amount of work that has been done by the object. ...
Discovery Education Science Connection ΠElementary School
... Today I decided to keep a journal to highlight the different ways I observe energy in my life. There are numerous examples, so I'll just write about a few instances I observed today. Before I woke this morning, kinetic energy was present inside me. My heart was beating, blood was flowing, and my mus ...
... Today I decided to keep a journal to highlight the different ways I observe energy in my life. There are numerous examples, so I'll just write about a few instances I observed today. Before I woke this morning, kinetic energy was present inside me. My heart was beating, blood was flowing, and my mus ...
Chapter 5 – Energy
... Thermodynamics- Thermodynamics is the study of the patterns of energy change. The "thermo" refers to energy, and "dynamics" means patterns of change First Law of Thermodynamics- the total amount of energy in the universe always stays the same. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be change ...
... Thermodynamics- Thermodynamics is the study of the patterns of energy change. The "thermo" refers to energy, and "dynamics" means patterns of change First Law of Thermodynamics- the total amount of energy in the universe always stays the same. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be change ...
Conservation of Energy
... • Did the bowling ball smack the teacher in the chin? Did it rise higher or lower than its original height? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most gravitational potential energy? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most kinetic energy? How do we know this? ...
... • Did the bowling ball smack the teacher in the chin? Did it rise higher or lower than its original height? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most gravitational potential energy? • At what point did the bowling ball have the most kinetic energy? How do we know this? ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... Standard 10: Various forms of energy are constantly being transformed into other types without any net loss of energy from the system. ...
... Standard 10: Various forms of energy are constantly being transformed into other types without any net loss of energy from the system. ...
Third Six Weeks SFA/Energy Transformation Review
... thermal energy in the hot beaker compared to the thermal energy in the tap water beaker, according to the graph. Thermal energy of the hot beaker is decreasing while the thermal energy of the tap water beaker is increasing. ...
... thermal energy in the hot beaker compared to the thermal energy in the tap water beaker, according to the graph. Thermal energy of the hot beaker is decreasing while the thermal energy of the tap water beaker is increasing. ...
Chapter 10: Heat Energy
... of a material. • You insulate something by wrapping it securely with a material that is not a good conductor of heat. • There are many instances in our everyday lives where it is important to keep heat from entering or leaving something. ...
... of a material. • You insulate something by wrapping it securely with a material that is not a good conductor of heat. • There are many instances in our everyday lives where it is important to keep heat from entering or leaving something. ...
Energy
... If the 2kg ball above starts with an initial velocity of 6.7m/s at 2m but only rolls up to a height of 3.1m, how much work is done by friction? A driver has a truck full of chickens. The chickens and truck have a combined mass of 2200kg. As the truck driver coasts down a frictionless hill, 300kg of ...
... If the 2kg ball above starts with an initial velocity of 6.7m/s at 2m but only rolls up to a height of 3.1m, how much work is done by friction? A driver has a truck full of chickens. The chickens and truck have a combined mass of 2200kg. As the truck driver coasts down a frictionless hill, 300kg of ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy powerpoint
... • When the position of an object is altered it, creates Potential Energy. • A yo-yo on the table, doesn’t have energy, but when picked up, it alters its position and now it has the ability (or potential) to do work. • A bow doesn’t have the capacity to do work, unless it’s held at an elevated posit ...
... • When the position of an object is altered it, creates Potential Energy. • A yo-yo on the table, doesn’t have energy, but when picked up, it alters its position and now it has the ability (or potential) to do work. • A bow doesn’t have the capacity to do work, unless it’s held at an elevated posit ...
work and energy
... These come from atoms. Electrons can transfer energy from a battery or a light bulb. They have electrical potential energy. ...
... These come from atoms. Electrons can transfer energy from a battery or a light bulb. They have electrical potential energy. ...
Review for Energy Test
... Gordon throws a baseball into the air. It rises, stops when it reaches its greatest height, and then falls back to the ground. At what point does kinetic energy convert to potential energy? ...
... Gordon throws a baseball into the air. It rises, stops when it reaches its greatest height, and then falls back to the ground. At what point does kinetic energy convert to potential energy? ...
Energy Transformations- Homework
... In any energy transfer or transformation, some energy is always “lost” as heat. Although energy cannot be created or destroyed, people often say that energy is “lost” because it is not available to do useful work. Friction is often why energy is transformed to thermal (heat) energy instead of anothe ...
... In any energy transfer or transformation, some energy is always “lost” as heat. Although energy cannot be created or destroyed, people often say that energy is “lost” because it is not available to do useful work. Friction is often why energy is transformed to thermal (heat) energy instead of anothe ...
Chapter 15 –Energy
... 10. Which of the following statement is true according to the law of conservation of energy? Energy cannot be destroyed Energy can be converted from one form to another Both statements 11. The equation E = mc2 relates energy and Force, mass, work 12. Biomass energy is what type of energy stored in l ...
... 10. Which of the following statement is true according to the law of conservation of energy? Energy cannot be destroyed Energy can be converted from one form to another Both statements 11. The equation E = mc2 relates energy and Force, mass, work 12. Biomass energy is what type of energy stored in l ...
Energy Notes - Student
... 3. On a frozen pond, a person kicks a 10.0 kg sled, giving it an initial speed of 2.2 m/s. How far does the sled move if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ice is 0.10? ...
... 3. On a frozen pond, a person kicks a 10.0 kg sled, giving it an initial speed of 2.2 m/s. How far does the sled move if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ice is 0.10? ...
Types of Energy - Plain Local Schools
... Energy carried by moving electrons forced along a path Examples: Electricity, lightning ...
... Energy carried by moving electrons forced along a path Examples: Electricity, lightning ...
File
... Describe what happens to the particles of colored liquid in the thermometer when the liquid’s volume decreases causing the line of colored liquid in the thermometer to go down. 17. What is the difference between heath and temperature? ...
... Describe what happens to the particles of colored liquid in the thermometer when the liquid’s volume decreases causing the line of colored liquid in the thermometer to go down. 17. What is the difference between heath and temperature? ...
Part I: Energy Transformations
... NAME___________________________________________DATE____________________________PERIOD________ ...
... NAME___________________________________________DATE____________________________PERIOD________ ...
green sheet
... _____ Calculate kinetic energy, including using the correct SI units (ch 12.3) _____ Use kinetic energy to predict mass and velocity of an object (ch 12.3) _____ Identify positions associated with maximum and minimum values of kinetic and gravitational potential energy (ch 12.3) _____ Solve problems ...
... _____ Calculate kinetic energy, including using the correct SI units (ch 12.3) _____ Use kinetic energy to predict mass and velocity of an object (ch 12.3) _____ Identify positions associated with maximum and minimum values of kinetic and gravitational potential energy (ch 12.3) _____ Solve problems ...
World energy consumption
World energy consumption refers to the total energy used by all of human civilization. Typically measured per year, it involves all energy harnessed from every energy source applied towards humanity's endeavors across every single industrial and technological sector, across every country. Being the power source metric of civilization, World Energy Consumption has deep implications for humanity's social-economic-political sphere.Institutions such as the International Energy Agency (IEA), the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), and the European Environment Agency record and publish energy data periodically. Improved data and understanding of World Energy Consumption may reveal systemic trends and patterns, which could help frame current energy issues and encourage movement towards collectively useful solutions.In 2012, the IEA estimated that the world energy consumption was 155,505 terawatt-hour (TWh), or 5.598 × 1020 joules. This works out to 17.7 TW, or a bit less than the estimated 20 TW produced by radioactive decay on earth. From 2000–2012 coal was the source of energy with the largest growth. The use of oil and natural gas also had considerable growth, followed by hydro power and renewable energy. Renewable energy grew at a rate faster than any other time in history during this period, which can possibly be explained by an increase in international investment in renewable energy. The demand for nuclear energy decreased, possibly due to the accidents at Chernobyl and Three Mile Island.In 2011, expenditures on energy totaled over 6 trillion USD, or about 10% of the world gross domestic product (GDP). Europe spends close to one quarter of the world energy expenditures, Americans close to 20%, and Japan 6%.