Chapter 3 Test – Energy! Name: ______ At its basic level, energy is
... 12. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that ___________________ can neither be created nor destroyed. 13. For example, when using an electric fan, some energy is converted to _________________ energy to turn the fan blades. 14. Some energy is converted into unwanted __________________ energy. ...
... 12. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that ___________________ can neither be created nor destroyed. 13. For example, when using an electric fan, some energy is converted to _________________ energy to turn the fan blades. 14. Some energy is converted into unwanted __________________ energy. ...
Types of Energy ANSWERS
... energy – energy stored in the deformation (stretch or compression) of an elastic object; a form of POTENTIAL energy. Example(s): stretching a rubber band, compressing a spring. ...
... energy – energy stored in the deformation (stretch or compression) of an elastic object; a form of POTENTIAL energy. Example(s): stretching a rubber band, compressing a spring. ...
Energy in Society
... – Specifies the main alternatives available – Estimate the tangible costs and list the intangible costs of each alternative – Compare the costs with the benefits – Choose the option where the benefits most out way the costs ...
... – Specifies the main alternatives available – Estimate the tangible costs and list the intangible costs of each alternative – Compare the costs with the benefits – Choose the option where the benefits most out way the costs ...
Economic cost of energy crisis in Pakistan and the
... economics. As a matter of fact, there has been an enormous increase in the global demand for energy in recent years as a result of industrial development and population growth. Supply of energy is, therefore, far less than the actual demand. Pakistan's energy concerns are now assuming serious and ho ...
... economics. As a matter of fact, there has been an enormous increase in the global demand for energy in recent years as a result of industrial development and population growth. Supply of energy is, therefore, far less than the actual demand. Pakistan's energy concerns are now assuming serious and ho ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... For this unit, we will build on the last unit and be studying the effects of forces … work and power. We will learn about how work is done and power is used in real life scenarios and calculate the amount of work done and power used. We will also study the types of energy involved in doing work (pot ...
... For this unit, we will build on the last unit and be studying the effects of forces … work and power. We will learn about how work is done and power is used in real life scenarios and calculate the amount of work done and power used. We will also study the types of energy involved in doing work (pot ...
TOPIC: Energy AIM: What is energy?
... because it is made from plants. To make ethanol we use yeast to ferment the sugars and starch in corn. Corn is the main ingredient for ethanol in the US due to its abundance and low price. The starch is fermented into sugar fermented into alcohol. Other crops such as, barley, wheat, rice, sorghum, ...
... because it is made from plants. To make ethanol we use yeast to ferment the sugars and starch in corn. Corn is the main ingredient for ethanol in the US due to its abundance and low price. The starch is fermented into sugar fermented into alcohol. Other crops such as, barley, wheat, rice, sorghum, ...
energy - Doral Academy Preparatory
... These resources often exist in a fixed amount, or are consumed much faster than nature can recreate them. • Energy that cannot be replaced once it is used or energy that is not being replaced as fast as it is being used • Used to describe energy sources that exist in a limited amount on Earth. Thus ...
... These resources often exist in a fixed amount, or are consumed much faster than nature can recreate them. • Energy that cannot be replaced once it is used or energy that is not being replaced as fast as it is being used • Used to describe energy sources that exist in a limited amount on Earth. Thus ...
SPH 4C - mackenziekim
... An engineer uses a single car to test the roller coaster track, shown in Fig. B. In answering the following questions, assume that friction can be ignored and the speed at A is O. In each case, give a reason for your answer. (a) Where is the gravitational potential energy the greatest? (b) Where is ...
... An engineer uses a single car to test the roller coaster track, shown in Fig. B. In answering the following questions, assume that friction can be ignored and the speed at A is O. In each case, give a reason for your answer. (a) Where is the gravitational potential energy the greatest? (b) Where is ...
potential energy.
... is called gravitational potential energy. It increases when an object is raised to a higher level. ...
... is called gravitational potential energy. It increases when an object is raised to a higher level. ...
When you drop a ball, what happens to its energy
... How are sound waves and light waves different? Explain why a ball rolled with the same force will go farther on a wood floor than a carpeted floor. Where does a hairdryer get its energy and what kinds of energy does it produce? Explain the greenhouse effect and how it makes life on earth possible. G ...
... How are sound waves and light waves different? Explain why a ball rolled with the same force will go farther on a wood floor than a carpeted floor. Where does a hairdryer get its energy and what kinds of energy does it produce? Explain the greenhouse effect and how it makes life on earth possible. G ...
Potential and Kinetic energy
... 2. Energy is measured in _________________ B. Potential energy (PE) – 1. There are two types of potential energy a. _____________________________ – energy of position - Examples b. _____________________________ – stored energy - Examples 2. Energy that is waiting to be released C. ______________ ...
... 2. Energy is measured in _________________ B. Potential energy (PE) – 1. There are two types of potential energy a. _____________________________ – energy of position - Examples b. _____________________________ – stored energy - Examples 2. Energy that is waiting to be released C. ______________ ...
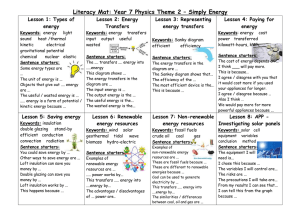
Theme 2 Simply Energ..
... non-renewable energy resources are ... These are fossil fuels because ... These are different to renewable energies because ... Coal can be used to generate electricity by ... This transfers ..... energy into ....energy by... The similarities / differences between coal, oil and gas are ... ...
... non-renewable energy resources are ... These are fossil fuels because ... These are different to renewable energies because ... Coal can be used to generate electricity by ... This transfers ..... energy into ....energy by... The similarities / differences between coal, oil and gas are ... ...
Nonrenewable Energy
... which can be turned into electricity and heat • Wind • Geothermal energy from heat inside the Earth • Biomass from plants, which includes firewood from trees, ethanol from corn, and biodiesel from vegetable oil • Hydropower from hydroturbines at a dam ...
... which can be turned into electricity and heat • Wind • Geothermal energy from heat inside the Earth • Biomass from plants, which includes firewood from trees, ethanol from corn, and biodiesel from vegetable oil • Hydropower from hydroturbines at a dam ...
Law of Conservation of Energy
... You may have heard that it’s important to conserve energy. What this means is it’s important to lower the consumption of energy sources like, electricity/ fuel oil/ natural gas/ etc. The Law of Conservation of Energy is only stating that energy in= energy out ...
... You may have heard that it’s important to conserve energy. What this means is it’s important to lower the consumption of energy sources like, electricity/ fuel oil/ natural gas/ etc. The Law of Conservation of Energy is only stating that energy in= energy out ...
Name Period ______ Date ______ Energy Pre/Post Test: Multiple
... 7. Our Earth gets energy from the sun. This energy is often referred to as ____________ energy. a. Light b. nuclear c. wind 8. Coal, petroleum, natural gas, and propane are fossil fuels. They are called fossil fuels because: a. They are burned to release energy and they cause air pollution b. They w ...
... 7. Our Earth gets energy from the sun. This energy is often referred to as ____________ energy. a. Light b. nuclear c. wind 8. Coal, petroleum, natural gas, and propane are fossil fuels. They are called fossil fuels because: a. They are burned to release energy and they cause air pollution b. They w ...
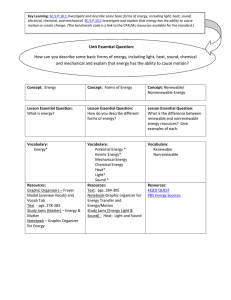
Energy Curriculum Map
... Key Learning: SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources av ...
... Key Learning: SC.5.P.10.1 Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources av ...
Energy - WEB . WHRSD . ORG
... What kinds of energy are there? Mechanical (potential, kinetic) electrical thermal light sound ...
... What kinds of energy are there? Mechanical (potential, kinetic) electrical thermal light sound ...
Energy Transformation Poster Rubric
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
Forms of Energy - Ms. Morgan's Science Spot
... For example: A car with the mass of 200 kilograms moving at 2 meters per second would have this kinetic energy: KE= (1/2)200 x 4 KE= 400 Joules ...
... For example: A car with the mass of 200 kilograms moving at 2 meters per second would have this kinetic energy: KE= (1/2)200 x 4 KE= 400 Joules ...
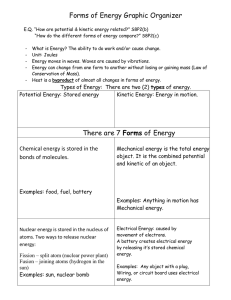
Forms of Energy
... What is Energy? The ability to do work and/or cause change. Unit: Joules Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
... What is Energy? The ability to do work and/or cause change. Unit: Joules Energy moves in waves. Waves are caused by vibrations. Energy can change from one form to another without losing or gaining mass (Law of Conservation of Mass). Heat is a byproduct of almost all changes in forms of energy. ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.