Weekly Overview - School District 27J
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
... Briefly describe the Law of Conservation of Mass (you are more than welcome to use your notes and textbook to help you). Based on your description, explain what you believe the Law of Conservation of Energy is. Support your answer with a real world example. ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
... Chemical energy: energy stored within a chemical substance. Electrical energy: energy associated with electrons moving along a conductor. Energy: the ability to do work. Exhaustible energy resources: materials that cannot be replaced. Fission: the process of splitting atoms to release vast quantitie ...
1.)$Solar$Power!"!energy!coming!from!the!sun! through!nuclear
... * Can be built anywhere with good transport links and water availability * Can be used directly in the home to provide heating disadvantages: * Combustion products can produce pollution, notably acid rain * Combustion products contain 'greenhouse' gases * Extraction of fossil fuels can damage the en ...
... * Can be built anywhere with good transport links and water availability * Can be used directly in the home to provide heating disadvantages: * Combustion products can produce pollution, notably acid rain * Combustion products contain 'greenhouse' gases * Extraction of fossil fuels can damage the en ...
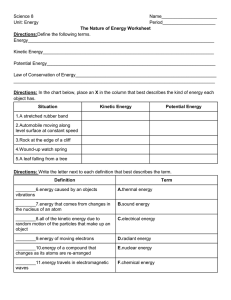
The Nature of Energy Worksheet
... level surface at constant speed 3.Rock at the edge of a cliff 4.Wound-up watch spring 5.A leaf falling from a tree Directions: Write the letter next to each definition that best describes the term. Definition ...
... level surface at constant speed 3.Rock at the edge of a cliff 4.Wound-up watch spring 5.A leaf falling from a tree Directions: Write the letter next to each definition that best describes the term. Definition ...
energy-powerpoint
... Forms of Potential Energy • Chemical Energy – Energy stored between bonds of atoms • Food has potential energy that can be digested. • Batteries have chemical energy stored to power everything from tools to toys. • Fuel has potential energy to combust and cause movement. ...
... Forms of Potential Energy • Chemical Energy – Energy stored between bonds of atoms • Food has potential energy that can be digested. • Batteries have chemical energy stored to power everything from tools to toys. • Fuel has potential energy to combust and cause movement. ...
Glossary of Terms Energy – the ability to do work or the ability to
... Energy – the ability to do work or the ability to move an object. Electrical energy is usually measured in kilowatthours (kWh), while heat energy is usually measured in British thermal units (Btu). Potential energy – stored energy and the energy of position. Kinetic energy – the energy of a body whi ...
... Energy – the ability to do work or the ability to move an object. Electrical energy is usually measured in kilowatthours (kWh), while heat energy is usually measured in British thermal units (Btu). Potential energy – stored energy and the energy of position. Kinetic energy – the energy of a body whi ...
Sc 9 Electricity Review Booklet
... 23. What is power and how is it calculated? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is energy and how is it calculated? What are the units of energy? _______________________ ...
... 23. What is power and how is it calculated? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is energy and how is it calculated? What are the units of energy? _______________________ ...
Energy - Maples Elementary School
... energy because of where it is. It has the potential to move because it is above the ground and has somewhere to go. ...
... energy because of where it is. It has the potential to move because it is above the ground and has somewhere to go. ...
Energy Transformations - Science with Mrs. Sinning
... – The food you eat allows you to move – The battery in your iPod is changed into electrical energy ...
... – The food you eat allows you to move – The battery in your iPod is changed into electrical energy ...
Energy
... atmospheric air. It has been used for hundreds of years for sailing, grinding grain, and for irrigation. Wind energy systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling have been in use since ancient times and since the beginning of the 2 ...
... atmospheric air. It has been used for hundreds of years for sailing, grinding grain, and for irrigation. Wind energy systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling have been in use since ancient times and since the beginning of the 2 ...
forms of energy worksheet
... Worksheet: forms of energy Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. ...
... Worksheet: forms of energy Fill in the blanks with the words at the bottom of the page. You can use words more than once. ...
2nd 6 Weeks - Forms of Energy, Circuits and Force
... Light energy – radiant energy that our eyes can see from the visible part of the electromagnetic ...
... Light energy – radiant energy that our eyes can see from the visible part of the electromagnetic ...
Cochise College
... An electric motor of 30% efficiency operates the elevator. (70% of the incoming electrical energy is lost in friction and heat.) If electrical energy costs the hotel 11 cents per kilowatthour, how much electrical energy in dollars does it take to move the elevator and its load up 32 floors? Assume ...
... An electric motor of 30% efficiency operates the elevator. (70% of the incoming electrical energy is lost in friction and heat.) If electrical energy costs the hotel 11 cents per kilowatthour, how much electrical energy in dollars does it take to move the elevator and its load up 32 floors? Assume ...
Name: Period:______ Date:______ Infinite Potential Forms of
... 12. What is work? Work is the energy needed to move an object a certain distance using a force. 13. What is the equation for work? W = F x d The unit for work is the joule because work is a form of energy. 14. What is power and what is its unit? Power is the rate at which work is performed, or how m ...
... 12. What is work? Work is the energy needed to move an object a certain distance using a force. 13. What is the equation for work? W = F x d The unit for work is the joule because work is a form of energy. 14. What is power and what is its unit? Power is the rate at which work is performed, or how m ...
What is Energy?
... • A form of energy whose source is the motion of molecules. When something is heated, the atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! ...
... • A form of energy whose source is the motion of molecules. When something is heated, the atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! ...
Chapter-9-Energy-notes
... The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of a force against gravity and against friction. The equation for work is ______________ The unit of work is Newton-meters or Nm is called ...
... The motion has to be the same ___________________ as the force. Is the female walking up the stairs a force against friction or against gravity? Write an example of a force against gravity and against friction. The equation for work is ______________ The unit of work is Newton-meters or Nm is called ...
Chemical Energy
... 3. Electromagnetic Energy – Energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic waves that can travel through space. 4. Gravitational Energy – Energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational a. field. 5. Kinetic Energy – Energy in the form of ...
... 3. Electromagnetic Energy – Energy that is reflected or emitted from objects in the form of electrical and magnetic waves that can travel through space. 4. Gravitational Energy – Energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational a. field. 5. Kinetic Energy – Energy in the form of ...
Week 3 CCA Review
... same. For example, if a cool spoon is placed into hot chocolate, the spoon’s temperature will increase and the hot chocolate’s temperature will decrease as the hot chocolate transfers some of its heat to the spoon. 14.Heat energy can be transferred from one substance to another in three ways: Conduc ...
... same. For example, if a cool spoon is placed into hot chocolate, the spoon’s temperature will increase and the hot chocolate’s temperature will decrease as the hot chocolate transfers some of its heat to the spoon. 14.Heat energy can be transferred from one substance to another in three ways: Conduc ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.