Energy
... Conserving Energy Industry: use fans to circulate heat Home: improve insulation Transport: car sharing ...
... Conserving Energy Industry: use fans to circulate heat Home: improve insulation Transport: car sharing ...
Energy Forms - Greenwood County School District 52
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
... A. Mechanical Energy • 1. The total amount of kinetic and potential energy • 2. Anything in motion has mechanical energy! • Example – a toy wind up car ...
Energy Vocabulary
... fossil fuels: include coal, oil, and natural gas; they formed from the remains of dead plants and animals heat energy: energy that moves between objects of different temperatures electrical energy: energy that comes from an electric current conductor: material that allows heat to move through it eas ...
... fossil fuels: include coal, oil, and natural gas; they formed from the remains of dead plants and animals heat energy: energy that moves between objects of different temperatures electrical energy: energy that comes from an electric current conductor: material that allows heat to move through it eas ...
energy
... Uranium is a radioactive, metal found in rocks all over the world. Used to make nuclear energy. (During nuclear fission, a small particle called a neutron hits the uranium atom and splits it, releasing a great amount of energy as heat and radiation) ...
... Uranium is a radioactive, metal found in rocks all over the world. Used to make nuclear energy. (During nuclear fission, a small particle called a neutron hits the uranium atom and splits it, releasing a great amount of energy as heat and radiation) ...
ENERGY
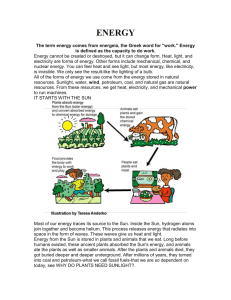
... ENERGY The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can ...
... ENERGY The term energy comes from energeia, the Greek word for "work." Energy is defined as the capacity to do work. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Heat, light, and electricity are forms of energy. Other forms include mechanical, chemical, and nuclear energy. You can ...
Physics Chapter 5 Vocabulary Section 1 Energy: the ability to do
... Mechanical energy: the total energy of motion and position of an object. ...
... Mechanical energy: the total energy of motion and position of an object. ...
Environmental Systems
... Forms of Energy • Joule: basic unit of energy (J) • Energy and Power a. energy-ability to do work power-rate at which work is done therefore, energy = power X time power = energy / time ...
... Forms of Energy • Joule: basic unit of energy (J) • Energy and Power a. energy-ability to do work power-rate at which work is done therefore, energy = power X time power = energy / time ...
Energy Vocabulary, Grade 4
... Energy Vocabulary, Grade 4 Directions: Prepare the definitions for the following science words. Add words as needed. ...
... Energy Vocabulary, Grade 4 Directions: Prepare the definitions for the following science words. Add words as needed. ...
TE AWATEA`S ENERGY
... Have you ever seen pictures of a volcano or a geyser If so then you’ve seen geothermal energy in action! Geo means from the earth and thermal means heat so this type of energy is found under the earth. The hot lava from a volcano and the hot steam from a geyser both come from underground heat and w ...
... Have you ever seen pictures of a volcano or a geyser If so then you’ve seen geothermal energy in action! Geo means from the earth and thermal means heat so this type of energy is found under the earth. The hot lava from a volcano and the hot steam from a geyser both come from underground heat and w ...
Types of Energy
... Types of Energy These are the two main types of energy: Kinetic: energy in motion Potential: stored energy The following forms of energy can be grouped into those two types. Heat (Thermal Energy): internal motion of molecules. Ex. water boiling, turning to steam. Mechanical: energy from motion and m ...
... Types of Energy These are the two main types of energy: Kinetic: energy in motion Potential: stored energy The following forms of energy can be grouped into those two types. Heat (Thermal Energy): internal motion of molecules. Ex. water boiling, turning to steam. Mechanical: energy from motion and m ...
Energy - ChemConnections
... Sources: History: EIA; Projections: Short-Term Energy Outlook, March 2002. ...
... Sources: History: EIA; Projections: Short-Term Energy Outlook, March 2002. ...
kinetic energy
... • Historically this is the resource that has been around the longest. (Burning and cook food) • The energy originates from the Sun. • Until mid 1800’s wood provided 90% of all energy for Americans. – (Now replaced by Coal, natural gas, petroleum ) ...
... • Historically this is the resource that has been around the longest. (Burning and cook food) • The energy originates from the Sun. • Until mid 1800’s wood provided 90% of all energy for Americans. – (Now replaced by Coal, natural gas, petroleum ) ...
Unit 9 Study Guide - Hewlett
... 8. How is power influenced by time? 9. Describe an instance where you can put a force on an object, but no work is done. ...
... 8. How is power influenced by time? 9. Describe an instance where you can put a force on an object, but no work is done. ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.