* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download energy - Doral Academy Preparatory
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Renewable portfolio standard (United States) wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
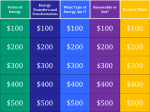
WHAT IS ENERGY? • THE ABILITY TO DO WORK OR CAUSE CHANGE IS CALLED ENERGY There are two basic kinds of energy… • KINETIC ENERGY- The energy an object has due to its motion. • POTENTIAL ENERGY-Stored energy That results from the position or shape of an object. • For example, a car parked in a driveway has potential energy. When the ignition is started and it drives away, the car gains kinetic energy as it moves. ENERGY TRANSFORMATION • Transfer of energy is called energy transformation • Most forms of energy can be transformed into other forms. • Some energy changes involve one transformation while others involve many transformations. • Single Transformations • Multiple Transformations • A toaster transforms electrical energy to thermal energy to toast your bread. • The mechanical energy used to strike a match is transformed first to thermal energy. The thermal energy causes the particles in the match to release stored chemical energy, which is transformed to thermal energy and electromagnetic energy you see as light. • A cell phone transforms electrical energy to electromagnetic energy that travels to other phones. • Your body transforms the chemical energy in your food to mechanical energy you need to move your muscles. CONSERVATION OF ENERGY • The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be destroyed or created. RENEWABLE ENERGY • Used to describe energy sources that are replenished by natural processes on a sufficiently rapid time-scale so that they can be used by humans more or less indefinitely, provided the quantity taken per unit of time is not too great. • Energy that can be replenished at the same rate as it is used Renewable energy sources • • • • Wind power Hydropower Solar energy Geothermal NON RENEWABLE ENERGY • A non-renewable resource is a natural resource which cannot be produced, re-grown, regenerated, or reused on a scale which can sustain its consumption rate. These resources often exist in a fixed amount, or are consumed much faster than nature can recreate them. • Energy that cannot be replaced once it is used or energy that is not being replaced as fast as it is being used • Used to describe energy sources that exist in a limited amount on Earth. Thus all available material could eventually be completely used up Non-Renewable energy sources • • • • Fossil fuels: coal petroleum natural gas • Nuclear power: • Uranium