Name: ______ Date:____________ Period:______ Chapter 12
... 1. _Energy_ is the ability to cause change. 2. What happens when you add heat to matter? When you take it away? _When you add heat to matter the atoms move faster. When you take away the heat the atoms will move slower 3. What is kinetic energy? What is an example? Kinetic energy is energy due to mo ...
... 1. _Energy_ is the ability to cause change. 2. What happens when you add heat to matter? When you take it away? _When you add heat to matter the atoms move faster. When you take away the heat the atoms will move slower 3. What is kinetic energy? What is an example? Kinetic energy is energy due to mo ...
Energy - Triton Science
... B. Conversions between kinetic and potential energy 1. Mechanical energy of a system: mechanical energy = potential energy + kinetic energy ...
... B. Conversions between kinetic and potential energy 1. Mechanical energy of a system: mechanical energy = potential energy + kinetic energy ...
Section 3.1 - CPO Science
... after it has been lit for awhile. • This is because 98% of the energy produced is Do you know what kind of heat and only 2% is light bulb can save energy? actual light energy. ...
... after it has been lit for awhile. • This is because 98% of the energy produced is Do you know what kind of heat and only 2% is light bulb can save energy? actual light energy. ...
Forms of Energy notes
... Examples of Potential Energy (stored energy and energy of position): A. ________________ ______________ is the energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, propane, coal, and food are examples of chemical energy. B. _______________ ________________ is the energ ...
... Examples of Potential Energy (stored energy and energy of position): A. ________________ ______________ is the energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, propane, coal, and food are examples of chemical energy. B. _______________ ________________ is the energ ...
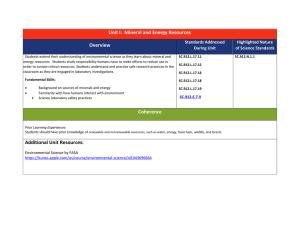
Unit I: Mineral and Energy Resources
... •Differentiate among various forms of energy and recognize that they can be transformed from one form to others. •Analyze past, present, and potential future consequences to the environment resulting from various energy production technologies. •Evaluate the costs and benefits of renewable and nonre ...
... •Differentiate among various forms of energy and recognize that they can be transformed from one form to others. •Analyze past, present, and potential future consequences to the environment resulting from various energy production technologies. •Evaluate the costs and benefits of renewable and nonre ...
energy! - SFP Online!
... Electrical Energy – another term for electricity. Energy stored in electric charges. Thermal Energy – type of energy that comes from heat and vibration of molecules. Light/Radiant Energy – energy associated with electromagnetic spectrum and light waves. ...
... Electrical Energy – another term for electricity. Energy stored in electric charges. Thermal Energy – type of energy that comes from heat and vibration of molecules. Light/Radiant Energy – energy associated with electromagnetic spectrum and light waves. ...
An object can store energy as the result of its position. For example
... demolition machine is storing energy when it is held at an elevated position. This stored energy of position is referred to as potential energy. Similarly, a drawn bow is able to store energy as the result of its position. When assuming its usual position (i.e., when not drawn), there is no energy s ...
... demolition machine is storing energy when it is held at an elevated position. This stored energy of position is referred to as potential energy. Similarly, a drawn bow is able to store energy as the result of its position. When assuming its usual position (i.e., when not drawn), there is no energy s ...
ENERGY - Regional School District 17
... cannot be replaced (except over millions of years) – creates pollution – ie. fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, coal) & uranium ...
... cannot be replaced (except over millions of years) – creates pollution – ie. fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, coal) & uranium ...
Chapter 3-4 Energy - Bakersfield College
... structure of space and time and showed that even light was subject to gravity. ...
... structure of space and time and showed that even light was subject to gravity. ...
Energy - Chapter 5-2 / 5-3
... 3. Nuclear energy nuclear reactions (fission, fusion), the sun 4. Solar energy sunlight, electromagnetic waves 5. Electrical energy electricity, movement of charged ions and electrons ...
... 3. Nuclear energy nuclear reactions (fission, fusion), the sun 4. Solar energy sunlight, electromagnetic waves 5. Electrical energy electricity, movement of charged ions and electrons ...
1 - Eickman
... As the ball is moving it has kinetic energy. It also has potential energy because it is above the ground. As the ball goes up, the potential energy increases and the kinetic decreases until it reaches the highest point. As the ball falls, the potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increas ...
... As the ball is moving it has kinetic energy. It also has potential energy because it is above the ground. As the ball goes up, the potential energy increases and the kinetic decreases until it reaches the highest point. As the ball falls, the potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increas ...
here
... (PART B) Calculate the velocity of the bicycle and the girl immediately after the boy has left the bicycle. (PART C) Calculate the total kinetic energy of the system (bicycle and both children) before and after the boy gets off. Explain the reason for any difference. Answer: PART A: His feet ...
... (PART B) Calculate the velocity of the bicycle and the girl immediately after the boy has left the bicycle. (PART C) Calculate the total kinetic energy of the system (bicycle and both children) before and after the boy gets off. Explain the reason for any difference. Answer: PART A: His feet ...
Vocabulary
... renewable energy energy resources that can be replaced in a relatively short period of time resources hydroelectric electric energy obtained from flowing water energy solar energy Sunlight (solar light includes all forms of electromagnetic radiation) that is converted into usable energy geothermal u ...
... renewable energy energy resources that can be replaced in a relatively short period of time resources hydroelectric electric energy obtained from flowing water energy solar energy Sunlight (solar light includes all forms of electromagnetic radiation) that is converted into usable energy geothermal u ...
Video Notes #5 – Introduction to Energy
... released during a _______________ change. Examples of chemical energy include: The burning of the chemicals stored in fuel to make heat, using chemicals stored in batteries to operate a toy, the digestion of chemicals found in food to give living things energy (chemical energy is potential energy be ...
... released during a _______________ change. Examples of chemical energy include: The burning of the chemicals stored in fuel to make heat, using chemicals stored in batteries to operate a toy, the digestion of chemicals found in food to give living things energy (chemical energy is potential energy be ...
Section 1:Energy
... Section 2 and 3: Forms of Energy - Potential and Kinetic Energy exist in many forms. Mechanical Energy •Energy in which objects are moving and perform __________ •Ex. Hammering a nail. •Ex. Pushing a car. Sound Energy •Energy that produces _________________ and may be ...
... Section 2 and 3: Forms of Energy - Potential and Kinetic Energy exist in many forms. Mechanical Energy •Energy in which objects are moving and perform __________ •Ex. Hammering a nail. •Ex. Pushing a car. Sound Energy •Energy that produces _________________ and may be ...
Different Forms of Energy
... Electrical Energy When you receive a shock from a metal doorknob, you experience electrical energy. Moving electric charges produce electricity, and the energy they carry is called electrical energy. You rely on electrical energy from batteries or power lines to run electrical devices such as radios ...
... Electrical Energy When you receive a shock from a metal doorknob, you experience electrical energy. Moving electric charges produce electricity, and the energy they carry is called electrical energy. You rely on electrical energy from batteries or power lines to run electrical devices such as radios ...
Section 1
... transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six forms: chemical energy, electrical energy, radiant energy, mechanical energy, nuclear energy and thermal energy. Wind is a form of solar energy. Wi ...
... transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six forms: chemical energy, electrical energy, radiant energy, mechanical energy, nuclear energy and thermal energy. Wind is a form of solar energy. Wi ...
Types and Forms of Energy
... • Energy contained in the nucleus of an atom • Nuclear energy is released when nuclei are split apart into several pieces, or when they are combined to form a single, larger nucleus ...
... • Energy contained in the nucleus of an atom • Nuclear energy is released when nuclei are split apart into several pieces, or when they are combined to form a single, larger nucleus ...
Energy - Warren County Schools
... converted to electrical energy by a generator at a power plant. ...
... converted to electrical energy by a generator at a power plant. ...
JAN – PATHFINDER SCIENCE Section 1
... transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six forms: chemical energy, electrical energy, radiant energy, mechanical energy, nuclear energy and thermal energy. Wind is a form of solar energy. Wi ...
... transform the food into energy to do work. When we run or walk or do some work, we ‘burn’ energy in our bodies. 2. B. II and IV Tip: Energy comes in six forms: chemical energy, electrical energy, radiant energy, mechanical energy, nuclear energy and thermal energy. Wind is a form of solar energy. Wi ...
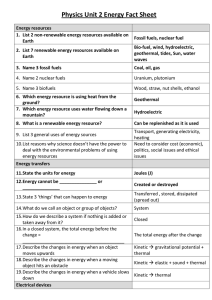
Physics Unit 2 Energy Fact Sheet
... 8. What is a renewable energy resource? 9. List 3 general uses of energy sources 10.List reasons why science doesn’t have the power to deal with the environmental problems of using energy resources ...
... 8. What is a renewable energy resource? 9. List 3 general uses of energy sources 10.List reasons why science doesn’t have the power to deal with the environmental problems of using energy resources ...
ENERGY VOCABULARY REVIEW
... 7. Nuclear Energy is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom that is released by joining (fusion) or splitting (fission) the atom. 8. Electrical Energy is the movement of electrons. It is the energy carried by the electric current that comes out of batteries and electrical outlets. 9. Motion En ...
... 7. Nuclear Energy is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom that is released by joining (fusion) or splitting (fission) the atom. 8. Electrical Energy is the movement of electrons. It is the energy carried by the electric current that comes out of batteries and electrical outlets. 9. Motion En ...
P1 2.1 Energy transfers
... • Energy is needed to keep us working, and to operate all the machines around us. • Different forms of energy include….. • Light, sound, electrical, potential and kinetic energy. • Energy can also be stored. Nuclear energy is stored inside atoms. Food, fuels and electric batteries are stores of Chem ...
... • Energy is needed to keep us working, and to operate all the machines around us. • Different forms of energy include….. • Light, sound, electrical, potential and kinetic energy. • Energy can also be stored. Nuclear energy is stored inside atoms. Food, fuels and electric batteries are stores of Chem ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.