Energy Test - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... D. All of the above 6. What is kinetic energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 7. What is potential energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 8. What is the movement of energy from one place or obje ...
... D. All of the above 6. What is kinetic energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 7. What is potential energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 8. What is the movement of energy from one place or obje ...
Chp. 13:3 Energy Transformations
... destroyed in the process. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed. ...
... destroyed in the process. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed. ...
LESSON 3: AN ENERGY MIX Renewable And Nonrenewable
... nonrenewables can be classified as either potential or kinetic energy, for instance petroleum, coal, and biomass can be categorized as potential energy or having stored energy and require a chemical reaction to be used for our needs, whereas wind and hydropower are better classified under kinetic en ...
... nonrenewables can be classified as either potential or kinetic energy, for instance petroleum, coal, and biomass can be categorized as potential energy or having stored energy and require a chemical reaction to be used for our needs, whereas wind and hydropower are better classified under kinetic en ...
Energy and Forms of Energy
... This type of energy stores potential energy in the nucleus of the atoms. It is released during a nuclear reaction. Power plants use nuclear fission, the splitting of atoms, to produce electricity. However, there is a much more destructive use of nuclear power. ...
... This type of energy stores potential energy in the nucleus of the atoms. It is released during a nuclear reaction. Power plants use nuclear fission, the splitting of atoms, to produce electricity. However, there is a much more destructive use of nuclear power. ...
*INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY* WORKSHEET
... Directions: Use the list of words to complete the following sentences. You may use words more than once. radiant electrical gravitational mechanical ...
... Directions: Use the list of words to complete the following sentences. You may use words more than once. radiant electrical gravitational mechanical ...
“INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY” WORKSHEET
... Directions: Use the list of words to complete the following sentences. You may use words more than once. radiant electrical gravitational mechanical ...
... Directions: Use the list of words to complete the following sentences. You may use words more than once. radiant electrical gravitational mechanical ...
Energy unit KUD
... Where does ‘energy’ come from? How does energy change from one form to another? By the end of this unit, students will know, understand, and be able to do the following main concepts. Know: All objects with mass have energy. Potential energy is the state of stored energy or energy of position. ...
... Where does ‘energy’ come from? How does energy change from one form to another? By the end of this unit, students will know, understand, and be able to do the following main concepts. Know: All objects with mass have energy. Potential energy is the state of stored energy or energy of position. ...
energy guided reading part 2
... ____________ sense? If energy can ___________ be created or destroyed, how can it be “used up”? “Using” energy When you “use” energy by turning on a ___________, you are really converting energy from one form (_______________) to other forms (light and __________). What gets “used up” is the _______ ...
... ____________ sense? If energy can ___________ be created or destroyed, how can it be “used up”? “Using” energy When you “use” energy by turning on a ___________, you are really converting energy from one form (_______________) to other forms (light and __________). What gets “used up” is the _______ ...
Kinetic Energy
... Katie, a 30.0 kg child, climbs a tree to rescue her cat that is afraid to jump 8.0m to the ground. How much work against gravity does Katie do in order to reach the cat? ...
... Katie, a 30.0 kg child, climbs a tree to rescue her cat that is afraid to jump 8.0m to the ground. How much work against gravity does Katie do in order to reach the cat? ...
energy - Petervaldivia
... we have a heavier nucleus and the release of energy • Scientists are working on creating fusion energy, so that someday there might be fusion power plants. ...
... we have a heavier nucleus and the release of energy • Scientists are working on creating fusion energy, so that someday there might be fusion power plants. ...
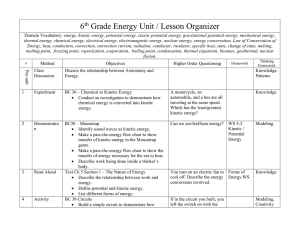
6th Grade Energy Unit / Lesson Organizer Domain Vocabulary
... BC72 Nuclear Power Identify the pros and cons of building more nuclear power plants. BC73 Quiz Review lessons 65 – 72 with a quiz. Play Energy Guess Who game to identify sources of energy. BC74 Distillation Review phases or states of matter and the properties of each state. Identify heat a ...
... BC72 Nuclear Power Identify the pros and cons of building more nuclear power plants. BC73 Quiz Review lessons 65 – 72 with a quiz. Play Energy Guess Who game to identify sources of energy. BC74 Distillation Review phases or states of matter and the properties of each state. Identify heat a ...
Energy types NOTES
... Temperature is a measurement of the internal kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance Thermal energy is the energy that makes the molecules move (kinetic energy) ...
... Temperature is a measurement of the internal kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance Thermal energy is the energy that makes the molecules move (kinetic energy) ...
Energy - Learning While Doing
... •Electrical energy is the movement of elections. •Lightning and static electricity are examples of electrical energy that occur naturally. •Science hasn't found a way to use natural forms of electrical energy, like lightning. Instead, we use different energy sources to create electrical energy by us ...
... •Electrical energy is the movement of elections. •Lightning and static electricity are examples of electrical energy that occur naturally. •Science hasn't found a way to use natural forms of electrical energy, like lightning. Instead, we use different energy sources to create electrical energy by us ...
Chapter 3 Energy
... energy needed to move a racecar come from. A. The energy comes from the combustion of the gasoline. The energy from the gasoline comes from dinosaurs. ...
... energy needed to move a racecar come from. A. The energy comes from the combustion of the gasoline. The energy from the gasoline comes from dinosaurs. ...
Lesson 3: An Energy Mix Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
... nonrenewables can be classified as either potential or kinetic energy, for instance petroleum, coal, and biomass can be categorized as potential energy or having stored energy and require a chemical reaction to be used for our needs, whereas wind and hydropower are better classified under kinetic en ...
... nonrenewables can be classified as either potential or kinetic energy, for instance petroleum, coal, and biomass can be categorized as potential energy or having stored energy and require a chemical reaction to be used for our needs, whereas wind and hydropower are better classified under kinetic en ...
Chapter 9.7 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... pedal). When a car brakes, the work is the friction force (supplied by the brakes) multiplied by the distance over which the friction force acts. KE is transformed by work (friction) into thermal energy, sound energy and larger-scale vibrations. ...
... pedal). When a car brakes, the work is the friction force (supplied by the brakes) multiplied by the distance over which the friction force acts. KE is transformed by work (friction) into thermal energy, sound energy and larger-scale vibrations. ...
Energy Review
... This energy comes from the motion of atoms and molecules. The faster the particles in an object move, the more thermal energy is produced. ...
... This energy comes from the motion of atoms and molecules. The faster the particles in an object move, the more thermal energy is produced. ...
What is energy?
... 3. Scientists define energy ___________________. Modern civilization is possible because we have learned how to ___________________________________________________ and then use it to do work for us. 4. What two forms of energy categorize the seven forms of energy?____________________________________ ...
... 3. Scientists define energy ___________________. Modern civilization is possible because we have learned how to ___________________________________________________ and then use it to do work for us. 4. What two forms of energy categorize the seven forms of energy?____________________________________ ...
TYPES OF ENERGY
... energy sources that we use every day. These sources are divided into two groups -- renewable (an energy source that we can use over and over again) and nonrenewable/conventional (an energy source that we are using up and cannot recreate in a short period of time). Renewable energy sources include so ...
... energy sources that we use every day. These sources are divided into two groups -- renewable (an energy source that we can use over and over again) and nonrenewable/conventional (an energy source that we are using up and cannot recreate in a short period of time). Renewable energy sources include so ...
Forms of Energy Basics
... including — chemical, gravitational, mechanical, and nuclear. Kinetic energy forms are doing work — like electrical, heat, light, motion, and sound. ...
... including — chemical, gravitational, mechanical, and nuclear. Kinetic energy forms are doing work — like electrical, heat, light, motion, and sound. ...
Chapter 15
... • ex. Coal, Petroleum (oil), natural gas, nuclear, etc. • usually produce pollution ...
... • ex. Coal, Petroleum (oil), natural gas, nuclear, etc. • usually produce pollution ...
Section 7.1 - CPO Science
... Define energy as a description of an object’s ability to change or cause change. Discuss examples of different forms of energy. Distinguish potential and kinetic energy and apply formulas to solve problems. ...
... Define energy as a description of an object’s ability to change or cause change. Discuss examples of different forms of energy. Distinguish potential and kinetic energy and apply formulas to solve problems. ...
Energy Resources
... Fuels contain stored chemical energy, which can be released by burning. The process of burning a fuel is called combustion. For example, most cars use a fuel called gasoline. The energy stored in fuels can be used to generate electricity. In most power plants, the thermal energy produced by burning ...
... Fuels contain stored chemical energy, which can be released by burning. The process of burning a fuel is called combustion. For example, most cars use a fuel called gasoline. The energy stored in fuels can be used to generate electricity. In most power plants, the thermal energy produced by burning ...
Lesson - nstacommunities.org
... 7. Next, students release the mass and measure the time it takes to complete 10 or more cycles from bottom to top and then back. Students divide the distance the oscillating mass travels during one cycle by the time needed for one cycle to find the average speed of the mass, vav . (The distance it t ...
... 7. Next, students release the mass and measure the time it takes to complete 10 or more cycles from bottom to top and then back. Students divide the distance the oscillating mass travels during one cycle by the time needed for one cycle to find the average speed of the mass, vav . (The distance it t ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.