* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Resources
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Grid energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Fossil fuel phase-out wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Fuel efficiency wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Indoor air pollution in developing nations wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of peak oil wikipedia , lookup
Alternative fuel wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
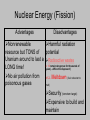
Energy Resources Building Background • What types of energy are there? • How is energy converted? Two Types of Energy • All energy can occur as two types: potential or kinetic energy 7 energy conversions Acronym: Mrs. Chen Mechanical Radiant Sound Chemical Heat Elastic Nuclear Mechanical Energy • The sum of an object’ s kinetic and gravitational potential energy Radiant (Light) Energy • Energy produced by vibrations of electrically charged particles Sound Energy • Energy caused by an object’s vibration Chemical Energy • Energy stored in chemical bonds of a substance that can be released when the substance reacts Heat(thermal) Energy • Energy related to particle motion. More motion more heat Elastic Potential Energy • Elastic potential energy-energy stored in elastic (ex: rubber band) Nuclear Energy • The form of energy associated with changes in the nucleus of an atom when it splits(fission) or comes together(fusion) Why is the sun so important? All of our energy can be traced back to our sun. Energy Conversions in Plants Light energy is given to plants to form chemical energy which is given to us for kinetic or thermal energy! (or others..) Energy Conversions in Plants • ALL food’s energy comes from the SUN – EVEN meat… animals eat plants and we eat animals Conversions involving electrical energy Common conversions of electrical energy Alarm Clock Electrical energy light energy and sound energy Battery Chemical energy electrical energy Light bulb Electrical energy light energy and thermal energy Blender Electrical energy kinetic energy and sound energy Chemical energy in your body is converted into kinetic energy when your muscle fibers contract and relax The chain moves and transfers energy to the back wheel, which gets you moving! Your legs transfer this kinetic energy to the pedals by pushing them around in a circle The pedals transfer this kinetic energy to the gear wheel, which transfers kinetic energy to the chain Summarizer Activity • How does energy change form? Two Types of Resources Frayer Diagram Energy Resources • Primary Energy Resources N O N R E N E W A B L R E S O U R C E S Fuels and Energy text pgs. 164-165 answer ?s 1-5 of reading guide • A fuel is a substance that provides a form of energy-such as heat, light, electricity, or motion—as a result of a chemical change. Energy can be converted (changed) from one form to another. Activity: Rub your hands together quickly for several seconds. Did you feel them becoming warmer? When you moved your hands, they had mechanical energy, the energy of motion. The friction of rubbing your hands together converted some of this mechanical energy to thermal energy, which you felt as heat. Energy is converted from one form to another. The process of burning a fuel is called combustion. • Science Geeks combustion • Energy stored in fuels can be used to generate electricity. What are Fossil Fuels? Text pgs. 166-167 RG #s 6-15 Formed hundreds of millions of years ago from the remains of: • dead plants • dead animals Three main fossil fuels: 1. Coal 2. Oil 3. Natural gas Fossil fuels are made of hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are energy-rich chemical compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms. During combustion, the carbon and hydrogen combine with oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide and water. This process releases energy in the forms of heat and light. Fossil fuels have more hydrocarbons per kg than most other fuels. For this reason, they are excellent source of energy. Combustion of one kg of coal, for example, provides twice as much heat as burning one kg of wood. Oil and natural gas provide three times the energy of wood. Combustion of Fossil Fuels Hydrogen Carbon Energy Production of Electricity Energy 101- Electricity Generation Fuels contain stored chemical energy, which can be released by burning. The process of burning a fuel is called combustion. For example, most cars use a fuel called gasoline. The energy stored in fuels can be used to generate electricity. In most power plants, the thermal energy produced by burning fuel is used to boil water, making steam. The mechanical energy of the steam turns the blades of a turbine. The shaft of the turbine is connected to a generator. The generator consists of powerful magnets surrounded by coils of copper wire. As the shaft rotates, the magnets turn inside the wire coil, producing an electric current. The electric current flows through power lines to homes and industries. How is electricity made and distributed First – some type of fuel is combusted and used to heat water and changes to steam Next – Turns a turbine (or piston) Next – energy is collected in a generator, producing electricity Next – transformer will step up the voltage Next – travels through high voltage lines Next – a substation transformer reduces power to be used locally Next – Distribution lines take it to your home Last – You turn on the lights! Jensen Steam Engine Hero's Engine Demo Fossil Fuel Formation • How are they made? Four things needed to change ancient living things into Fossil Fuels Saturated Environment Must have moist environment (swamp, sea, ocean) Anaerobic Lacks exposure to air; so things don’t rot; no oxygen Tremendous Pressure Layers and layers of sediment compress remains Tremendous Heat Piles of sediments create heat as layers and layers build Let’s start with coal. Coal is a solid fossil fuel formed from plant remains. Advantages: Easy to transport Most plentiful fuel in US Provides lots of energy when burned Disadvantages: Dangerous job Destroys ecosystems Produces the most CO2 when burned along with other poisonous gases Contributes to acid in streams and in rain Stages of Coal Pete Likes Biting Ants clip Stages of coal: • 1. Peat (hence the word Pete) • 2. Lignite • 3. Bituminous • 4. Anthracite Coal is mined from the ground either by stripping the land or digging deep mines. Coal Formation peat lignite Bituminous coal Anthracite coal ? • • How is coal formed? Coal is a solid fossil fuel formed from plant remains. Coal is formed from the remains of trees and other plants that grew in a swamp, hundreds of millions of years ago. Layers of dead organic material settle to the swamp’s bottom forming a basic fuel called peat. Over time, the peat continues to be compressed and as it ages, it changes into a more dense material called lignite. Eventually lignite changes to bituminous coal then into anthracite coal. Finally, coal may change into ?, but rarely. How do they get it? • Take a ride into a mine • Strip Mining and Shaft Mining • Coal Power Plant (PA’s future???) Oil (clip) and Natural Gas Text pgs. 168-169 RG #s 16-23 • Oil – LIQUID fossil fuel AKA petroleum(16) formed from decaying plant and microscopic animals over million of years • Fuels most cars, airplanes, trains, and ships(17) • The US consumes a third of all the petroleum produced in the world • 3% of the world’s petroleum is located in the US • Scientists can use sound waves(18) to test an area for oil without drilling • Oil directly from the earth is called CRUDE oil.(19) Petroleum (oil) • Edwin Drake couldn’t possibly have known what he started when he drilled the first oil well in Titusville, PA, in 1859. Oil had been known before that event for thousands of years , but it was used only in limited ways, such as lighting, cooking, and the waterproofing of ships. • After 1859, the availability of oil greatly increased its demand. It soon became a necessity after the invention of the internal combustion engine, and the introduction of Henry Ford’s Model T car in 1910. • The Story Of Petroleum • drilling for oil wkst.pdf Oil must be REFINED or cleaned before it can be used. A factory where crude oil is separated into fuels and other products by heating called a refinery (20). • Fractional Distillation • oil refinery products key Oil • Advantages: • Disadvantages: • Makes many products through petrochemicals (21) (compounds made from oil such as Destroys ecosystems Possibly catch on fire Air pollution when burned 1 out of 6 wells drilled produce useable oil Mostly purchased from other countries (global dependency) Oil spills during drilling and transport synthetic rubber, medicines, plastics, paints, textiles, etc.) • Great lubricant • Great energy • More than 50% is consumed for transportation • Also widely used for heating homes and fuel for power plants Natural Gas a mixture of methane and other gases History of Natural Gas (includes fracking) • Forms from the same • Pipelines transport organisms as gas from its source to petroleum the places where it is • It is less dense than oil, used. so it often rises above • It can be compressed the oil deposit (23) into a liquid and is • Can also get trapped in stored in tanks as fuel for trucks and buses porous rock such as shale Do not confuse Natural Gas with gasoline! Advantages: • Produces large amounts of energy (22) • Lowest levels of pollutants (CO2) than coal and oil • Can be compressed to a liquid for transporting Disadvantages: • Leaks can cause violent explosions or fire (no odor) • Destroys ecosystems • May taint groundwater • Possibly triggers earthquakes • Highly flammable (22) Fossil Fuels Advantages Cost (relatively cheap to produce) Already have Fossil Fuel plants Provides lots of energy Disadvantages Pollution (both land and air) Nonrenewable (24) resource (we will eventually run out of Fossil Fuels) Fossil Fuel Shortages • Fossil fuels are limited - they take a very long time to replace –take hundreds of millions of years to form (25) • New sources of energy are needed to (25) replace decreasing fossil fuel reserves • Conservation of fossils fuels is the best way to provide energy for the future! Make sure your dishwasher is full Turn your refrigerator down Turn the water off while brushing your teeth Turn off the lights when you leave a room Keep your heat a little lower and your air conditioning a little higher Walk, ride a bike or take public transportation when possible Detour • The Problems for Nonrenewable Resources • SEE GLOBAL WARMING PPT AND CLIPS Nuclear Energy text pgs. 181-185 • Non-renewable even though we have plenty of Uranium to last a very long time. The central core of an atom that contains the protons and neutrons is called the 1.nucleus. • Two types of nuclear reactions – 2.fission and fusion fission and fusion explained 3. Nuclear reactions convert matter into energy. • Albert Einstein’s formula,4. E= mc2, describes the relationship between energy and matter. Fission Fission 5. Nuclear fission– the splitting of an atomic nucleus (of a 6. Uranium 235 atom, an isotope into two smaller nuclei, during which nuclear energy is released. This energy produces heat which boils water which spins the turbine which drives the generator to produce electricity. Radioactive wastes are produced. Once the first nucleus (the center core of an atom that contains protons and neutrons) is split, it continues to split in a process called a nuclear chain reaction How is electricity produced in a nuclear power plant? How a nuclear reactor works Parts of a Reactor • B. Reactor Vessel • A. Fuel Rod • Is where nuclear fission occurs • Contains the Uranium • D. Control rod • Controls the reaction (usually made from cadmium or boron) • C.Heat exchanger • Changes hot water to steam Nuclear Energy (Fission) Advantages Disadvantages Nonrenewable Harmful radiation resource but TONS of potential Uranium around to last a Radioactive wastes 13.remain dangerous for thousands of LONG time! years) –difficult to dispose of) No air pollution from 12. Meltdown ( fuel rods start to poisonous gases melt) Security (terrorism target) Expensive to build and maintain 14.Nuclear Fusion - the combining of two atomic nuclei to produce a single larger nucleus • One kind of hydrogen (H2) has one proton and one neutron and the other kind (H3) has one proton and two neutrons. The tremendous heat and pressure cause them to combine and create a helium nucleus with two protons and two neutrons. This helium nucleus has slightly less mass than the total mass of the two hydrogen nuclei. The difference is converted into energy. Nuclear Energy (Fusion) Advantages 15.Resource water is readily available No air pollution from poisonous gases Produces much more energy per atom than fission Disadvantages 15.Difficult to control large-scale fusion reaction Extreme temperatures and pressure are needed Takes more energy to generate than it creates Nuclear Disasters • Chernobyl and Three Mile Island Revisited • Chernobyl disaster • Understanding the Accident of Fukushima Disaster R E N E W A B L E R E S O U R C E S 1-2 Energy from the Sun Energy From the Sun Solar Energy Passive Solar Heating • In passive solar-heating systems, the windows of a building are positioned so that sunlight enters directly and heats the building. Shades keep the heat in at night. Awnings are constructed to keep too much heat from entering during the summer. Active Solar Heating • Energy from the sun heats tubes filled with water in the solar collector. This heated liquid travels to the water storage tank. The water in the tank is heated up because of the hot tubes. This heated water is sent to various areas in the house for hot water. Solar Cells • Solar Cells (AKA photovoltaic cells) convert sunlight directly into electricity. Silicon is used to stimulate a flow of electrons across the cell. This flow of electrons IS an electric current! Power Towers • An array of mirrors focuses sunlight onto a boiler mounted on a tower. The boiler produces steam which spins the turbine to drive the generator which creates electricity. Solar Energy Advantages Renewable (free fuel) Tremendous potential (1 hour of sunlight = electricity for one year) No pollution Disadvantages Cost - very expensive No sun = no energy Need back up for cloudy days and night Takes up a large space Wind Power • Indirect form of solar energy because without the sun we would have no wind! • Wind spins the turbine to drive the generator which creates electricity. Wind Energy Advantages Renewable (free fuel) No pollution Disadvantages No wind = no energy Takes up a lot of space birds in turbines Bats can die! Water Power (Hydroelectric) • Indirect form of solar energy because without the sun we would have no water cycle! • How it works Water Energy Advantages Renewable (free fuel) No pollution Relatively inexpensive Disadvantages Limited locations Harmful to environment (flooding, plant and fish) Most places that can be dammed are already Geothermal Energy • Energy produced from the heat energy within the Earth itself. • Steam from geysers can heat homes • Well can be dug where water is heated to produce steam • ground source geothermal Geothermal Energy Advantages Renewable (free fuel) No pollution Constant temperatures close to surface if earth 50-55 degrees Disadvantages Limited locations for volcanic access Must have big enough area for install Tidal Energy • When the movement of water going from high tide to low tide is captured, energy can be produced. • The movement of water turns the turbine…etc. • Disadvantages – very limited locations • wave energy example Tidal Energy Advantages Renewable (free fuel) No pollution Disadvantages Limited locations (only along coastlines) Animals can be caught in turbines Biomass • Any materials that come from living things. • This material can be burned to produce heat. algae to fuel E SUGAR CANE SUNFLOWER ═ ═ N E R G Y Biomass Energy Advantages Disadvantages Inexhaustible fuel source Alcohols (like ethanol) and other fuels produced by biomass are efficient, viable, and relatively clean-burning Available throughout the world Could contribute a great deal to global warming and particulate pollution if directly burned Still an expensive source in terms of how much energy is used to produce it Hydrogen • Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless gas that accounts for 75 percent of the entire universe's mass. Hydrogen is found on Earth only in combination with other elements such as oxygen, carbon and nitrogen. To use hydrogen, it must be separated from these other elements. Hydrogen Key technology for the future • Today, hydrogen is used primarily in ammonia manufacturing, petroleum refining and synthesis of methanol. It's also used in NASA's space program as fuel for the space shuttles, and in fuel cells that provide heat, electricity and drinking water for astronauts. Fuel cells are devices that directly convert hydrogen into electricity. In the future, hydrogen could be used to fuel vehicles (such as the DaimlerChrysler NeCar 4shown in the picture to the right) and aircraft, and provide power for our homes and offices. • How hydrogen fuel is made