Notes
... On a roller coaster the greatest kinetic energy is at the lowest point This is where the roller coaster has the highest velocity (fastest) ...
... On a roller coaster the greatest kinetic energy is at the lowest point This is where the roller coaster has the highest velocity (fastest) ...
Name: Date: Period:______ Chapter 12 Study Guide Honors
... An energy resource that is available in limited amounts or that is used faster than it can be replaced in nature. Examples: Fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, propane, and coal) Nuclear energy 15. Swimmers have to eat well before a meet because the food has which type of energy? Chemical energy 1 ...
... An energy resource that is available in limited amounts or that is used faster than it can be replaced in nature. Examples: Fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, propane, and coal) Nuclear energy 15. Swimmers have to eat well before a meet because the food has which type of energy? Chemical energy 1 ...
As the great debate on energy conservation continues in the political
... Energy comes in different forms like heat (thermal), light (radiant), and motion (Kinetic), electrical, chemical, nuclear energy and gravitational. There is two types of energy as well as different sources of energy. Two types of energy, one being stored which is potential energy and working also k ...
... Energy comes in different forms like heat (thermal), light (radiant), and motion (Kinetic), electrical, chemical, nuclear energy and gravitational. There is two types of energy as well as different sources of energy. Two types of energy, one being stored which is potential energy and working also k ...
Potential Energy
... For examination purposes, you should explain this statement by saying that this means that energy can be transformed from one form to another but it can neither be created nor destroyed — the total energy of a closed system will be the same before an interaction as after it. When energy is transform ...
... For examination purposes, you should explain this statement by saying that this means that energy can be transformed from one form to another but it can neither be created nor destroyed — the total energy of a closed system will be the same before an interaction as after it. When energy is transform ...
Chapter 5 Study Guide “Energy and Power”
... This guide will help you study for a test covering the important information about energy. If you study for 10 minutes a night, for at least up to 5 nights, and have your parents sign off on this form, I will give you 5 extra credit points on the test. You must bring this signed study guide on the d ...
... This guide will help you study for a test covering the important information about energy. If you study for 10 minutes a night, for at least up to 5 nights, and have your parents sign off on this form, I will give you 5 extra credit points on the test. You must bring this signed study guide on the d ...
Energy - Catawba County Schools
... The Law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. * Energy is often converted into other forms. * Friction is often the cause of energy changes (reduces efficiency) * Gravitational potential energy of an object is converted to the kinetic energy of motion as the ob ...
... The Law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. * Energy is often converted into other forms. * Friction is often the cause of energy changes (reduces efficiency) * Gravitational potential energy of an object is converted to the kinetic energy of motion as the ob ...
Potential Energy
... Electrical energy = the energy that makes a TV work Thermal energy = the energy in a hot cup of tea Chemical energy = the energy in food Nuclear energy = the energy in an atom’s nucleus Radiant energy = a lamp giving off light ...
... Electrical energy = the energy that makes a TV work Thermal energy = the energy in a hot cup of tea Chemical energy = the energy in food Nuclear energy = the energy in an atom’s nucleus Radiant energy = a lamp giving off light ...
unit-6 - unit-1
... energy in rubbing hands as a result heat is produced. In this process of rubbing hands, mechanical energy is converted into heat energy. Example-2 : Some of heat energy from sun is taken up by water in the oceans. This increase the thermal energy. Thermal energy causes water to evaporate from the su ...
... energy in rubbing hands as a result heat is produced. In this process of rubbing hands, mechanical energy is converted into heat energy. Example-2 : Some of heat energy from sun is taken up by water in the oceans. This increase the thermal energy. Thermal energy causes water to evaporate from the su ...
Energy - Mr. Jones`s Science Class
... vibration of particles in a solid, liquid, or gas can be impacted by temperature and pressure must have a medium (usually air) to travel through - cannot travel through empty space sound in a vacuum ...
... vibration of particles in a solid, liquid, or gas can be impacted by temperature and pressure must have a medium (usually air) to travel through - cannot travel through empty space sound in a vacuum ...
Energy - Mr. Jones`s Science Class
... vibration of particles in a solid, liquid, or gas can be impacted by temperature and pressure must have a medium (usually air) to travel through - cannot travel through empty space sound in a vacuum ...
... vibration of particles in a solid, liquid, or gas can be impacted by temperature and pressure must have a medium (usually air) to travel through - cannot travel through empty space sound in a vacuum ...
Measuring Kinetic and Potential Energy
... Chemical energy is stored in the bonds of molecules. This is a form of potential energy until the bonds are broken. Fossil fuels and biomass store chemical energy. ...
... Chemical energy is stored in the bonds of molecules. This is a form of potential energy until the bonds are broken. Fossil fuels and biomass store chemical energy. ...
10PRESEnergyChapter-5-sec
... • Uses of Fossil Fuels Oil and natural gas, shown on the next slide, as well as coal, are the most common fossil fuels. •All fossil fuels contain stored energy from the sun, which can be converted into other kinds of energy. • Electrical Energy from Fossil Fuels One way to generate electrical energy ...
... • Uses of Fossil Fuels Oil and natural gas, shown on the next slide, as well as coal, are the most common fossil fuels. •All fossil fuels contain stored energy from the sun, which can be converted into other kinds of energy. • Electrical Energy from Fossil Fuels One way to generate electrical energy ...
Unit 4: Energy
... 2kg x 9.8m/s 2 x 1m = 19.6 J • What is the kinetic energy of a 3 kg ball that is rolling at 2 m/s? ...
... 2kg x 9.8m/s 2 x 1m = 19.6 J • What is the kinetic energy of a 3 kg ball that is rolling at 2 m/s? ...
Mechanical Energy (pages 151–152)
... Key Concept: Forms of energy associated with the particles of objects include thermal energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy, and electromagnetic energy. • Thermal energy is the total energy in the particles of an object. Hot things have more thermal energy than cold things. • El ...
... Key Concept: Forms of energy associated with the particles of objects include thermal energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy, and electromagnetic energy. • Thermal energy is the total energy in the particles of an object. Hot things have more thermal energy than cold things. • El ...
Energy and its importance script
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Energy is found in many sources in nature, including sunlight, wind, water, plants, and animals. All activities of living things need energy. Appliances and machines need energy to work too. Therefore, energy is very important to mankind. The Differe ...
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. Energy is found in many sources in nature, including sunlight, wind, water, plants, and animals. All activities of living things need energy. Appliances and machines need energy to work too. Therefore, energy is very important to mankind. The Differe ...
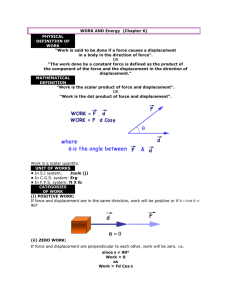
chapter 4 - work and energy
... Geothermal energy is produced wherever water is heated by magma or hot rocks beneath the Earth’s surface and makes its way to the surface to be utilized as a heat source. Geothermal sources in Oregon, Idaho, and California are in use today. Hydrogen gas can be used to store energy for later use sin ...
... Geothermal energy is produced wherever water is heated by magma or hot rocks beneath the Earth’s surface and makes its way to the surface to be utilized as a heat source. Geothermal sources in Oregon, Idaho, and California are in use today. Hydrogen gas can be used to store energy for later use sin ...
Forms of Energy Basics What is energy? Energy makes change
... Energy makes change possible. We use it to do things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen in the freezer. It plays our favorite songs on the radio and lights our homes. Energy is needed for our bodies to grow and it allows ou ...
... Energy makes change possible. We use it to do things for us. It moves cars along the road and boats over the water. It bakes a cake in the oven and keeps ice frozen in the freezer. It plays our favorite songs on the radio and lights our homes. Energy is needed for our bodies to grow and it allows ou ...
Lesson 1 Energy - Tony Ford Science
... things such as a person riding a bike, an engine driving a car or chemicals making an explosion. Energy Sources The energy you use comes originally from a place or object. Natural sources include the sun, wind, coal, petrol, gas, waves and tides, hot springs, rivers and water channels, plants ...
... things such as a person riding a bike, an engine driving a car or chemicals making an explosion. Energy Sources The energy you use comes originally from a place or object. Natural sources include the sun, wind, coal, petrol, gas, waves and tides, hot springs, rivers and water channels, plants ...
TYPES OF ENERGY
... o Energy caused by the movement of electrons (magnetism) o Easily transported through power lines and converted into other forms of energy ...
... o Energy caused by the movement of electrons (magnetism) o Easily transported through power lines and converted into other forms of energy ...
Energy * Learning Outcomes
... e.g. A mass of 5 kg travelling at 20 m s-1 collides with and sticks to a mass of 2 kg which is at rest. Find the velocity of the combined mass after the collision. Find the loss in kinetic energy. e.g. A small mass of 5 kg is suspended from a fixed point by a light string 2 m long. Another mas ...
... e.g. A mass of 5 kg travelling at 20 m s-1 collides with and sticks to a mass of 2 kg which is at rest. Find the velocity of the combined mass after the collision. Find the loss in kinetic energy. e.g. A small mass of 5 kg is suspended from a fixed point by a light string 2 m long. Another mas ...
Chapter 12: Energy and Energy Resources
... • A natural resource that can be converted by humans into another form of energy to do useful work. • Can be nonrenewable or renewable. ...
... • A natural resource that can be converted by humans into another form of energy to do useful work. • Can be nonrenewable or renewable. ...
Energy - Science Class Rocks!
... perform work – Ex: hammer striking a nail, a jack lifting a car, pedals turning the wheel of a bike – Sound is a type of mechanical energy ...
... perform work – Ex: hammer striking a nail, a jack lifting a car, pedals turning the wheel of a bike – Sound is a type of mechanical energy ...
Energy Test - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... D. All of the above 6. What is kinetic energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 7. What is potential energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 8. What is the movement of energy from one place or obje ...
... D. All of the above 6. What is kinetic energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 7. What is potential energy? A. energy in motion B. energy an object has because of its position (stored energy) 8. What is the movement of energy from one place or obje ...
Energy policy of Australia
The energy policy of Australia is subject to the regulatory and fiscal influence of all three levels of Government in Australia, although only the State and Federal levels determine policy for primary industries such as coal.Federal energy policies continue to support the coal mining and natural gas industries through subsidies for fossil fuel use and production as the exports by those industries contribute significantly to the earnings of foreign exchange and government revenues. Australia is one of the most coal-dependent countries in the world. Coal and natural gas, along with oil-based products, are currently the primary sources of Australian energy usage, despite the fact that the coal industry produces approximately 38% of Australia's total greenhouse gas emissions. Federal policy has reverted to a pro-coal economy with drastic cuts to alternate and renewable energy government offices, targets and subsidies ""With proposals to repeal the carbon price, dismantle the Climate Change Authority and the Clean Energy Finance Corporation, and the dilution of the Renewable Energy Target already in train, the budget measures, which include the closure of the Australian Renewable Energy Agency, the dumping of the million solar roofs program (both contrary to election promises) and the research funding cuts at the CSIRO, Bureau of Meteorology and elsewhere,...the obliteration of the Clean Energy Future package] is complete"". The Conservative government has implemented many of the 75-point wish list drawn up by the influential Institute of Public Affairs. The Institute of Public Affairs (IPA) is a right-wing, corporate funded think tank based in Melbourne. It has close links to the Liberal Party of Australia. The IPA's key policy positions include: advocacy for privatisation and deregulation; attacks on the positions of unions and non-government organisations; support of assimilationist indigenous policy (cf. the Bennelong Society) and refutation of the science involved with environmental issues such as climate change. Federal policy was beginning to change during the previous Liberal government with the publication of the Garnaut report and Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme White Paper, the announcement of an Emissions Trading Scheme to commence in 2010, and the announcement of a national mandatory renewable energy target of 20% of electricity supply in Australia by 2020.State energy policies such as Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets ensure that renewable energy contributes a greater percentage of the country's energy supply.Due to Australia's reliance on coal and gas for energy, in 2000 the country was the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world, irrespective of whether or not emissions from land clearing were included. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report.Renewable energy commercialisation in Australia is an area of relatively minor activity compared to the fossil fuels industry. Australia's renewable energy industries are diverse, covering numerous energy sources and scales of operation, and currently contribute about 8–10% of Australia's total energy supply. The major area where renewable energy is growing is in electricity generation following the introduction of government Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets. The two most populous states, New South Wales and Victoria have renewable energy targets of 20% and 25% respectively by 2020.