CP2: Optics Why study optics? The problem of teaching optics
... plane. If the object is not at infinity then must move lens away from detector or decrease its focal length ...
... plane. If the object is not at infinity then must move lens away from detector or decrease its focal length ...
Microscope
... Stage clips hold the slides in place. If your microscope has a mechanical stage, you will be able to move the slide around by turning two stage clips knobs. One moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down. ...
... Stage clips hold the slides in place. If your microscope has a mechanical stage, you will be able to move the slide around by turning two stage clips knobs. One moves it left and right, the other moves it up and down. ...
Experimental Phys - Delta University!
... Experiment No. (01) Power of Spherical Lenses ---------------------------------------------------------------- 3 1. Determination of the Focal Length and the Power of a Converging (Convex) Lens ------------------------- 3 1.1. Coincidence Method: ----------------------------------------------------- ...
... Experiment No. (01) Power of Spherical Lenses ---------------------------------------------------------------- 3 1. Determination of the Focal Length and the Power of a Converging (Convex) Lens ------------------------- 3 1.1. Coincidence Method: ----------------------------------------------------- ...
Optical laser beam scanner lens relay system
... with standard, i.e. commonly available lenses. Nevertheless, a very good performance can be obtained with a little bit of care in the design. Even a very simple design using achromats is adequate, although significantly improved performance can be obtained if meniscus lenses are added. The general r ...
... with standard, i.e. commonly available lenses. Nevertheless, a very good performance can be obtained with a little bit of care in the design. Even a very simple design using achromats is adequate, although significantly improved performance can be obtained if meniscus lenses are added. The general r ...
PPT
... region of the mirror was flatter than it should be - by just one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. This is equivalent to only four wavelengths of visible light, but it was enough. One insider said that the Hubble mirror was "very accurate, very accurately the wrong shape". ...
... region of the mirror was flatter than it should be - by just one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. This is equivalent to only four wavelengths of visible light, but it was enough. One insider said that the Hubble mirror was "very accurate, very accurately the wrong shape". ...
Plane Mirrors
... angle of incidence is an angle that light hits the mirror relative to the normal. The angle of reflection is an angle of that light's reflection, on the other part of the normal, and is equal to the angle of incidence. The image seen in a plane mirror seems to be behind the mirror. This is an exampl ...
... angle of incidence is an angle that light hits the mirror relative to the normal. The angle of reflection is an angle of that light's reflection, on the other part of the normal, and is equal to the angle of incidence. The image seen in a plane mirror seems to be behind the mirror. This is an exampl ...
What is a Fresnel Lens?
... uniformity of brightness across the entire screen, a Fresnel lens can be placed against the ground glass on the side facing the camera’s lens. There, the Fresnel element functions as a field lens by intercepting light already focused at the screen and refracts it toward the viewer’s eye. Rays that ...
... uniformity of brightness across the entire screen, a Fresnel lens can be placed against the ground glass on the side facing the camera’s lens. There, the Fresnel element functions as a field lens by intercepting light already focused at the screen and refracts it toward the viewer’s eye. Rays that ...
Intraocular Lenses
... Optics of Intraocular Lenses (IOLs) I. IOL Overview II. Monofocal IOLs III. Accommodating IOLs IV. Multifocal IOLs I. IOL Overview Primary (optical) functions of the crystalline lens: 1. Provide additional refractive power (~ 20 D) to supplement cornea (~ 40 D) for distance vision. 2. Provide accomm ...
... Optics of Intraocular Lenses (IOLs) I. IOL Overview II. Monofocal IOLs III. Accommodating IOLs IV. Multifocal IOLs I. IOL Overview Primary (optical) functions of the crystalline lens: 1. Provide additional refractive power (~ 20 D) to supplement cornea (~ 40 D) for distance vision. 2. Provide accomm ...
PHYS 202 Notes, Week 10
... • The aqueous humor, index of refraction n = 1.336. • The crystalline lens, index of refraction n = 1.437. • The vitreous humor, index of refraction n = 1.336. In order to form a sharp image, the image point of the eye needs to be exactly on the retina surface. Given that the retina is in a fixed lo ...
... • The aqueous humor, index of refraction n = 1.336. • The crystalline lens, index of refraction n = 1.437. • The vitreous humor, index of refraction n = 1.336. In order to form a sharp image, the image point of the eye needs to be exactly on the retina surface. Given that the retina is in a fixed lo ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Exercise 6: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
... Exercise 6: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
Guided Discovery and Lesson Notes on Mirrors and Applications
... 1. Parallel rays far from the axis do converge at a point slightly closed to the mirror than the focal point: thus, the image formed by parallel rays is a disk instead of a point. 2. This deviation from an ideal point is called spherical aberration. 3. Spherical aberration can be eliminated using pa ...
... 1. Parallel rays far from the axis do converge at a point slightly closed to the mirror than the focal point: thus, the image formed by parallel rays is a disk instead of a point. 2. This deviation from an ideal point is called spherical aberration. 3. Spherical aberration can be eliminated using pa ...
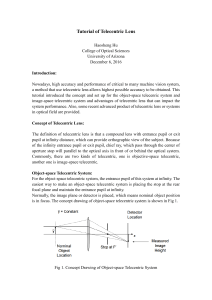
Tutorial of Telecentric Lens
... Nowadays, high accuracy and performance of critical to many machine vision system, a method that use telecentric lens allows highest possible accuracy to be obtained. This tutorial introduced the concept and set up for the object-space telecenric system and image-space telecentric system and advanta ...
... Nowadays, high accuracy and performance of critical to many machine vision system, a method that use telecentric lens allows highest possible accuracy to be obtained. This tutorial introduced the concept and set up for the object-space telecenric system and image-space telecentric system and advanta ...
Laboratory Exercise 3: Microscopy The microscope is a tool for the
... power field of view. An image on the edge of the low power field of view will be lost under high power unless it is first centered. Oil Immersion Lens - in light microscopy, optimal magnification and resolving power is achieved with the oil immersion objective. This lens has high resolution and hig ...
... power field of view. An image on the edge of the low power field of view will be lost under high power unless it is first centered. Oil Immersion Lens - in light microscopy, optimal magnification and resolving power is achieved with the oil immersion objective. This lens has high resolution and hig ...
Optics Observations
... Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength ...
... Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Exercise 5: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
... Exercise 5: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
ppt
... Image forms at the point where the light rays converge. When real light rays converge Real Image When imaginary extension of L.R. converge Virtual Image Only real image can be viewed on screen placed at the spot. ...
... Image forms at the point where the light rays converge. When real light rays converge Real Image When imaginary extension of L.R. converge Virtual Image Only real image can be viewed on screen placed at the spot. ...
Modulation Transfer Function
... one point is over the first zero of the second. Using the known size of the Airy disc, we find that two points are resolved if they are a distance d apart, where d= ...
... one point is over the first zero of the second. Using the known size of the Airy disc, we find that two points are resolved if they are a distance d apart, where d= ...
Astronomy 101 Lab: Telescopes
... to determine the focal lengths of these lenses. Notice the lamp near the front of the room. You want the light from this lamp to pass through each lens and project an image on the wall. Hold one of the lenses up near the wall such that the side of the tube containing the lens is closest to the wall. ...
... to determine the focal lengths of these lenses. Notice the lamp near the front of the room. You want the light from this lamp to pass through each lens and project an image on the wall. Hold one of the lenses up near the wall such that the side of the tube containing the lens is closest to the wall. ...
Exposure and Imaging
... – Primary reduction camera in WTC-MFL uses a projection lens with f/6.8 and f = 9.5 in. = 241.3 mm. – Lens diameter is D = 241.3 mm/6.8 = 35.5 mm = 1.40 in. – The numerical aperture is NA = 1/2*6.8 = 0.074. – For exposure in the middle green, λ= 550 nm. – Thus, the minimum feature size is b = 550 nm ...
... – Primary reduction camera in WTC-MFL uses a projection lens with f/6.8 and f = 9.5 in. = 241.3 mm. – Lens diameter is D = 241.3 mm/6.8 = 35.5 mm = 1.40 in. – The numerical aperture is NA = 1/2*6.8 = 0.074. – For exposure in the middle green, λ= 550 nm. – Thus, the minimum feature size is b = 550 nm ...
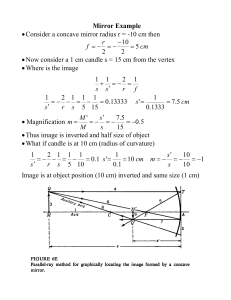
Mirror Example • Consider a concave mirror radius r =
... (a) where diverge beam forms parallel light Concave surface (b) where light appears to converge when it is converted into a parallel beam ...
... (a) where diverge beam forms parallel light Concave surface (b) where light appears to converge when it is converted into a parallel beam ...
AQA GCSE Physics P3 Revision Worksheet
... How does a transformer work? Fill the missing words: An …………………………………………………………… current in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic ………………………. in the iron core and hence in the secondary coil. This …………………………………………………….. an alternating ………………..………………… difference across the ends of the ……………………… ...
... How does a transformer work? Fill the missing words: An …………………………………………………………… current in the primary coil produces a changing magnetic ………………………. in the iron core and hence in the secondary coil. This …………………………………………………….. an alternating ………………..………………… difference across the ends of the ……………………… ...
Optical Prescriptions Spectacle Lenses
... energy transmitted through the lens to the amount incident on the front surface. It is expressed as a percentage. Luminous transmittance- describes the visual characteristics of tinted lens ...
... energy transmitted through the lens to the amount incident on the front surface. It is expressed as a percentage. Luminous transmittance- describes the visual characteristics of tinted lens ...
Understanding Determinant Geometrically
... where ~u1 , ~u2 , ~u3 is obtained from {~v1 , ~v2 , ~v3 } by the Gram-Schmidt process. 2. Imagine the image of the standard unit cube under the linear transformation defined by multiplication by A. Why do ~v1 , ~v2 , and ~v3 form three of its edges? Compare to the picture in the book in Section 6.3. ...
... where ~u1 , ~u2 , ~u3 is obtained from {~v1 , ~v2 , ~v3 } by the Gram-Schmidt process. 2. Imagine the image of the standard unit cube under the linear transformation defined by multiplication by A. Why do ~v1 , ~v2 , and ~v3 form three of its edges? Compare to the picture in the book in Section 6.3. ...
RESOLVING POWER AND MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION
... small extent, arbitrary since the existence of two instead of one peak may be recognized with higher or lower contrast as shown in fig. 3 (C). However, introducing that contrast (M) into the MTF („limiting resolution“ in fig. 2) of an optical system, the maximum spatial frequency imageable by that s ...
... small extent, arbitrary since the existence of two instead of one peak may be recognized with higher or lower contrast as shown in fig. 3 (C). However, introducing that contrast (M) into the MTF („limiting resolution“ in fig. 2) of an optical system, the maximum spatial frequency imageable by that s ...