Lect03_Bi177_MicroscopeOptics
... • Frequency remains constant while light travels through different media. Wavelength and speed change. ...
... • Frequency remains constant while light travels through different media. Wavelength and speed change. ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the image formed would be upside down and larger. Overhead projectors form this type of image, which is then turned right side up by a mirror ...
... from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the image formed would be upside down and larger. Overhead projectors form this type of image, which is then turned right side up by a mirror ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the image formed would be upside down and larger. Overhead projectors form this type of image, which is then turned right side up by a mirror ...
... from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the image formed would be upside down and larger. Overhead projectors form this type of image, which is then turned right side up by a mirror ...
Forensic Science
... •The examiner studying a specimen under a microscope can simultaneously obtain the visible absorption spectrum or IR spectrum of the material being observed. •This instrument is especially useful in the examination of trace evidence, paint, fiber, and ink evidence. The Scanning Electron Microscope ...
... •The examiner studying a specimen under a microscope can simultaneously obtain the visible absorption spectrum or IR spectrum of the material being observed. •This instrument is especially useful in the examination of trace evidence, paint, fiber, and ink evidence. The Scanning Electron Microscope ...
Many other important inventions involve the use of
... transmission of visible light and greater absorption of ultraviolet light. Some plastics have a greater index of refraction than most types of glass, this is useful in the making of corrective lenses shaped to correct various vision abnormalities like myopia, allowing thinner lenses for a given pres ...
... transmission of visible light and greater absorption of ultraviolet light. Some plastics have a greater index of refraction than most types of glass, this is useful in the making of corrective lenses shaped to correct various vision abnormalities like myopia, allowing thinner lenses for a given pres ...
Acknowledgments
... In mechanical engineering, a primary motivation for studying optics is to learn how to use optical techniques for making measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved bas ...
... In mechanical engineering, a primary motivation for studying optics is to learn how to use optical techniques for making measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved bas ...
Single-Photon Synchronous Detection
... Evaluation of intensity and phase of an impinging ray of multi- or monochromatic light has shown its usefulness in a number of applications. One of the first applications of phase-based imaging has been historically optical rangefinding, where the time-of-flight (TOF) of a reflected ray of light is ...
... Evaluation of intensity and phase of an impinging ray of multi- or monochromatic light has shown its usefulness in a number of applications. One of the first applications of phase-based imaging has been historically optical rangefinding, where the time-of-flight (TOF) of a reflected ray of light is ...
Image formation with broad bundles of rays
... Wave surfaces are surfaces of constant phase. The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all thes ...
... Wave surfaces are surfaces of constant phase. The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all thes ...
Lens Design OPTI 517 Syllabus
... There are nine homework sets. Each homework set must be organized, clear, and neatly presented as if it were intended for a customer or your supervisor. There will be one week of grace period to turn in the HW's. After that there will be a 20%, HW grade, penalty for each week that the HW is late sta ...
... There are nine homework sets. Each homework set must be organized, clear, and neatly presented as if it were intended for a customer or your supervisor. There will be one week of grace period to turn in the HW's. After that there will be a 20%, HW grade, penalty for each week that the HW is late sta ...
Inleiding Optica 2010
... -If you can take it apart you should be able to put it back together -Do unto others as you would have them do to you ...
... -If you can take it apart you should be able to put it back together -Do unto others as you would have them do to you ...
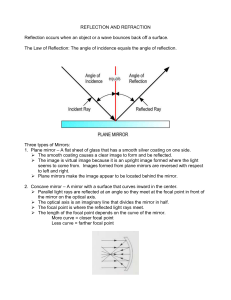
Reflection - TeacherWeb
... 1. Plane mirror – A flat sheet of glass that has a smooth silver coating on one side. The smooth coating causes a clear image to form and be reflected. The image is virtual image because it is an upright image formed where the light seems to come from. Images formed from plane mirrors are revers ...
... 1. Plane mirror – A flat sheet of glass that has a smooth silver coating on one side. The smooth coating causes a clear image to form and be reflected. The image is virtual image because it is an upright image formed where the light seems to come from. Images formed from plane mirrors are revers ...
Lesson-2 Light Microscopy
... screen kept at other side of lens. Conjugate foci vary in position. If object is nearer the lens, the image will be formed further away, at a greater magnification and inverted. This “real” image is formed by objective lens of microscope. If the object is placed within focal point of lens, image is ...
... screen kept at other side of lens. Conjugate foci vary in position. If object is nearer the lens, the image will be formed further away, at a greater magnification and inverted. This “real” image is formed by objective lens of microscope. If the object is placed within focal point of lens, image is ...
pp. 273
... characterizes the storage process. The resulting retrievals* are shown in Fig. 13. Crosstalk in this case is disturbing, while in Fig. 11 it is virtually undetectable. One technique to suppress the crosstalk associated with nonlinear storage is to control the carrier's transmission geometry. The dev ...
... characterizes the storage process. The resulting retrievals* are shown in Fig. 13. Crosstalk in this case is disturbing, while in Fig. 11 it is virtually undetectable. One technique to suppress the crosstalk associated with nonlinear storage is to control the carrier's transmission geometry. The dev ...
Read more... Using the Document Camera
... For better resolution of the projected text, images or objects, turn up the front teaching space lighting using the lighting panel controls on the lectern and monitor the effect of doing so on the projected screen image of what you the document camera is capturing. Typically, more light produces bri ...
... For better resolution of the projected text, images or objects, turn up the front teaching space lighting using the lighting panel controls on the lectern and monitor the effect of doing so on the projected screen image of what you the document camera is capturing. Typically, more light produces bri ...
Lecture 18 - Purdue Physics
... • Using ray diagrams, the is exactly the same distance behind the plane mirror as the object is in front of it. ...
... • Using ray diagrams, the is exactly the same distance behind the plane mirror as the object is in front of it. ...
Light microscopy
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
the optical (light) microscope
... and reflections within the microscope. The field diaphragm is stopped down to the edge of the field of view. A second adjustable-iris diaphragm, the aperture diaphragm, is placed in the light path before the vertical illuminator. Opening or closing this diaphragm alters the amount of light and t ...
... and reflections within the microscope. The field diaphragm is stopped down to the edge of the field of view. A second adjustable-iris diaphragm, the aperture diaphragm, is placed in the light path before the vertical illuminator. Opening or closing this diaphragm alters the amount of light and t ...
EE119 Homework 7: Microscopes, Projectors and Photomultiplier
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
startest
... The observer probes through focus and across the field to determine the type, direction, and magnitude of aberrations present. For ease of carrying out the test, the magnifying power should be such that the smallest significant detail subtends an easily resolvable 10 to 15 minutes of arc at the eye. ...
... The observer probes through focus and across the field to determine the type, direction, and magnitude of aberrations present. For ease of carrying out the test, the magnifying power should be such that the smallest significant detail subtends an easily resolvable 10 to 15 minutes of arc at the eye. ...
Chester F - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... 9. The Center for Imaging Science is considering putting a small telescope, equipped with CCD camera (at the telescope focal plane), on the roof of the Carlson building. The telescope would be a 16" (~ 0.4 m) diameter f/10 reflector. It is estimated that (1) telescope vibrations, due to such things ...
... 9. The Center for Imaging Science is considering putting a small telescope, equipped with CCD camera (at the telescope focal plane), on the roof of the Carlson building. The telescope would be a 16" (~ 0.4 m) diameter f/10 reflector. It is estimated that (1) telescope vibrations, due to such things ...
Physics 44
... end of the optical track. 2. Determine the focal length of the objective lens by doing the following: a) Turn the optical track so that it points toward a distant, bright object with the objective lens at the end of the track toward the bright object. b) Move a clean white sheet of paper back and fo ...
... end of the optical track. 2. Determine the focal length of the objective lens by doing the following: a) Turn the optical track so that it points toward a distant, bright object with the objective lens at the end of the track toward the bright object. b) Move a clean white sheet of paper back and fo ...
Following the path of light: recovering and
... screen on a smaller tube sliding inside the camera, we can see the stenopeic images by looking direclty inside the camera. ...
... screen on a smaller tube sliding inside the camera, we can see the stenopeic images by looking direclty inside the camera. ...
09Optics
... sharper; more pronounced: – Maxima are located by the same geometry as used for Young’s double slit: sinθ = mλ/d; m=0, 1, 2, 3, … – Edges of wider two-slit peaks are removed by destructive interference by light coming through slits much further ...
... sharper; more pronounced: – Maxima are located by the same geometry as used for Young’s double slit: sinθ = mλ/d; m=0, 1, 2, 3, … – Edges of wider two-slit peaks are removed by destructive interference by light coming through slits much further ...
Refraction
... • A person who is farsighted (hyperopia) can see far objects clearly but near objects seem blurry. This is because the lenses focus light at a point behind the retina rather than on the retina. • A person who is nearsighted (myopia) can see near objects clearly but far objects seem blurry. ...
... • A person who is farsighted (hyperopia) can see far objects clearly but near objects seem blurry. This is because the lenses focus light at a point behind the retina rather than on the retina. • A person who is nearsighted (myopia) can see near objects clearly but far objects seem blurry. ...
Modellistica 3D di Componenti Cellulari
... cells, . . . were indeed the first microscopical pores I ever saw, and perhaps, that were ever seen, for I had not met with any Writer or Person, that had made any mention of them before this. . . ...
... cells, . . . were indeed the first microscopical pores I ever saw, and perhaps, that were ever seen, for I had not met with any Writer or Person, that had made any mention of them before this. . . ...