Microscopy
... Set a laser beam to reflect off of the processed side of the provided silicon wafer. Set a screen at the laser end of the table to catch the far-field diffraction pattern. There should be a slight angle between the incoming and reflected beams. ...
... Set a laser beam to reflect off of the processed side of the provided silicon wafer. Set a screen at the laser end of the table to catch the far-field diffraction pattern. There should be a slight angle between the incoming and reflected beams. ...
Much Physics - Little Effort
... One can notice that the pipe rotates around a vertical axis while rolling on its circumference. If you press e.g. the red dot, you can see this red dot four times at the same time. It is also obvious that one can see just that very dot which has been pressed during the start. The other dot is more o ...
... One can notice that the pipe rotates around a vertical axis while rolling on its circumference. If you press e.g. the red dot, you can see this red dot four times at the same time. It is also obvious that one can see just that very dot which has been pressed during the start. The other dot is more o ...
Introduction Reflection of Light
... A light microscope is an instrument that uses lenses to make enlarged images of objects that are too small for the unaided eye to see. A common type of light microscope is a compound microscope, like the one in Figure below. A compound microscope has at least two convex lenses: one or more objective ...
... A light microscope is an instrument that uses lenses to make enlarged images of objects that are too small for the unaided eye to see. A common type of light microscope is a compound microscope, like the one in Figure below. A compound microscope has at least two convex lenses: one or more objective ...
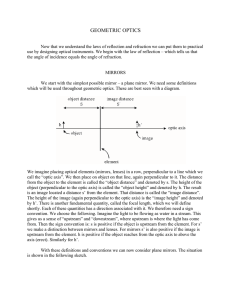
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... shortly. Each of these quantities has a direction associated with it. We therefore need a sign convention. We choose the following. Imagine the light to be flowing as water in a stream. This gives us a sense of “upstream” and “downstream”, where upstream is where the light has come from. Then the si ...
... shortly. Each of these quantities has a direction associated with it. We therefore need a sign convention. We choose the following. Imagine the light to be flowing as water in a stream. This gives us a sense of “upstream” and “downstream”, where upstream is where the light has come from. Then the si ...
focusing of light by corneal lenses in a reflecting superposition eye
... properties of the lenses. To make full use of this potentially finer-focused image with increased resolution would require the geometry of the ' aberration-free' superposition eye (outlined by Land, 1979) which would, in the case of Cherax, result in the points of focus of all the converging beams c ...
... properties of the lenses. To make full use of this potentially finer-focused image with increased resolution would require the geometry of the ' aberration-free' superposition eye (outlined by Land, 1979) which would, in the case of Cherax, result in the points of focus of all the converging beams c ...
Close-range videometry -
... The ordinary frame rate of CCD-cameras (CCIR, European standard) is 25 Hz, i.e., 25 images are captured per second. Without interlacing it is possible to use only one of the two videofields to gain a doubled rate. In measurements of fast moving objects this is a quite common method (e.g., Baltsavias ...
... The ordinary frame rate of CCD-cameras (CCIR, European standard) is 25 Hz, i.e., 25 images are captured per second. Without interlacing it is possible to use only one of the two videofields to gain a doubled rate. In measurements of fast moving objects this is a quite common method (e.g., Baltsavias ...
RAY OPTICS I
... We do this by considering three special rays emanating from a given point A on the object, rays that we can call the principal rays radiating from that point. 1. The first principal ray is the ray that goes through the center of the lens. Near the center of the lens, the front and back surfaces of t ...
... We do this by considering three special rays emanating from a given point A on the object, rays that we can call the principal rays radiating from that point. 1. The first principal ray is the ray that goes through the center of the lens. Near the center of the lens, the front and back surfaces of t ...
Chapter 23 Ray Optics
... A triangular glass prism with an apex angle of Ф=60o has an index of refraction n=1.5. What is the smallest angle of incidence for which a light ray can emerge from the other side? ...
... A triangular glass prism with an apex angle of Ф=60o has an index of refraction n=1.5. What is the smallest angle of incidence for which a light ray can emerge from the other side? ...
The optical microscopy with virtual image breaks
... gold films in contrast to superlenses where a weakly dissipating silver layer produces enhancement of evanescent wave7 (note, that such superlenses increase resolution and do not produce magnification of the image). In summary, we have demonstrated that optically transparent microspheres are high pe ...
... gold films in contrast to superlenses where a weakly dissipating silver layer produces enhancement of evanescent wave7 (note, that such superlenses increase resolution and do not produce magnification of the image). In summary, we have demonstrated that optically transparent microspheres are high pe ...
MIRRORS reflect light and obey the law
... When rays reflect from a mirror and ______________________________, they pass through the image. The image can be seen on a __________________________ or a piece of paper. This image is called a _________________ ___________________. ...
... When rays reflect from a mirror and ______________________________, they pass through the image. The image can be seen on a __________________________ or a piece of paper. This image is called a _________________ ___________________. ...
Reflection
... • Spherical aberration can be avoided by using a parabolic reflector; which are only a little more difficult/expensive to make. • Typically used in Telescopes, Camera lenses Lab equipment, shaving/make-up Mirrors, and this solar fire-lighter for campers! • Mirrors are preferred to lenses in many ...
... • Spherical aberration can be avoided by using a parabolic reflector; which are only a little more difficult/expensive to make. • Typically used in Telescopes, Camera lenses Lab equipment, shaving/make-up Mirrors, and this solar fire-lighter for campers! • Mirrors are preferred to lenses in many ...
A crash course in optics
... Ray of light Ray of light/light ray: ideally, an infinitely thin beam of light Propagation: light ray travels in a straight line at speed c. The speed of light in vacuum is 300,000 km/s = 3×108 m/s – almost the same in air. Reflection: light ray is bounced back from a surface Refraction: light ray ...
... Ray of light Ray of light/light ray: ideally, an infinitely thin beam of light Propagation: light ray travels in a straight line at speed c. The speed of light in vacuum is 300,000 km/s = 3×108 m/s – almost the same in air. Reflection: light ray is bounced back from a surface Refraction: light ray ...
Exercise 13 Geometrical and Technical Optics WS 2013/2014
... Achromatization with diffractive optical elements In the lecture a hybrid achromatic lens consisting of a refractive lens and a diffractive optical element has been discussed. a) Design a hybrid achromatic lens with a planoconvex lens made of BK7 and a plane diffractive optical element on the plane ...
... Achromatization with diffractive optical elements In the lecture a hybrid achromatic lens consisting of a refractive lens and a diffractive optical element has been discussed. a) Design a hybrid achromatic lens with a planoconvex lens made of BK7 and a plane diffractive optical element on the plane ...
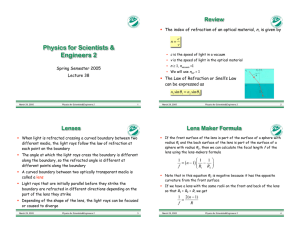
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
... ! The angle at which the light rays cross the boundary is different along the boundary, so the refracted angle is different at different points along the boundary ! A curved boundary between two optically transparent media is called a lens ...
... ! The angle at which the light rays cross the boundary is different along the boundary, so the refracted angle is different at different points along the boundary ! A curved boundary between two optically transparent media is called a lens ...
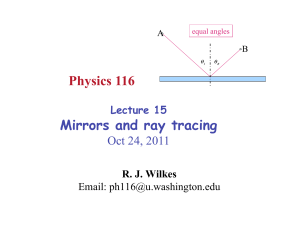
Physics 116 Mirrors and ray tracing
... •! Home experiment: Put shaving mirror on floor, facing up, and hold your hand above it while gazing into mirror: if f is right, you will see a real image of your hand apparently floating in space above the mirror! –! Looks spooky because you expect images in mirrors to be behind the glass, not in f ...
... •! Home experiment: Put shaving mirror on floor, facing up, and hold your hand above it while gazing into mirror: if f is right, you will see a real image of your hand apparently floating in space above the mirror! –! Looks spooky because you expect images in mirrors to be behind the glass, not in f ...
Optical and Electron Microscopy
... There exist two main families of electron microscope. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) is an instrument that achieves the highest resolution. (The terms TEM and HREM are to some extent interchangeable, although the TEM is not used exclusively for high-resolution observations). The TEM, as ...
... There exist two main families of electron microscope. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) is an instrument that achieves the highest resolution. (The terms TEM and HREM are to some extent interchangeable, although the TEM is not used exclusively for high-resolution observations). The TEM, as ...
Optical Diffraction and Image Formation
... produces the image of two stars in its focal plane, and a microscope that produces the image of two fluorescent molecules at distance b (that can be often treated an virtually infinitely positioned screen). In both cases the resolution is 1.22 !a/d (where a=f for b>>a). ...
... produces the image of two stars in its focal plane, and a microscope that produces the image of two fluorescent molecules at distance b (that can be often treated an virtually infinitely positioned screen). In both cases the resolution is 1.22 !a/d (where a=f for b>>a). ...
Imaging properties of a metamaterial superlens
... Metamaterials have opened an exciting gateway to create unprecedented physical properties and functionality unattainable from naturally existing materials. The ‘‘atoms’’ and ‘‘molecules’’ in metamaterials can be tailored in shape and size; the lattice constant and interatomic interaction can be arti ...
... Metamaterials have opened an exciting gateway to create unprecedented physical properties and functionality unattainable from naturally existing materials. The ‘‘atoms’’ and ‘‘molecules’’ in metamaterials can be tailored in shape and size; the lattice constant and interatomic interaction can be arti ...
Sign convention
... Real Image t’ t If you can’t see the light by placing a screen at the plane where it is in focus, then it is virtual. Equivalently, an image is virtual if you need another lens (e.g. an eye) to make the image real. Equivalently, real (virtual) objects are to the left (right) of the surface and real ...
... Real Image t’ t If you can’t see the light by placing a screen at the plane where it is in focus, then it is virtual. Equivalently, an image is virtual if you need another lens (e.g. an eye) to make the image real. Equivalently, real (virtual) objects are to the left (right) of the surface and real ...
Quiz 9
... The radius of the hemisphere is 8.00 cm and the index of refraction is 1.50. A mirror is in contact with the hemisphere at the vertex and it is perpendicular to the principal axis. Determine the point at which the beam is focused. (Assume paraxial rays-that is, assume that all rays are located close ...
... The radius of the hemisphere is 8.00 cm and the index of refraction is 1.50. A mirror is in contact with the hemisphere at the vertex and it is perpendicular to the principal axis. Determine the point at which the beam is focused. (Assume paraxial rays-that is, assume that all rays are located close ...
Presentation - University of Arizona
... Cardinal points and planes-continue Nodal planes have the characteristic of identity angular magnification. When the optical system is in air, nodal points/planes coincide with the principal points/planes. Principal points/planes can be described using Newtonian equations or Gaussian equations w ...
... Cardinal points and planes-continue Nodal planes have the characteristic of identity angular magnification. When the optical system is in air, nodal points/planes coincide with the principal points/planes. Principal points/planes can be described using Newtonian equations or Gaussian equations w ...
Subject: Precision Optics II Grade: 10
... order aberrations. Students will construct an illustrated essay. This essay will indicate the student’s level of understanding about how lenses are designed to control light. ...
... order aberrations. Students will construct an illustrated essay. This essay will indicate the student’s level of understanding about how lenses are designed to control light. ...
5_Locating Images in a Plane Mirror
... 5. A periscope is a device that is used to see around corners, over a wall, or above water. Simple periscopes contain two plane mirrors. a. Predict how these mirrors are arranged. b. Draw a diagram to illustrate how such a periscope would work. 6. Emergency vehicles make use of lateral inversion whe ...
... 5. A periscope is a device that is used to see around corners, over a wall, or above water. Simple periscopes contain two plane mirrors. a. Predict how these mirrors are arranged. b. Draw a diagram to illustrate how such a periscope would work. 6. Emergency vehicles make use of lateral inversion whe ...
Off-Axis Aperture Camera: 3D Shape Reconstruction
... Hartmann Mask or Scheiner Disk, has been invented to correct of quantify defocus by the Jesuit astronomer Christoph Scheiner (1572-1650). This technique is based on the principle that, unless the scene is brought into focus, the two apertures will generate an effect similar to double vision. ...
... Hartmann Mask or Scheiner Disk, has been invented to correct of quantify defocus by the Jesuit astronomer Christoph Scheiner (1572-1650). This technique is based on the principle that, unless the scene is brought into focus, the two apertures will generate an effect similar to double vision. ...
Chapter O5
... the light rays leaving the microscope and entering the eye must all be parallel. Figure O5.2 shows the lenses and rays that form the simple microscope. To understand the workings of this device, we will work backwards through the device. Thus, if all the light rays leaving the eyepiece are to be par ...
... the light rays leaving the microscope and entering the eye must all be parallel. Figure O5.2 shows the lenses and rays that form the simple microscope. To understand the workings of this device, we will work backwards through the device. Thus, if all the light rays leaving the eyepiece are to be par ...