Full text
... In Fig. 4, the TAG lens was driven at a frequency of 989 kHz (upper picture) and 531 kHz (lower picture) implying that toggling times between two adjacent patterns are theoretically as short as 0.5 and 0.9 µs, respectively. This converts to a switching frequency of approximately 1–2 MHz. Although th ...
... In Fig. 4, the TAG lens was driven at a frequency of 989 kHz (upper picture) and 531 kHz (lower picture) implying that toggling times between two adjacent patterns are theoretically as short as 0.5 and 0.9 µs, respectively. This converts to a switching frequency of approximately 1–2 MHz. Although th ...
Ophthalmic lens
... No one knows for certain when eyeglasses were invented, although documents from the 13th century prove the existence of eyeglasses at that time. Several sources quote a manuscript written in Rome in 1289 by a member of the Popozo family that says, "I am so debilitated by age that without the glasses ...
... No one knows for certain when eyeglasses were invented, although documents from the 13th century prove the existence of eyeglasses at that time. Several sources quote a manuscript written in Rome in 1289 by a member of the Popozo family that says, "I am so debilitated by age that without the glasses ...
A high numerical aperture (NA = 0.92)
... than 100 × 100 lattice sites in a typical optical lattice. Figure 1(b) shows a close-up, recorded with our objective lens, of two adjacent cesium atoms, which are trapped in an optical lattice with a lattice constant of 612 nm. Lens design. Due to their large collection angle, objective lenses with ...
... than 100 × 100 lattice sites in a typical optical lattice. Figure 1(b) shows a close-up, recorded with our objective lens, of two adjacent cesium atoms, which are trapped in an optical lattice with a lattice constant of 612 nm. Lens design. Due to their large collection angle, objective lenses with ...
Fluoroscopic Unit (Bushong, chapter 21)
... standard sizes: output phosphor: 2.5-5 cm input phosphor: 10-35 cm brightness gain of most II is 5000-20,000 and it decreases with tube age and use. Explain multifield image intensification. How does vigneting occur? b. Multifield Image Intensification: flexibility w/fluoro; standard w/digital ...
... standard sizes: output phosphor: 2.5-5 cm input phosphor: 10-35 cm brightness gain of most II is 5000-20,000 and it decreases with tube age and use. Explain multifield image intensification. How does vigneting occur? b. Multifield Image Intensification: flexibility w/fluoro; standard w/digital ...
Ch30
... For a diverging lens, an incident beam of light parallel to the principal axis is diverged so that the light appears to originate from a single point. The focal length of a lens, whether converging or diverging, is the distance between the center of the lens and its focal point. When the lens is thi ...
... For a diverging lens, an incident beam of light parallel to the principal axis is diverged so that the light appears to originate from a single point. The focal length of a lens, whether converging or diverging, is the distance between the center of the lens and its focal point. When the lens is thi ...
F045033337
... which can offer dramatic improvement in the processing speed of image information [3].The maximum resolution is achievable which is in digital image processing limited by the density of pixels. It is possible to implement optical image processing even in the case of relatively low beam intensity usi ...
... which can offer dramatic improvement in the processing speed of image information [3].The maximum resolution is achievable which is in digital image processing limited by the density of pixels. It is possible to implement optical image processing even in the case of relatively low beam intensity usi ...
Microscopy 1: Optical
... Iris diaphragm - Regulates the amount of light into the condenser. Condenser - Focuses the ray of light through the specimen. Stage - The fixed stage is a horizontal platform that holds the specimen. Nosepiece - The portion of the body that holds the objectives over the stage. Objective - ...
... Iris diaphragm - Regulates the amount of light into the condenser. Condenser - Focuses the ray of light through the specimen. Stage - The fixed stage is a horizontal platform that holds the specimen. Nosepiece - The portion of the body that holds the objectives over the stage. Objective - ...
Aberration-Free Ultrathin Flat Lenses and Axicons at Telecom
... right. Insets: close up of patterned antennas. The distance between two neighboring antennas is fixed at Δ = 750 nm in both directions for all the devices. ...
... right. Insets: close up of patterned antennas. The distance between two neighboring antennas is fixed at Δ = 750 nm in both directions for all the devices. ...
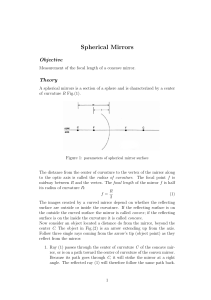
Spherical Mirrors
... The distance from the center of curvature to the vertex of the mirror along to the optic axis is called the radius of curvature. The focal point f is midway between R and the vertex. The focal length of the mirror f is half its radius of curvature R: ...
... The distance from the center of curvature to the vertex of the mirror along to the optic axis is called the radius of curvature. The focal point f is midway between R and the vertex. The focal length of the mirror f is half its radius of curvature R: ...
To determine the wavelength of a monochromatic source of light
... Apparatus The biprism consists of two prisms, each of very small refracting angle (of the order of 10 or even less than 10) placed base to base. In practice, the biprism is constructed from a single plate of glass by suitable grinding and polishing, the obtuse angle of the prism (which is only sligh ...
... Apparatus The biprism consists of two prisms, each of very small refracting angle (of the order of 10 or even less than 10) placed base to base. In practice, the biprism is constructed from a single plate of glass by suitable grinding and polishing, the obtuse angle of the prism (which is only sligh ...
Microscopes
... Kohler illumination Basic format for all transmitted light systems Ensures that: ...
... Kohler illumination Basic format for all transmitted light systems Ensures that: ...
Image Quality Criteria - University of Arizona
... shows this phenomenon. Because of the obscuration, the central core of the PSF gets smaller, but more of the energy in the PSF is diffracted outside of the central core causing a blurred or less sharp image. In other words there is a reduction of contrast in the mid spatial frequency range of the im ...
... shows this phenomenon. Because of the obscuration, the central core of the PSF gets smaller, but more of the energy in the PSF is diffracted outside of the central core causing a blurred or less sharp image. In other words there is a reduction of contrast in the mid spatial frequency range of the im ...
The Compound Microscope
... • The Optical System – Illuminator: artificial light, usually supplied by a light bulb, to illuminate the specimen. • Transmitted Illumination: when the light is directed up through the specimen from the base. • Vertical or Reflected Illumination: when the light comes from above and reflects off the ...
... • The Optical System – Illuminator: artificial light, usually supplied by a light bulb, to illuminate the specimen. • Transmitted Illumination: when the light is directed up through the specimen from the base. • Vertical or Reflected Illumination: when the light comes from above and reflects off the ...
Articles of Confederation
... The Court House in New Castle, Delaware, served as the Delaware State Capitol from 1776-1777. Typically in capitols with bicameral legislatures, the two houses would either meet in different wings of the capitol building, or one “house” would meet on the first floor of the capitol, and the other “ho ...
... The Court House in New Castle, Delaware, served as the Delaware State Capitol from 1776-1777. Typically in capitols with bicameral legislatures, the two houses would either meet in different wings of the capitol building, or one “house” would meet on the first floor of the capitol, and the other “ho ...
Ch7 Microscopes Notes Powerpoint
... directed up through the specimen from the base. • Vertical or Reflected Illumination: when the light comes from above and reflects off the specimen. ...
... directed up through the specimen from the base. • Vertical or Reflected Illumination: when the light comes from above and reflects off the specimen. ...
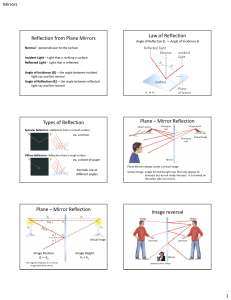
Reflection from Plane Mirrors Law of Reflection Types of Reflection
... 2. Draw a line parallel to the optical axis from where this line hits the mirror and draw the line out past the back of the mirror. 3. Draw a line from the tip of the object straight to the mirror. 4. Draw a line from the F, through the point where the last line hit the mirror, and out past the ...
... 2. Draw a line parallel to the optical axis from where this line hits the mirror and draw the line out past the back of the mirror. 3. Draw a line from the tip of the object straight to the mirror. 4. Draw a line from the F, through the point where the last line hit the mirror, and out past the ...
acknowledgements
... between two adjacent lines in the scale is 50 m. b) Reconstruction of DOE in a) given by He-Ne laser light (transmission mode). The micropositioning device can displace the substrate by linear increments as small as 10 m. However, due to the hole dimensions and the film distortions, a high qualit ...
... between two adjacent lines in the scale is 50 m. b) Reconstruction of DOE in a) given by He-Ne laser light (transmission mode). The micropositioning device can displace the substrate by linear increments as small as 10 m. However, due to the hole dimensions and the film distortions, a high qualit ...
Lens 101 review
... APO" elements (UD, SUD, CaF2, LD, SLD, ED etc.) improve contrast and sharpness by reducing chromatic aberration (color defects) that usually occur in tele lenses. These elements are able to focus different wave lengths of one light ray in one point (see picture below). These elements are quite expen ...
... APO" elements (UD, SUD, CaF2, LD, SLD, ED etc.) improve contrast and sharpness by reducing chromatic aberration (color defects) that usually occur in tele lenses. These elements are able to focus different wave lengths of one light ray in one point (see picture below). These elements are quite expen ...
Document
... The coherence length depends on the spectral bandwidth in an analog fashion to the coherence area dependence on solid angle (Eq. 21). This is not surprising as both types of correlations depend on their respective frequency bandwidth. ...
... The coherence length depends on the spectral bandwidth in an analog fashion to the coherence area dependence on solid angle (Eq. 21). This is not surprising as both types of correlations depend on their respective frequency bandwidth. ...
image
... • Each point in an object scatters the incident illumination into a spherical wave, according to the Huygens principle. • A few microns away from the object surface, the rays emanating from all object points become entangled, delocalizing object details. • To relocalize object details, a method must ...
... • Each point in an object scatters the incident illumination into a spherical wave, according to the Huygens principle. • A few microns away from the object surface, the rays emanating from all object points become entangled, delocalizing object details. • To relocalize object details, a method must ...
PPT
... – maybe a lens isn’t big enough – maybe your eye’s pupil isn’t big enough, or is improperly placed ...
... – maybe a lens isn’t big enough – maybe your eye’s pupil isn’t big enough, or is improperly placed ...
Light and Optics: We just learned that light is a wave (an
... But in many cases, you can safely ignore the wave nature of light! Light was studied for a long time (obviously), long before Maxwell, and very well understood. People thought about light as sort of like a stream of "particles" that travel in straight lines (called "light rays"). Unlike particles, w ...
... But in many cases, you can safely ignore the wave nature of light! Light was studied for a long time (obviously), long before Maxwell, and very well understood. People thought about light as sort of like a stream of "particles" that travel in straight lines (called "light rays"). Unlike particles, w ...
Optics Studio Manual - Department of Physics
... • Use a positive lens with a focal length of ca. 5 cm. Hold this close to your eye and then bring an object, e.g., a printed page up to the lens until you can view the magnified virtual image of this object through the lens. How far is the object from your eye/the lens? • Now remove the lens and hol ...
... • Use a positive lens with a focal length of ca. 5 cm. Hold this close to your eye and then bring an object, e.g., a printed page up to the lens until you can view the magnified virtual image of this object through the lens. How far is the object from your eye/the lens? • Now remove the lens and hol ...
Word - WM Keck Observatory
... greater than the PSF FWHM, implying values of the abscissa above of one or above. ...
... greater than the PSF FWHM, implying values of the abscissa above of one or above. ...
... In recent years important progress has been made in the generation of ultrashort laser pulses. The maximum intensity is fundamental in many applications, therefore the measurement of these pulses is also fundamental. It is important that these measurements be performed with optical elements that do ...