4.6 Lenses
... principal focus (F) is on the object side of the lens secondary focus (F’) is on the far side of the lens from the object 2F is sort of like the centre of curvature (C) in mirrors O is the optical centre of the mirror, where the vertical line through the lens & the PA intersect at 90 (like the vert ...
... principal focus (F) is on the object side of the lens secondary focus (F’) is on the far side of the lens from the object 2F is sort of like the centre of curvature (C) in mirrors O is the optical centre of the mirror, where the vertical line through the lens & the PA intersect at 90 (like the vert ...
Click To
... Market Applications: - Coherent optical imaging - Free space optical communications (FSO) - Applications where an incoherent, narrow bandwidth, optical source is needed Key Advantages: - Five concepts, each optimized for a specific application o Concept 1: effective operability of 100% o Concept 2: ...
... Market Applications: - Coherent optical imaging - Free space optical communications (FSO) - Applications where an incoherent, narrow bandwidth, optical source is needed Key Advantages: - Five concepts, each optimized for a specific application o Concept 1: effective operability of 100% o Concept 2: ...
Some Issues from Advanced Lithography General
... In air, NA obviously than has a maximum value of 1. The best lenses built so far have a NA of about 0.8; but 0.9 is already aimed for Keep in mind that what you gain in resolution by increasing NA, you loose in the depth of focus. Large NA lenses thus only make sense in the context of rather perfect ...
... In air, NA obviously than has a maximum value of 1. The best lenses built so far have a NA of about 0.8; but 0.9 is already aimed for Keep in mind that what you gain in resolution by increasing NA, you loose in the depth of focus. Large NA lenses thus only make sense in the context of rather perfect ...
exam solutions
... The object at d = 50 cm should be seen by the aided eye as if it comes from an object distance so = ∞. Therefore, a negative lens is required that produces a virtual image at d of an object at so = ∞. Without any calculation, the result is therefore f = – 500 mm. (d) Design a lens for eyesight corre ...
... The object at d = 50 cm should be seen by the aided eye as if it comes from an object distance so = ∞. Therefore, a negative lens is required that produces a virtual image at d of an object at so = ∞. Without any calculation, the result is therefore f = – 500 mm. (d) Design a lens for eyesight corre ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... The apparatus consists of an optical bench which serves as a convenient holder for objects, lenses and a ground glass screen for locating images. The object is an arrow painted on a piece of ground glass illuminated from behind by a collimated light bulb. Measure the focal point of the 5cm convergin ...
... The apparatus consists of an optical bench which serves as a convenient holder for objects, lenses and a ground glass screen for locating images. The object is an arrow painted on a piece of ground glass illuminated from behind by a collimated light bulb. Measure the focal point of the 5cm convergin ...
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz
... the focal length of the eyepiece is increased. the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece is decreased. ...
... the focal length of the eyepiece is increased. the distance between the objective lens and eyepiece is decreased. ...
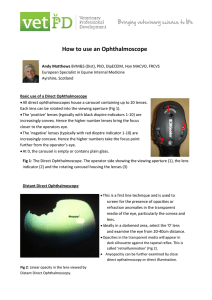
How to use an Ophthalmoscope
... For the operator with normal refraction and the instrument held 3-5cm from the horse’s eye, at 0 the optic disc can typically be brought into sharp focus (Fig 3). This will vary with the refraction of the operator’s eye and with the viewing distance selected. The fundic image is upright and magn ...
... For the operator with normal refraction and the instrument held 3-5cm from the horse’s eye, at 0 the optic disc can typically be brought into sharp focus (Fig 3). This will vary with the refraction of the operator’s eye and with the viewing distance selected. The fundic image is upright and magn ...
The Very Basics of Geometric Optics 5.1.2 Basic Geometric Optics
... The NA for a single lens is roughly the quotient of (possibly aperture defined) diameter / focal length; i.e. a crude measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus ...
... The NA for a single lens is roughly the quotient of (possibly aperture defined) diameter / focal length; i.e. a crude measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus ...
Optics 101 for non-optical engineers
... and focusing on a subject at the same distance, a longer focal length lens will have a shallower depth of field (even though the pictures will show something entirely different). ...
... and focusing on a subject at the same distance, a longer focal length lens will have a shallower depth of field (even though the pictures will show something entirely different). ...
Refraction and Lenses Learning Guide
... refraction for water, glass, most plastic depends on wavelength 15. Which is greater, the index of refraction for blue light or red light? greater for blue than red 16. What is chromatic aberration and how can it be reduced with lenses? since different colors are refracted at different angles, they ...
... refraction for water, glass, most plastic depends on wavelength 15. Which is greater, the index of refraction for blue light or red light? greater for blue than red 16. What is chromatic aberration and how can it be reduced with lenses? since different colors are refracted at different angles, they ...
PDF - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... The f-number is the same as for a camera. For a telescope it is obtained by dividing the focal length by the aperture. The lower the f-number the “faster” is the optical system. Important for those interested in imaging. Refractor The very simplest telescope is the refractor, as used by Galileo. It ...
... The f-number is the same as for a camera. For a telescope it is obtained by dividing the focal length by the aperture. The lower the f-number the “faster” is the optical system. Important for those interested in imaging. Refractor The very simplest telescope is the refractor, as used by Galileo. It ...
f = l - UCSD Department of Physics
... It focuses light emanating from different objects onto the retina to produce sharp images. Most of the focusing job is done by the cornea, which acts as a fixed lens with a focal distance of 23 mm. The lens is only doing some fine tuning to move the focusing from objects which are far-far away to ob ...
... It focuses light emanating from different objects onto the retina to produce sharp images. Most of the focusing job is done by the cornea, which acts as a fixed lens with a focal distance of 23 mm. The lens is only doing some fine tuning to move the focusing from objects which are far-far away to ob ...
Optics-Optical Instruments_ppt_RevW10
... objective mirror. The first real image is then viewed with a second short focal length (high diopter power) eyepiece lens • The first real image is brought to the side by means of a small flat mirror so that the eyepiece and observer can be out of the way of the incoming light ...
... objective mirror. The first real image is then viewed with a second short focal length (high diopter power) eyepiece lens • The first real image is brought to the side by means of a small flat mirror so that the eyepiece and observer can be out of the way of the incoming light ...
reflection, refraction, lense and optical instruments
... The apparatus consists of an optical bench which serves as a convenient holder for objects, lenses and a ground glass screen for locating images. The object is an arrow painted on a piece of ground glass illuminated from behind by a collimated light bulb. Measure the focal point of the 5cm convergin ...
... The apparatus consists of an optical bench which serves as a convenient holder for objects, lenses and a ground glass screen for locating images. The object is an arrow painted on a piece of ground glass illuminated from behind by a collimated light bulb. Measure the focal point of the 5cm convergin ...
CHAPTER 6 Human Eye Notes FIB
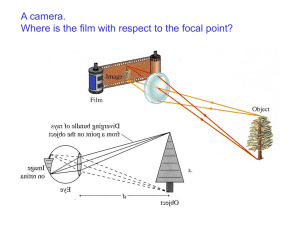
... Cameras: gathers and bends light with a ____________ lens. The lens projects an image onto a light detector to record a digital image. The image formed is ____________ and ____________. o ____________ – the opening where light enters the camera. o Wide‐angle lens – have ____________ focal length ...
... Cameras: gathers and bends light with a ____________ lens. The lens projects an image onto a light detector to record a digital image. The image formed is ____________ and ____________. o ____________ – the opening where light enters the camera. o Wide‐angle lens – have ____________ focal length ...
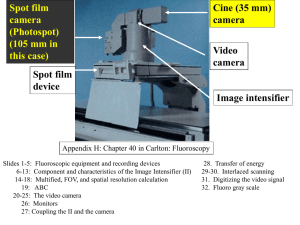
No Slide Title
... Spot films (Photospots) recorded on a spot film (photospot) camera 105 mm identifiable by sprockets ...
... Spot films (Photospots) recorded on a spot film (photospot) camera 105 mm identifiable by sprockets ...
Real-Time Image Processing Requirements
... Aerosols are particles floating in the air. Insects, pollen, and airborne seeds all scatter light very strongly. When they pass in front of the telescope’s aperture these appear as bright, fuzzy blobs which wander across the field of view (see Figure 1) in times scales of ~1 second (depending on win ...
... Aerosols are particles floating in the air. Insects, pollen, and airborne seeds all scatter light very strongly. When they pass in front of the telescope’s aperture these appear as bright, fuzzy blobs which wander across the field of view (see Figure 1) in times scales of ~1 second (depending on win ...
Lab 11 - Optical Ray Tracing
... In the previous exercise, the phenomenon of spherical aberration was observed as a slight divergence at the ideal focal point. This is due to the fact that rays striking the edges of the len are refracted more strongly that the paraxial ones. A quick remedy is to use an iris to block off the perimet ...
... In the previous exercise, the phenomenon of spherical aberration was observed as a slight divergence at the ideal focal point. This is due to the fact that rays striking the edges of the len are refracted more strongly that the paraxial ones. A quick remedy is to use an iris to block off the perimet ...
6.2 Refraction
... • for a material with normal dispersion, violet light will get bent toward the surface normal to a _________ extent than red light • when the high index material is shaped into prism, light gets refracted twice - with violet bending more than red both times • different wavelengths of light will then ...
... • for a material with normal dispersion, violet light will get bent toward the surface normal to a _________ extent than red light • when the high index material is shaped into prism, light gets refracted twice - with violet bending more than red both times • different wavelengths of light will then ...
Physics 425L Optics Laboratory Chromatic Aberration
... readings of the dial indicator (The dial indicator reads in inches.) and from the rail you will be able to precisely determine the focal length of the lens for blue light. Replace the blue interference filter with the yellow one, and repeat your measurements. To insure accurate measurements, you sho ...
... readings of the dial indicator (The dial indicator reads in inches.) and from the rail you will be able to precisely determine the focal length of the lens for blue light. Replace the blue interference filter with the yellow one, and repeat your measurements. To insure accurate measurements, you sho ...
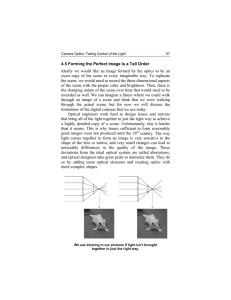
4.5 Forming the Perfect Image Is a Tall Order Ideally we would like
... an idea of this sensitivity, if the lens in your digital camera misses the location where the light should come together by a distance of about ten hair widths or more, you will likely see a noticeable blurring in the image. How can we measure how well our camera optics is pulling the light together ...
... an idea of this sensitivity, if the lens in your digital camera misses the location where the light should come together by a distance of about ten hair widths or more, you will likely see a noticeable blurring in the image. How can we measure how well our camera optics is pulling the light together ...
Optics
... Focal length can change the feeling of a shot. Depth of field can change a character’s size as they move within the frame and represent a character’s size relative to other characters within the frame. Wide Angle lenses provide greater depth of field, so action can be staged in depth. Teleph ...
... Focal length can change the feeling of a shot. Depth of field can change a character’s size as they move within the frame and represent a character’s size relative to other characters within the frame. Wide Angle lenses provide greater depth of field, so action can be staged in depth. Teleph ...