Chapter 25
... The cornea and lens do not have sufficient focusing power to bring nearby objects into focus on the retina Condition can be corrected with converging lenses ...
... The cornea and lens do not have sufficient focusing power to bring nearby objects into focus on the retina Condition can be corrected with converging lenses ...
mirrors and lenses - Appoquinimink High School
... where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
... where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... •The parallel rays converge at the second focal point F‘. •The first focal point is at the front. All rays originated at This point become parallel to the axis after the lens. ...
... •The parallel rays converge at the second focal point F‘. •The first focal point is at the front. All rays originated at This point become parallel to the axis after the lens. ...
Thin Lenses
... magnification equations are as follows: fis + for a converging lens fis - for a diverging lens do is + if the object in front of lens dois - if the object is in back of lens diis + if the image is in back of lensdiis - if the image is front of lens R1and R2are + if the center of curvature for each s ...
... magnification equations are as follows: fis + for a converging lens fis - for a diverging lens do is + if the object in front of lens dois - if the object is in back of lens diis + if the image is in back of lensdiis - if the image is front of lens R1and R2are + if the center of curvature for each s ...
Parts of the Microscope and Their Function
... Complete the chart below with the proper name of the microscope part: Name of part: ...
... Complete the chart below with the proper name of the microscope part: Name of part: ...
Lenses - Cloudfront.net
... through a larger angle with the use of a lens than with out the lens, and allows more detail to be seen A converging lens will only magnify when the object is between the focal point and the lens Virtual Image – an image formed through reflection or refraction that can be seen by an observer but can ...
... through a larger angle with the use of a lens than with out the lens, and allows more detail to be seen A converging lens will only magnify when the object is between the focal point and the lens Virtual Image – an image formed through reflection or refraction that can be seen by an observer but can ...
Ray Tracing
... Ray tracing is the graphical solution to problems with thin lenses aka geometric optics. Given a single, double, or any number of thin lenses, one can follow this simple procedure to achieve a satisfactory solution. Basically all of these problems are about locating the final image given an object a ...
... Ray tracing is the graphical solution to problems with thin lenses aka geometric optics. Given a single, double, or any number of thin lenses, one can follow this simple procedure to achieve a satisfactory solution. Basically all of these problems are about locating the final image given an object a ...
S.6 Phy revision Quiz 1
... 5. An object is placed in front of a concave lens and an image is formed. The image must be ____________, ____________ and ____________. 6. Dispersion occurs when white light passes through a prism. This is because A different colours of light are reflected at different angles. B different colours ...
... 5. An object is placed in front of a concave lens and an image is formed. The image must be ____________, ____________ and ____________. 6. Dispersion occurs when white light passes through a prism. This is because A different colours of light are reflected at different angles. B different colours ...
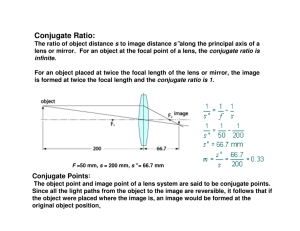
Conjugate Ratio:
... measure of lens aberrations and diffraction. All singlet lenses have significant amount of aberrations. ...
... measure of lens aberrations and diffraction. All singlet lenses have significant amount of aberrations. ...
Problem Sheet
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
Problem Sheet
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that a ...
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that a ...
Light Sources
... focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatial frequency components). ...
... focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatial frequency components). ...
Part 1
... fields oscillate in perpendicular directions and the wave travels in a direction perpendicular to each field’s oscillation axis. For a wave traveling along the x-axis in a non-conducting medium, the fields obey the wave equations of the form ...
... fields oscillate in perpendicular directions and the wave travels in a direction perpendicular to each field’s oscillation axis. For a wave traveling along the x-axis in a non-conducting medium, the fields obey the wave equations of the form ...
Entry Task
... Refraction and Rainbows • Rainbows are cause by refraction and reflection of light through spherical water drops which act as prisms. – Like a prism, water drops separate the wavelengths of sunlight to produce a spectrum. – Unlike a prism, only one color reaches your eye from each drop. • Red appea ...
... Refraction and Rainbows • Rainbows are cause by refraction and reflection of light through spherical water drops which act as prisms. – Like a prism, water drops separate the wavelengths of sunlight to produce a spectrum. – Unlike a prism, only one color reaches your eye from each drop. • Red appea ...
Light and Optics Unit
... understand and apply the terms center of curvature, focus, focal length, principal axis, and vertex as they apply to curved mirrors understand the difference between concave (converging) and convex (diverging mirrors) be able to locate the image of an object using ray diagrams and describe its ch ...
... understand and apply the terms center of curvature, focus, focal length, principal axis, and vertex as they apply to curved mirrors understand the difference between concave (converging) and convex (diverging mirrors) be able to locate the image of an object using ray diagrams and describe its ch ...
File
... light passes through. The larger the aperture, the greater the amount of light that can be collected by the camera. Almost all cameras use a convex lens to refract light rays onto a light detector ...
... light passes through. The larger the aperture, the greater the amount of light that can be collected by the camera. Almost all cameras use a convex lens to refract light rays onto a light detector ...
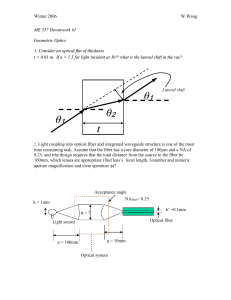
ME 557 Howmwork #1
... 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find lens’s focal length, f-number and numeric apeture magnification and clear aperature )? ...
... 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find lens’s focal length, f-number and numeric apeture magnification and clear aperature )? ...
Fraunhofer diffraction from gratings In this exercise we use a two
... While Bragg’s law is given by the expression 2d sin n , we get for a two-dimensional grating that d sin 1 sin 2 n . Here , 1 are 2 are the Bragg angle, the angle of incidence and the angle of exit, is the wavelength, d the distance between the lines in the grating (periodicity ...
... While Bragg’s law is given by the expression 2d sin n , we get for a two-dimensional grating that d sin 1 sin 2 n . Here , 1 are 2 are the Bragg angle, the angle of incidence and the angle of exit, is the wavelength, d the distance between the lines in the grating (periodicity ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
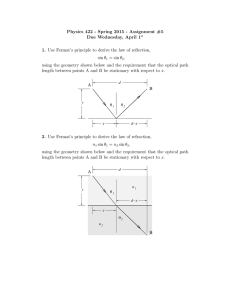
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #5
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...