Chapter 22: Magnetism
... Light reflected from a horizontal surface has a polarization in the horizontal direction. It follows that when you sit upright, with the transmission axis of your glasses in the vertical direction, they will block most of the reflected light. When you lie on your side, however, the transmission axis ...
... Light reflected from a horizontal surface has a polarization in the horizontal direction. It follows that when you sit upright, with the transmission axis of your glasses in the vertical direction, they will block most of the reflected light. When you lie on your side, however, the transmission axis ...
Nucleic Acids - Spring Branch ISD
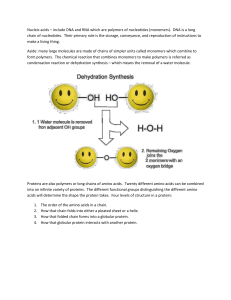
... Polymer- a chain of monomers joined chemically in a dehydration synthesis reaction (a Hydrogen of one monomer joins with an OH- of another monomer and creates water as a byproduct. The remaining “loose ends of the two monomer join together) Molecule- a chemically bonded combination of 2 or more atom ...
... Polymer- a chain of monomers joined chemically in a dehydration synthesis reaction (a Hydrogen of one monomer joins with an OH- of another monomer and creates water as a byproduct. The remaining “loose ends of the two monomer join together) Molecule- a chemically bonded combination of 2 or more atom ...
Sections 5.3-5.5 - BridgesToLiteracy.com
... communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances. all of these important things are what helps a membrane to function. nucleic acids they store and transmit hereditary information. there are two types of nucleic acids, there's deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). t ...
... communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances. all of these important things are what helps a membrane to function. nucleic acids they store and transmit hereditary information. there are two types of nucleic acids, there's deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). t ...
Lecture 25
... The light from one portion of the slit can interfere with light from another portion The resultant intensity on the screen depends on the direction θ ...
... The light from one portion of the slit can interfere with light from another portion The resultant intensity on the screen depends on the direction θ ...
Light is a
... Students will be able to calculate the wavelength, frequency or energy of light given two of these values. Students will be able to label a wave diagram identifying the wavelength, amplitude, trough and crest. ...
... Students will be able to calculate the wavelength, frequency or energy of light given two of these values. Students will be able to label a wave diagram identifying the wavelength, amplitude, trough and crest. ...
Protein Chemistry
... Tertiary structure - the overall three-dimensional shape that a protein assumes. This includes all of the secondary structures and the side groups as well as any prosthetic groups. This level is also where one looks for native vs. denatured state. The hydrophobic effect, salt bridges And other molec ...
... Tertiary structure - the overall three-dimensional shape that a protein assumes. This includes all of the secondary structures and the side groups as well as any prosthetic groups. This level is also where one looks for native vs. denatured state. The hydrophobic effect, salt bridges And other molec ...
Middle East Jeopardy
... The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the specific molecular formula for a polymer made by linking 11 glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? ...
... The molecular formula for glucose is C6H12O6. What would be the specific molecular formula for a polymer made by linking 11 glucose molecules together by dehydration reactions? ...
Supplementary data 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9 include N, Total (ProtScore)
... The definitions of the table fields are described as follows: N is the rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Total (ProtScore) a measure of the total amount of evidence for a detected protein. The Total ProtScore is calculated using all of the ...
... The definitions of the table fields are described as follows: N is the rank of the specified protein relative to all other proteins in the list of detected proteins. Total (ProtScore) a measure of the total amount of evidence for a detected protein. The Total ProtScore is calculated using all of the ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Physics
... insight into the rapidly changing method of conducting scientific research. What an awesome opportunity to learn cutting edge research and then have the ability to share it with our students.” – Tracy Blondis and Jeff Toller ...
... insight into the rapidly changing method of conducting scientific research. What an awesome opportunity to learn cutting edge research and then have the ability to share it with our students.” – Tracy Blondis and Jeff Toller ...
Center for Biological Physics* Math and Science Teachers Fellows
... insight into the rapidly changing method of conducting scientific research. What an awesome opportunity to learn cutting edge research and then have the ability to share it with our students.” – Tracy Blondis and Jeff Toller ...
... insight into the rapidly changing method of conducting scientific research. What an awesome opportunity to learn cutting edge research and then have the ability to share it with our students.” – Tracy Blondis and Jeff Toller ...
Proteins & Nucleic Acids - St. Mary Catholic Secondary School
... Ladder shape – Rails - A series of alternating phosphates and sugars linked by covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds. Rungs of the ladder are made of the nitrogenous bases and their hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases involved with DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. The adenine ...
... Ladder shape – Rails - A series of alternating phosphates and sugars linked by covalent bonds known as phosphodiester bonds. Rungs of the ladder are made of the nitrogenous bases and their hydrogen bonds. The nitrogenous bases involved with DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine. The adenine ...
Biomolecules
... BIOMOLECULES • Large complex molecules in cells • Formed from repeating subunits • Most biomolecules are formed from a carbon backbone • Six most common elements in living organisms is • CHONPS ...
... BIOMOLECULES • Large complex molecules in cells • Formed from repeating subunits • Most biomolecules are formed from a carbon backbone • Six most common elements in living organisms is • CHONPS ...
Introduction to Spectroscopy mod4 - Rose
... Absorbance spectroscopy is frequently used to measure concentration. According to the Beer-Lambert law measurements of absorbance for molecules of known ε allow calculation of concentration. Alternatively, if the concentration of the absorbing species is known, the ε can be determined. Absorbance is ...
... Absorbance spectroscopy is frequently used to measure concentration. According to the Beer-Lambert law measurements of absorbance for molecules of known ε allow calculation of concentration. Alternatively, if the concentration of the absorbing species is known, the ε can be determined. Absorbance is ...
Proteins - Northwest ISD Moodle
... - the interactions of the R groups on each amino acid cause the molecule to bend and fold – different arrangements create different shapes - as a result- the order of amino acids determines the shape of the protein - shape determines function - changing a single amino acid can change a protein’s sha ...
... - the interactions of the R groups on each amino acid cause the molecule to bend and fold – different arrangements create different shapes - as a result- the order of amino acids determines the shape of the protein - shape determines function - changing a single amino acid can change a protein’s sha ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.