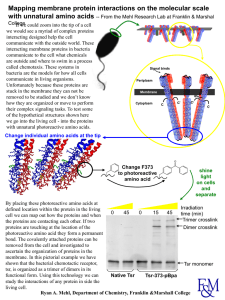
Molecules of Life – Part 2
... A. Proteins make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight (referred to as biomass). B. This is another important example of the theme: Structure = Function. (These are very large 3-D Molecules.) C. The monomer “building blocks” are Amino Acids (There are 20 different Amino Acids that can be in ...
... A. Proteins make up greater than 50% of an organisms dry weight (referred to as biomass). B. This is another important example of the theme: Structure = Function. (These are very large 3-D Molecules.) C. The monomer “building blocks” are Amino Acids (There are 20 different Amino Acids that can be in ...
biochemistry/docs/Protein structure 1
... Primary sequence- The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide, listed from N-terminus to C-terminus. Secondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins stabilized exclusively by hydrogen bonds between peptide bond elements. Supersecondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins c ...
... Primary sequence- The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide, listed from N-terminus to C-terminus. Secondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins stabilized exclusively by hydrogen bonds between peptide bond elements. Supersecondary structure- Recurring structural feature of proteins c ...
Midterm Study Game 2014
... • Which term include all activities to keep an organism alive? • metabolism ...
... • Which term include all activities to keep an organism alive? • metabolism ...
An Active Metamaterial Platform for Chiral Responsive Optoelectronics
... Chiral metamaterials are an important metamaterial species that give rise to enormously strong chiroptical responses. The past few years have witnessed an explosive development of chiral optical metamaterials that exhibit circular dichroism and optical rotation orders of magnitude larger than natura ...
... Chiral metamaterials are an important metamaterial species that give rise to enormously strong chiroptical responses. The past few years have witnessed an explosive development of chiral optical metamaterials that exhibit circular dichroism and optical rotation orders of magnitude larger than natura ...
Proteins
... It is a process in which proteins can lose their structures and function, without breaking the peptide bonds by denaturing agents such as: 1.Heat, U.V radiation. 2.Heavy metal as mercury. 3.Soaps. 4.Organic acids as acetic acid. 5.Strong acids and bases as sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide. Note: D ...
... It is a process in which proteins can lose their structures and function, without breaking the peptide bonds by denaturing agents such as: 1.Heat, U.V radiation. 2.Heavy metal as mercury. 3.Soaps. 4.Organic acids as acetic acid. 5.Strong acids and bases as sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide. Note: D ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... Q1. a) The primary structure of a protein is the level of protein structure which refers to the specific sequence of amino acids. When two amino acids are in such a position that the carboxyl groups of each amino acid are adjacent to each other, they can be combined by undergoing a dehydration react ...
... Q1. a) The primary structure of a protein is the level of protein structure which refers to the specific sequence of amino acids. When two amino acids are in such a position that the carboxyl groups of each amino acid are adjacent to each other, they can be combined by undergoing a dehydration react ...
2016 N1 Week 4
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
The Milky Way
... about what you can see with your eyes alone or aided by telescopes. In this chapter, you begin using modern astrophysics to search out secrets that lie beyond what you can see. ...
... about what you can see with your eyes alone or aided by telescopes. In this chapter, you begin using modern astrophysics to search out secrets that lie beyond what you can see. ...
Singapour_presentation_iGEM2
... Registry, we start to build our biological systems over the summer. The perspective of the Jamboree in November at MIT and the project design is exceptionally motivating, in addition to the fact that this is a good learning experience. ...
... Registry, we start to build our biological systems over the summer. The perspective of the Jamboree in November at MIT and the project design is exceptionally motivating, in addition to the fact that this is a good learning experience. ...
Organic molecules
... • They are the foundation for the structure and function of every living cell in every organism. • They are the building materials and the storehouse for energy. ...
... • They are the foundation for the structure and function of every living cell in every organism. • They are the building materials and the storehouse for energy. ...
Section 16.3 - CPO Science
... the structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... the structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
Introduction to Molecular forces and Macromolecules
... . Ready made jell-o (on ice), fruits pieces, .add a piece of raw or heated fruit (cooled on ice) onto jello surface. .examine during next two hours (effect of gelatinase from plant origin on the jell-O . ...
... . Ready made jell-o (on ice), fruits pieces, .add a piece of raw or heated fruit (cooled on ice) onto jello surface. .examine during next two hours (effect of gelatinase from plant origin on the jell-O . ...
The Milky Way - Computer Science Technology
... why the spectrum of an object can be so informative. In the chapters that follow, you will learn about stars, galaxies, and planets, often using the rich information derived from their spectra to uncover the secrets of their internal structures and histories. ...
... why the spectrum of an object can be so informative. In the chapters that follow, you will learn about stars, galaxies, and planets, often using the rich information derived from their spectra to uncover the secrets of their internal structures and histories. ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.