EM Waves history & Polarization APIB
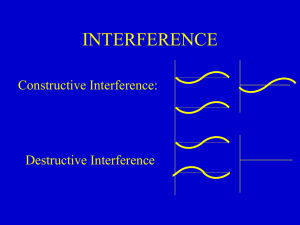
... Every point of a wave front may be considered the source of secondary wavelets that spread out in all directions with a speed equal to the speed of propagation of the waves. ...
... Every point of a wave front may be considered the source of secondary wavelets that spread out in all directions with a speed equal to the speed of propagation of the waves. ...
Chapter 3 Presentation: Macromolecules
... • Once amino acids are added to the polypeptide, they begin to interact with the other amino acids on the growing polypeptide. • The sequence then determines the 3D conformation the protein will take. • The conformation of the protein determines ...
... • Once amino acids are added to the polypeptide, they begin to interact with the other amino acids on the growing polypeptide. • The sequence then determines the 3D conformation the protein will take. • The conformation of the protein determines ...
LIGHT - University of Virginia
... Start with two uncharged spheres. Bring a positive sphere nearby. Then connect the two spheres by a wire. Now remove the wire, then remove the positive sphere. Question: Do the two original spheres have any charge on them? If so, what sign? ...
... Start with two uncharged spheres. Bring a positive sphere nearby. Then connect the two spheres by a wire. Now remove the wire, then remove the positive sphere. Question: Do the two original spheres have any charge on them? If so, what sign? ...
Lesson One: The Four Basic Food Molecules
... shapes. Two important shapes are the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet. Proteins are often denatured by heat or acid. Proteins can coagulate. Enzymes are a specific type of proteins. Fats and Oils The major constituent of natural fats and oils is the triglyceride, a combination of three fatty a ...
... shapes. Two important shapes are the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet. Proteins are often denatured by heat or acid. Proteins can coagulate. Enzymes are a specific type of proteins. Fats and Oils The major constituent of natural fats and oils is the triglyceride, a combination of three fatty a ...
Section 13.3 - CPO Science
... structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
... structure of many different molecules. Describe the importance of carbon to living organisms. Compare and contrast the structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. ...
Teacher`s Copy Biochem test prep
... 19. In what class of organic molecules would hemoglobin, insulin, albumin, and maltase, all of which are composed of chains of amino acids, be placed into? 1) proteins 3) lipids ...
... 19. In what class of organic molecules would hemoglobin, insulin, albumin, and maltase, all of which are composed of chains of amino acids, be placed into? 1) proteins 3) lipids ...
Protein structure
... • Group of residues with high contact density, number of contacts within domains is higher than the number of contacts between domains. • A stable unit of protein structure that can fold autonomously • A rigid body linked to other domains by flexible linkers. • A portion of the protein that can be a ...
... • Group of residues with high contact density, number of contacts within domains is higher than the number of contacts between domains. • A stable unit of protein structure that can fold autonomously • A rigid body linked to other domains by flexible linkers. • A portion of the protein that can be a ...
Sample Final File
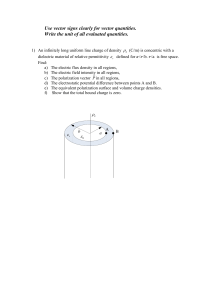
... 1) An infinitely long uniform line charge of density L (C/m) is concentric with a dielectric material of relative permittivity r defined for a
... 1) An infinitely long uniform line charge of density L (C/m) is concentric with a dielectric material of relative permittivity r defined for a
AS 2.1.1 Protein Structure
... • Ionic bonds: the R groups are sometimes charged (+ve or –ve) so they attract each other • Hydrogen bonds: +ve hydrogen atoms and –ve oxygen ...
... • Ionic bonds: the R groups are sometimes charged (+ve or –ve) so they attract each other • Hydrogen bonds: +ve hydrogen atoms and –ve oxygen ...
37151
... Proteomics is usually carried out to study the complement of protein expressed by a cell at any one time or at a particular stage ...
... Proteomics is usually carried out to study the complement of protein expressed by a cell at any one time or at a particular stage ...
Lecture_11
... • Overall goal - directly solve enough structures directly to be able to computationally model all future proteins. ...
... • Overall goal - directly solve enough structures directly to be able to computationally model all future proteins. ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.