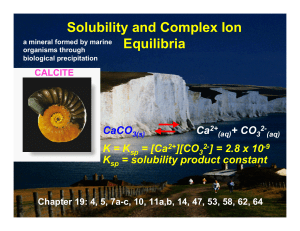
Solubility Solubility is defined as the amount of solute that will
... compare experiment 1 to experiment 2 we held the concentration of NO constant and doubled the concentration of H2, and we saw a doubling in the rate. This would indicate that the reaction is 1st order with respect to H2. . rate = k [H2] [NO]2 We can use the data from experiment 1 to determine the ra ...
... compare experiment 1 to experiment 2 we held the concentration of NO constant and doubled the concentration of H2, and we saw a doubling in the rate. This would indicate that the reaction is 1st order with respect to H2. . rate = k [H2] [NO]2 We can use the data from experiment 1 to determine the ra ...
equilibrium - eVirtualGuru
... equilibrium can be demonstrated in the synthesis of ammonia by Haber’s process. In a series of experiments, Haber started with known amounts of dinitrogen and dihydrogen maintained at high temperature and pressure and at regular intervals determined the amount of ammonia present. He was successful i ...
... equilibrium can be demonstrated in the synthesis of ammonia by Haber’s process. In a series of experiments, Haber started with known amounts of dinitrogen and dihydrogen maintained at high temperature and pressure and at regular intervals determined the amount of ammonia present. He was successful i ...
Packet 4
... a = molar absorptivity (a constant that depends on the nature of the material under test) b = path length (the length of the sample that the light passes through) c = concentration When absorbance measurements are made at a fixed wavelength, in a cell of constant path length, a and b are constant an ...
... a = molar absorptivity (a constant that depends on the nature of the material under test) b = path length (the length of the sample that the light passes through) c = concentration When absorbance measurements are made at a fixed wavelength, in a cell of constant path length, a and b are constant an ...
Solubility
... [CrO42-] = 0.01M, [Ag+] = 1.0x10-5 (calculated previously) Ksp = [Ag+][Br-] = (1.0x10-5M)[Br-] = 5.0x10-13 [Br-] = 5.0x10-8M So if we stop the addition of AgNO3 just before Ag2CrO4 starts to precipitate... [Br-] drops from 0.01M to 5.0x10-8M. What % of Br- is left? 5.0x10-8M / 1.0x10-2M *100% ...
... [CrO42-] = 0.01M, [Ag+] = 1.0x10-5 (calculated previously) Ksp = [Ag+][Br-] = (1.0x10-5M)[Br-] = 5.0x10-13 [Br-] = 5.0x10-8M So if we stop the addition of AgNO3 just before Ag2CrO4 starts to precipitate... [Br-] drops from 0.01M to 5.0x10-8M. What % of Br- is left? 5.0x10-8M / 1.0x10-2M *100% ...
contents 2002 MAY
... Chlorination leads to an increased pz orbital occupation of inner carbon atoms. Using finite perturbation technique , proton coupling constants of butatriene are also calculated. ...
... Chlorination leads to an increased pz orbital occupation of inner carbon atoms. Using finite perturbation technique , proton coupling constants of butatriene are also calculated. ...
Smith Reaction- HW PSI Chemistry
... 13) Which of the following is NOT a true statement concerning what happens in all chemical reactions? A) The ways in which atoms are joined together are changed. B) New atoms are formed as products. C) The starting materials are named reactants. D) The bonds of the reactants are broken and new bonds ...
... 13) Which of the following is NOT a true statement concerning what happens in all chemical reactions? A) The ways in which atoms are joined together are changed. B) New atoms are formed as products. C) The starting materials are named reactants. D) The bonds of the reactants are broken and new bonds ...
Insertion of SO2 into the Metal−Carbon Bonds of Rhodium and
... (Cp*Rh(PMe3)(Cl)2) was a stable species, unable to bind the free methane sulfinic acid. In the second case (HOTf, HBF4), the inability to form a strong bond between the metal and the labile counterion prevented the release of free sulfinic acid. A third case can be imagined corresponding to an inter ...
... (Cp*Rh(PMe3)(Cl)2) was a stable species, unable to bind the free methane sulfinic acid. In the second case (HOTf, HBF4), the inability to form a strong bond between the metal and the labile counterion prevented the release of free sulfinic acid. A third case can be imagined corresponding to an inter ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... 3.2.1 Describe and explain the periodic trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed i ...
... 3.2.1 Describe and explain the periodic trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, ionization energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed i ...
What is the pH of a 0.100 M
... Kw = [H3O+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14 Le Chatelier: What happens if more H+ is added to water? What happens if more OH- is added to water? The equilibrium of water, H3O+ and OH- means if we know either the concentration of H3O+ or the concentration of OH- in an aqueous solution, then we know the concentrat ...
... Kw = [H3O+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14 Le Chatelier: What happens if more H+ is added to water? What happens if more OH- is added to water? The equilibrium of water, H3O+ and OH- means if we know either the concentration of H3O+ or the concentration of OH- in an aqueous solution, then we know the concentrat ...
Class Notes
... out of solution. That is why it remains as a compound in the complete ionic equation. Only ionic compounds in aqueous solution are dissociated into their component ions in ionic equations. Some ions remain the same before and after the reaction. These are known as “spectator ions” because they do no ...
... out of solution. That is why it remains as a compound in the complete ionic equation. Only ionic compounds in aqueous solution are dissociated into their component ions in ionic equations. Some ions remain the same before and after the reaction. These are known as “spectator ions” because they do no ...
Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel by Benzopyranone Derivative in
... of interaction are responsible for adsorption of inhibitor to metal surface. One is physisorption, which requires the presence of both electrically charged metal surface and charged species on the bulk of the solution. The other is chemisorption, which involves direct adsorption on the basis of dono ...
... of interaction are responsible for adsorption of inhibitor to metal surface. One is physisorption, which requires the presence of both electrically charged metal surface and charged species on the bulk of the solution. The other is chemisorption, which involves direct adsorption on the basis of dono ...
Reactions in Aqueous Solution (Brown 13th-Fossum
... • The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge. • Nonmetals tend to have negative oxidation numbers, although some are positive in certain compounds or ions. Oxygen has an oxidation number of −2, except in the peroxide ion in which it has an oxidation number of −1. Hydrogen ...
... • The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge. • Nonmetals tend to have negative oxidation numbers, although some are positive in certain compounds or ions. Oxygen has an oxidation number of −2, except in the peroxide ion in which it has an oxidation number of −1. Hydrogen ...
Unit 1 review
... reactant, and you can calculate for either product, but the product must be the same for both in order for the amounts to be compared. ...
... reactant, and you can calculate for either product, but the product must be the same for both in order for the amounts to be compared. ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... Balancing Chemical Equations • Write formula for each reactant and product on the correct side of the “reaction arrow” • Count atoms of each element on both sides of arrow • Start with the compound which has the most complex formula • Add coefficients to chemical formulas to balance numbers of each ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations • Write formula for each reactant and product on the correct side of the “reaction arrow” • Count atoms of each element on both sides of arrow • Start with the compound which has the most complex formula • Add coefficients to chemical formulas to balance numbers of each ...
Pre-AP Chemistry - Simple Rules for Electron Exchange Simple
... Rule #3: In a compound or polyatomic ion, oxygen is always -2. There are some exceptions, but we deal with them in AP Chemistry. Rule #4: When paired with a negative ion (mono- or polyatomic) hydrogen is always +1. Examples: H2S, any acid (HCl, HNO3, etc.) Rule #5: In ionic compounds made of non-met ...
... Rule #3: In a compound or polyatomic ion, oxygen is always -2. There are some exceptions, but we deal with them in AP Chemistry. Rule #4: When paired with a negative ion (mono- or polyatomic) hydrogen is always +1. Examples: H2S, any acid (HCl, HNO3, etc.) Rule #5: In ionic compounds made of non-met ...
The masses of reactants and products are equal.
... He concluded that a gas in the air, which he called oxygen, had combined with the mercury to form the new product. Lavoisier conducted many experiments of this type and found in all cases that the mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products. This conclusion, called the law of conserva ...
... He concluded that a gas in the air, which he called oxygen, had combined with the mercury to form the new product. Lavoisier conducted many experiments of this type and found in all cases that the mass of the reactants is equal to the mass of the products. This conclusion, called the law of conserva ...
Polarization quantum beat spectroscopy of HCF„A˜1A …. I. 19F and
... should be linear, with zero intercept and slope equal to ⫺ā. We derived the g aa ( ⬘ ) via global fits of the Zeeman data for each vibrational level, with the hyperfine constants fixed to the values determined from analysis of the zero-field data. In practice, letting the hyperfine parameters flo ...
... should be linear, with zero intercept and slope equal to ⫺ā. We derived the g aa ( ⬘ ) via global fits of the Zeeman data for each vibrational level, with the hyperfine constants fixed to the values determined from analysis of the zero-field data. In practice, letting the hyperfine parameters flo ...