Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
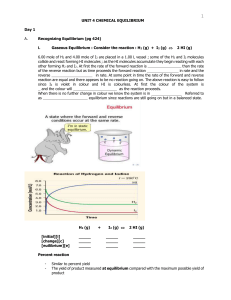
... N2 ( g ) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 ( g ) increase conc. of N2 -----> stress too much to relieve stress equilibrium shifts to the ; thus conc. of H2 will and conc. of NH3 will ____________ Consider the equ. conc to be N2 = 1.0 moL/L; H2 = 3.0 moL/L and NH3 = 2.0 moL/L If an additional 0.5 moL/L of N2 is add ...
... N2 ( g ) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 ( g ) increase conc. of N2 -----> stress too much to relieve stress equilibrium shifts to the ; thus conc. of H2 will and conc. of NH3 will ____________ Consider the equ. conc to be N2 = 1.0 moL/L; H2 = 3.0 moL/L and NH3 = 2.0 moL/L If an additional 0.5 moL/L of N2 is add ...
Chemistry Exam 2 Specifications and Sample Exam
... • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No credit will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the ...
... • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given full marks. • show all working in your answers to numerical questions. No credit will be given for an incorrect answer unless it is accompanied by details of the ...
Review Final 111 Lect
... d. none of these (Hint: You need to write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of CaF2 given above) 37. When barium chloride is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4(s), which of the following will result?(Hint: Write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of BaSO4 (s).) a. The concentr ...
... d. none of these (Hint: You need to write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of CaF2 given above) 37. When barium chloride is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4(s), which of the following will result?(Hint: Write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of BaSO4 (s).) a. The concentr ...
Part II - KFUPM Faculty List
... Most of the reactions take place in states other than their standard states. Thus, in order to determine spontaneity of a reaction, we need to know how to calculate ΔG when the reaction is not occurring at standard states. ΔG = ΔG + RT lnQ where: o ΔG is the non‐standard free energy. o ΔG° is ...
... Most of the reactions take place in states other than their standard states. Thus, in order to determine spontaneity of a reaction, we need to know how to calculate ΔG when the reaction is not occurring at standard states. ΔG = ΔG + RT lnQ where: o ΔG is the non‐standard free energy. o ΔG° is ...
Chemical Reactions
... magnetism and is ferrimagnetic, but is sometimes incorrectly described as ferromagnetic. Its most extensive use is as a black pigment which is synthesised rather than being extracted from the naturally occurring mineral as the particle size and shape can be varied by the method of production. ...
... magnetism and is ferrimagnetic, but is sometimes incorrectly described as ferromagnetic. Its most extensive use is as a black pigment which is synthesised rather than being extracted from the naturally occurring mineral as the particle size and shape can be varied by the method of production. ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... having a special property: they are in equilibrium. It is not straightforward to determine if a piece of matter is in equilibrium. Putting this piece of matter into a “container,” it would come to rest sooner or later and its properties would not depend on time and typically not on the spatial posit ...
... having a special property: they are in equilibrium. It is not straightforward to determine if a piece of matter is in equilibrium. Putting this piece of matter into a “container,” it would come to rest sooner or later and its properties would not depend on time and typically not on the spatial posit ...
Ionization methods - 2-CI - Florida International University
... depends on the relative affinities of the conjugate base of the reactant ion (CH 4, NH3 and so on) and the compound M. • Decrease in PA (proton affinity) of the conjugate base (or increase in acidity of the reactant gas ion) causes increase in fragmentation because more energy is transferred to them ...
... depends on the relative affinities of the conjugate base of the reactant ion (CH 4, NH3 and so on) and the compound M. • Decrease in PA (proton affinity) of the conjugate base (or increase in acidity of the reactant gas ion) causes increase in fragmentation because more energy is transferred to them ...
S - Valdosta State University
... • At any point along the reaction, the reactants are not under standard conditions. • To calculate DG at these points: ...
... • At any point along the reaction, the reactants are not under standard conditions. • To calculate DG at these points: ...
Diffusion current - Prof Dr Hisham E Abdellatef
... b- Internal standards or Pilot ion method: This method is based on the fact that the relative diffusion current constants I are independent of the particular capillary used, provided the nature and concentration Of supporting electrolyte and the temperature are kept constant. Hence , upon determinin ...
... b- Internal standards or Pilot ion method: This method is based on the fact that the relative diffusion current constants I are independent of the particular capillary used, provided the nature and concentration Of supporting electrolyte and the temperature are kept constant. Hence , upon determinin ...
CHE 1402 Lab Manual
... The first part of this experiment will be a demonstration of Boyle's law. You will vary the pressure of a fixed amount of trapped air at constant temperature, using a special gas buret. The second portion of this experiment concerns the determination of the molar mass of a volatile liquid using equa ...
... The first part of this experiment will be a demonstration of Boyle's law. You will vary the pressure of a fixed amount of trapped air at constant temperature, using a special gas buret. The second portion of this experiment concerns the determination of the molar mass of a volatile liquid using equa ...
Effect of the Electrical Double Layer on
... tenths of a nanometer of the electrode surface. When a faradaic reaction, e.g., A+ + eA, occurs at an electrode a thin depletion layer is established in the solution adjacent to the electrode as a consequence of the finite rate at which the reactant can be transported from the bulk to the surcm, the ...
... tenths of a nanometer of the electrode surface. When a faradaic reaction, e.g., A+ + eA, occurs at an electrode a thin depletion layer is established in the solution adjacent to the electrode as a consequence of the finite rate at which the reactant can be transported from the bulk to the surcm, the ...
2013 us national chemistry olympiad
... f. Carbon-11 undergoes positron emission during a PET scan. 6. [13] Consider the highly reactive molecule SF3Cl. a. Draw all of the possible structures of SF3Cl with S as the central atom. b. Use VSEPR theory to predict the most stable structure in a. and justify your answer. c. Recent calculations ...
... f. Carbon-11 undergoes positron emission during a PET scan. 6. [13] Consider the highly reactive molecule SF3Cl. a. Draw all of the possible structures of SF3Cl with S as the central atom. b. Use VSEPR theory to predict the most stable structure in a. and justify your answer. c. Recent calculations ...
Chemical Thermodynamics Survival Kit
... We must always use information about the actual process to find the entropy change of the thermal surroundings. If sufficient information is not provided about the surroundings, then this quantity cannot be calculated. This is a weakness of the entropy criterion for spontaneity. The entropy change o ...
... We must always use information about the actual process to find the entropy change of the thermal surroundings. If sufficient information is not provided about the surroundings, then this quantity cannot be calculated. This is a weakness of the entropy criterion for spontaneity. The entropy change o ...
+ NO 2
... CHEMICAL REACTION (BONDS MUST BREAK) • SURFACE AREA/ CONTACT AREA (OPPORTUNITY FOR COLLISIONS) • CONCENTRATION ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • TEMPERATURE ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • CATALYST ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) • NATURE OF REACTANTS ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) ...
... CHEMICAL REACTION (BONDS MUST BREAK) • SURFACE AREA/ CONTACT AREA (OPPORTUNITY FOR COLLISIONS) • CONCENTRATION ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • TEMPERATURE ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • CATALYST ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) • NATURE OF REACTANTS ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) ...
More Than You Ever Cared to Know About Solution Thermodynamics
... G = nA µA + nB µB regenerates Equation 4.2 (Euler’s theorem for G), i.e., using equations 7.1 and 7.2 we obtain ...
... G = nA µA + nB µB regenerates Equation 4.2 (Euler’s theorem for G), i.e., using equations 7.1 and 7.2 we obtain ...
Paper
... ΔμE3= RT(2 ln(X3Sr/X3Srp/(1-x1-x2))+ln(X3O/X3Op/(1-x1-x2))+½ln(x1+x2+1)), (9) where vector {Xikp} (k = Si, B, O, Sr) is the solution of the system (5) for pure i-th component, i.e. for xi = 1. Using this computational scheme the results shown in Fig.1 and Fig.2 were obtained. For our test of modifi ...
... ΔμE3= RT(2 ln(X3Sr/X3Srp/(1-x1-x2))+ln(X3O/X3Op/(1-x1-x2))+½ln(x1+x2+1)), (9) where vector {Xikp} (k = Si, B, O, Sr) is the solution of the system (5) for pure i-th component, i.e. for xi = 1. Using this computational scheme the results shown in Fig.1 and Fig.2 were obtained. For our test of modifi ...