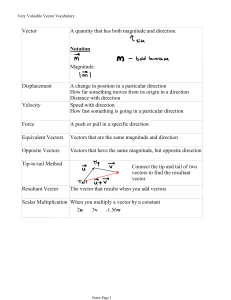
Vector A quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Notation
... A change in position in a particular direction How far something moves from its origin in a direction Distance with direction Speed with direction How fast something is going in a particular direction ...
... A change in position in a particular direction How far something moves from its origin in a direction Distance with direction Speed with direction How fast something is going in a particular direction ...
List of Topics for the Final Exam
... Speed, velocity, acceleration, average speed vs. instantaneous speed scalar vs. vector quantities the three general equations: d = vt + = ½ at2 vf = vi + at vf2 = vi2 + 2ad d = vt horizontal motion, constant velocity v =at (or v = gt) finds peak time in flight d = ½ at2 (vertical distance in free fa ...
... Speed, velocity, acceleration, average speed vs. instantaneous speed scalar vs. vector quantities the three general equations: d = vt + = ½ at2 vf = vi + at vf2 = vi2 + 2ad d = vt horizontal motion, constant velocity v =at (or v = gt) finds peak time in flight d = ½ at2 (vertical distance in free fa ...
student notes - science
... From lesson 15 of the Mechanics Module (G481.2) we know that: His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in moti ...
... From lesson 15 of the Mechanics Module (G481.2) we know that: His 2nd law said that the force applied to an object is directly proportional to its acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in moti ...
Name____________________________________
... 9. A ball will fall to the ground at a constant speed because of gravity. ...
... 9. A ball will fall to the ground at a constant speed because of gravity. ...
Newton`s 3rd Law of Motion
... For every action there is an equal but opposite reaction. All forces act in pairs with one object exerting a force on a second object, and the second object exerting a force back ...
... For every action there is an equal but opposite reaction. All forces act in pairs with one object exerting a force on a second object, and the second object exerting a force back ...
Name - Noviellan Physics
... c. A woman swimming upstream is not moving with respect to the shore. Is she doing any work? If she stops swimming and merely floats, is work done on her? d. Is the work done by kinetic friction always negative? Consider what happens to dishes on a table cloth when you pull the cloth. e. Why is it t ...
... c. A woman swimming upstream is not moving with respect to the shore. Is she doing any work? If she stops swimming and merely floats, is work done on her? d. Is the work done by kinetic friction always negative? Consider what happens to dishes on a table cloth when you pull the cloth. e. Why is it t ...
Physics Test MC. Thru 10 Two wires have the same diameter and
... 9. A uniform, solid cylinder rolls without slipping down an incline. At the bottom of the incline, the speed, v, of the cylinder is measured and the translational and rotational kinetic energies (K’tr , K’rot) are calculated. A hole is drilled through the cylinder along its axis and the experiment i ...
... 9. A uniform, solid cylinder rolls without slipping down an incline. At the bottom of the incline, the speed, v, of the cylinder is measured and the translational and rotational kinetic energies (K’tr , K’rot) are calculated. A hole is drilled through the cylinder along its axis and the experiment i ...
template - charlestuttle
... 11. An 800. kg Geo Metro can go from rest to a speed of 36 m/s in 9.0s. What average net force acts on the car? ...
... 11. An 800. kg Geo Metro can go from rest to a speed of 36 m/s in 9.0s. What average net force acts on the car? ...
Take Home Test - cloudfront.net
... a. What will be the total gravitational energy of this rocket while sitting on the surface of Triton? b. With what velocity must this rocket be launched from the surface of Triton in order for it to escape the gravitational effect of Triton? c. Suppose that this rocket is launched from the surface o ...
... a. What will be the total gravitational energy of this rocket while sitting on the surface of Triton? b. With what velocity must this rocket be launched from the surface of Triton in order for it to escape the gravitational effect of Triton? c. Suppose that this rocket is launched from the surface o ...
Application of Definite Integrals
... A force F = 3x2 - 2x acts on a body moving along the x-axis. Here x is in meters and F is in Newtons (N). If the force is applied at an angle of 300 with the direction of motion, find the work done by the force in moving the object from x = 1m to x = 2m. Solution: The work is calculated from equatio ...
... A force F = 3x2 - 2x acts on a body moving along the x-axis. Here x is in meters and F is in Newtons (N). If the force is applied at an angle of 300 with the direction of motion, find the work done by the force in moving the object from x = 1m to x = 2m. Solution: The work is calculated from equatio ...
Forces Physical Science Chapter 2
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
... Fig 1 - shows the magnitude & direction of the 2 vectors we are adding Fig 2 – we move the beginning of vector B to the end of Vector A, making sure to keep the magnitude & direction exactly the same Fig 3 – Connect the beginning of Vector A to the end of Vector B, this is your “Resultant” C. ...
Rotational and Projectile Motion
... When the vfinal - vinitial vector is moved to the circle, you can see the direction of the vector points toward the center of the circle. Regardless of where on the circle the vectors are chosen, the ∆v difference vector will always point toward the center of the circle. The conclusion is that the a ...
... When the vfinal - vinitial vector is moved to the circle, you can see the direction of the vector points toward the center of the circle. Regardless of where on the circle the vectors are chosen, the ∆v difference vector will always point toward the center of the circle. The conclusion is that the a ...
Unit 13: Periodic Motion
... motion is called simple harmonic motion (SHM). o The circle of reference construction uses a rotating vector called a phasor, having a length equal to the amplitude of the motion. o The angular frequency, frequency, and period in SHM do not depend on the amplitude, but only on the mass and force con ...
... motion is called simple harmonic motion (SHM). o The circle of reference construction uses a rotating vector called a phasor, having a length equal to the amplitude of the motion. o The angular frequency, frequency, and period in SHM do not depend on the amplitude, but only on the mass and force con ...