7 - Tarman Physics
... A. the weight of the candle = buoyant force B. V is the volume of fluid displaced C. is the density of wax D. there is no normal force on the candle E. all statements are true ...
... A. the weight of the candle = buoyant force B. V is the volume of fluid displaced C. is the density of wax D. there is no normal force on the candle E. all statements are true ...
Force & Motion - Independent School District 196
... Can an object’s acceleration be a negative number? Why or why not? Yes. When an object slows down and the final speed is less than the initial speed, the object’s acceleration will be a negative number. ...
... Can an object’s acceleration be a negative number? Why or why not? Yes. When an object slows down and the final speed is less than the initial speed, the object’s acceleration will be a negative number. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... college he wrote his ideas in a journal. Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. He also had ideas about gravity, the diffraction of light, and forces. His accomplishments laid the foundations for modern science and revolutionized the world. ...
... college he wrote his ideas in a journal. Newton had new ideas about motion, which he called his three laws of motion. He also had ideas about gravity, the diffraction of light, and forces. His accomplishments laid the foundations for modern science and revolutionized the world. ...
Second practice midetrm key (Word document)
... Dy/dt = 10.2176 t – 7.7054 Evaluate at t= .4756 Dy/dt = -2.846 m/s If a ball was released from rest and fell 41cm before striking the lab table, how long would that fall take? T = sqrt (2 * h /g) = sqrt (2 *.41 /9.8) = 0.289 s If the initial velocity were 3.15 m/s, what would be the theoretical rang ...
... Dy/dt = 10.2176 t – 7.7054 Evaluate at t= .4756 Dy/dt = -2.846 m/s If a ball was released from rest and fell 41cm before striking the lab table, how long would that fall take? T = sqrt (2 * h /g) = sqrt (2 *.41 /9.8) = 0.289 s If the initial velocity were 3.15 m/s, what would be the theoretical rang ...
Physics Midterm Study Guide
... The average velocity of any object is its displacement divided by the total time it took, including rest time. The length or shape of the path traveled, or changes in speed during the trip are not relevant. Its defining equation is v = Δx / Δt You should know and understand all of the above, and be ...
... The average velocity of any object is its displacement divided by the total time it took, including rest time. The length or shape of the path traveled, or changes in speed during the trip are not relevant. Its defining equation is v = Δx / Δt You should know and understand all of the above, and be ...
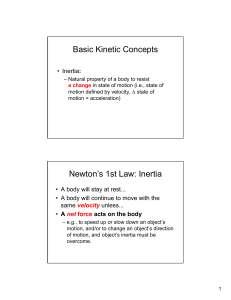
Basic Kinetic
... equal magnitude but opposite direction – example: Vertical jumping • “Action” force is applied by person (via muscles) and acts on ground. • “Reaction” force is applied by ground and acts on person. ...
... equal magnitude but opposite direction – example: Vertical jumping • “Action” force is applied by person (via muscles) and acts on ground. • “Reaction” force is applied by ground and acts on person. ...
Slideshow
... If a force is applied to a moving object, the object can speed up, slow down or come to a stop. ...
... If a force is applied to a moving object, the object can speed up, slow down or come to a stop. ...
1. What happens when an unbalanced force is
... 1. What happens when an unbalanced force is applied to an object at rest? A. It accelerates B. It remains at rest C. It gains mass D. It loses momentum 2. Which of the following is a unit of acceleration? A. 40 kilometers per hour B. 40 newtons per gram C. 40 meters per second per second D. 40 joule ...
... 1. What happens when an unbalanced force is applied to an object at rest? A. It accelerates B. It remains at rest C. It gains mass D. It loses momentum 2. Which of the following is a unit of acceleration? A. 40 kilometers per hour B. 40 newtons per gram C. 40 meters per second per second D. 40 joule ...
18. More Circular Motion
... • Suppose now the light disk is in a • Vhas zero vertical plane, free to rotate about a horizontal axis. Light disk • If the red mass is at rest at the axle lowest point, and is then displaced slightly, the torque from the gravitational force mg will pull it back towards the center. This is called s ...
... • Suppose now the light disk is in a • Vhas zero vertical plane, free to rotate about a horizontal axis. Light disk • If the red mass is at rest at the axle lowest point, and is then displaced slightly, the torque from the gravitational force mg will pull it back towards the center. This is called s ...
Centripetal Force
... Centripetal force is not another force to add to our list of forces such as weight, normal, etc. It is a characteristic of a force, force component, or combination of forces. For example, a bicycle rounding a flat curve will have a static force of friction maintain its circular motion. A bicycle rou ...
... Centripetal force is not another force to add to our list of forces such as weight, normal, etc. It is a characteristic of a force, force component, or combination of forces. For example, a bicycle rounding a flat curve will have a static force of friction maintain its circular motion. A bicycle rou ...
Worksheet on W=mgh
... the object moves. Or: W=(F)(d). If the force is at an angle to the object’s motion, only the component of the force that is parallel to the object’s motion is used to determine the work on the object. Work is defined as negative when the force is in the direction opposite the displacement. Friction ...
... the object moves. Or: W=(F)(d). If the force is at an angle to the object’s motion, only the component of the force that is parallel to the object’s motion is used to determine the work on the object. Work is defined as negative when the force is in the direction opposite the displacement. Friction ...
Newton Review
... Speed = Distance/ Time; 20 ft/s = 200 ft/10 s 13. What is the acceleration of an object that goes from 50 m/s to 100 m/s in 10 seconds? ∆ speed/time = acceleration; 100 m/s – 50 m/s / 10 s = 50 m/s / 10 s = 5 m/s2 Fill in the blanks for the following questions below. 14. Air resistance is a kind of ...
... Speed = Distance/ Time; 20 ft/s = 200 ft/10 s 13. What is the acceleration of an object that goes from 50 m/s to 100 m/s in 10 seconds? ∆ speed/time = acceleration; 100 m/s – 50 m/s / 10 s = 50 m/s / 10 s = 5 m/s2 Fill in the blanks for the following questions below. 14. Air resistance is a kind of ...