Force - Purdue Physics
... A non zero force action on an object causes its state of motion to change. ...
... A non zero force action on an object causes its state of motion to change. ...
advanced placement chemistry
... 3. What is the final velocity (vf) of a car that accelerates from rest (vi = 0) at a rate of a = 10 m/s2 for 20 seconds? 4. The escape velocity to escape the earth’s gravity is 11,200 m/s. What is the constant acceleration necessary if it takes 5 hours to reach the escape velocity starting from rest ...
... 3. What is the final velocity (vf) of a car that accelerates from rest (vi = 0) at a rate of a = 10 m/s2 for 20 seconds? 4. The escape velocity to escape the earth’s gravity is 11,200 m/s. What is the constant acceleration necessary if it takes 5 hours to reach the escape velocity starting from rest ...
Speed, velocity and acceleration
... rest, a body in motion tends to keep moving along at a constant speed and in a straight-line path unless interfered with by some external forces. ...
... rest, a body in motion tends to keep moving along at a constant speed and in a straight-line path unless interfered with by some external forces. ...
AP Physics Chapter 5-8 Key Equations and Ideas Forces (pulleys
... displacement, and it does negative work when it has a vector component in the opposite direction. The force does zero work when it is perpendicular to the displacement. ...
... displacement, and it does negative work when it has a vector component in the opposite direction. The force does zero work when it is perpendicular to the displacement. ...
PHY 101 Lecture 4 - Force
... “Force” started with Isaac Newton, in the Three Laws of Motion. /1/ If the net force acting on an object is 0, then the object moves with constant velocity. /2/ If the net force is F, then the object undergoes acceleration; a = F /m where m is the mass. /3/ For every action there is an equal but ...
... “Force” started with Isaac Newton, in the Three Laws of Motion. /1/ If the net force acting on an object is 0, then the object moves with constant velocity. /2/ If the net force is F, then the object undergoes acceleration; a = F /m where m is the mass. /3/ For every action there is an equal but ...
Announcements True or False: When a rocket blasts off, it pushes off
... either fall to Earth, continually free-fall (orbit), or escape the force of Earth’s gravity. The minimum velocity required to escape the force of the Earth’s gravity is called the escape velocity. ...
... either fall to Earth, continually free-fall (orbit), or escape the force of Earth’s gravity. The minimum velocity required to escape the force of the Earth’s gravity is called the escape velocity. ...
Ch5CTa
... Answer: Both cars have the same acceleration. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity: a = dv/dt. Both cars have a velocity vector which is changing in the same way. (Since this is circular motion with constant speed, the direction of the acceleration is toward the center of the circle and th ...
... Answer: Both cars have the same acceleration. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity: a = dv/dt. Both cars have a velocity vector which is changing in the same way. (Since this is circular motion with constant speed, the direction of the acceleration is toward the center of the circle and th ...
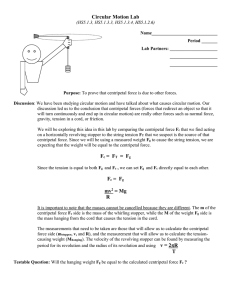
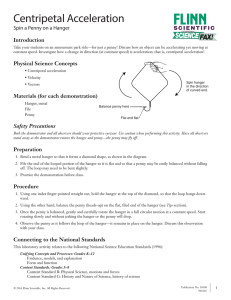
Chapter 7 – Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • Solve problems involving centripetal acceleration. • Solve problems involving centripetal force. • Explain how the apparent existence of an outward force in circular motion can be explained as inertia resisting the centripetal force. A. Tangential Speed 1. The tangential speed (vt) of an object in ...
... • Solve problems involving centripetal acceleration. • Solve problems involving centripetal force. • Explain how the apparent existence of an outward force in circular motion can be explained as inertia resisting the centripetal force. A. Tangential Speed 1. The tangential speed (vt) of an object in ...
Crust
... An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force An object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Consider the Following Inertia: tendency to resist a change in motion ...
... An object at rest remains at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force An object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Consider the Following Inertia: tendency to resist a change in motion ...
L05_projectile
... – Questions 2, 3, 4 evaluated Standard 1 (DVA) – Still need to fix if not all were correct – Mechanism TBA – I’m trying to figure how to post standards strandings ...
... – Questions 2, 3, 4 evaluated Standard 1 (DVA) – Still need to fix if not all were correct – Mechanism TBA – I’m trying to figure how to post standards strandings ...
File
... 4. A curious kitten pushes a ball of yarn at rest with its nose, displacing the ball of yarn 17.5 cm in 2.00 s. Calculate the acceleration of the ball of yarn. 5. A man hikes 6.6 km north along a straight path with an average velocity of 4.2 km/h to the north. He rests at a bench for 15 min. Then, h ...
... 4. A curious kitten pushes a ball of yarn at rest with its nose, displacing the ball of yarn 17.5 cm in 2.00 s. Calculate the acceleration of the ball of yarn. 5. A man hikes 6.6 km north along a straight path with an average velocity of 4.2 km/h to the north. He rests at a bench for 15 min. Then, h ...