centripetal force. Section 1 Circular Motion
... Centripetal Acceleration, continued • You have seen that centripetal acceleration results from a change in direction. • In circular motion, an acceleration due to a change in speed is called tangential acceleration. • To understand the difference between centripetal and tangential acceleration, cons ...
... Centripetal Acceleration, continued • You have seen that centripetal acceleration results from a change in direction. • In circular motion, an acceleration due to a change in speed is called tangential acceleration. • To understand the difference between centripetal and tangential acceleration, cons ...
cyclotron
... experiences a force in the electric field which is set up between the 2 chambers. It accelerates and enters into the chamber which is at low potential (-ve). Inside the chamber electric field is 0 but the magnetic field changes the direction of the particle into semi-circular path. By the time it co ...
... experiences a force in the electric field which is set up between the 2 chambers. It accelerates and enters into the chamber which is at low potential (-ve). Inside the chamber electric field is 0 but the magnetic field changes the direction of the particle into semi-circular path. By the time it co ...
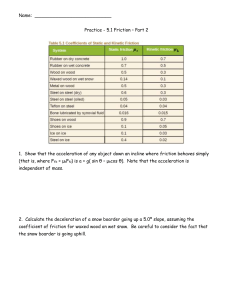
Name: Practice - 5.1 Friction – Part 2 1. Show that the acceleration of
... 1. Show that the acceleration of any object down an incline where friction behaves simply (that is, where Ffk = μkFN) is a = g( sin θ – μkcos θ). Note that the acceleration is independent of mass. ...
... 1. Show that the acceleration of any object down an incline where friction behaves simply (that is, where Ffk = μkFN) is a = g( sin θ – μkcos θ). Note that the acceleration is independent of mass. ...
PROJECTILE MOTION
... the object in motion initially but, while it is moving through the air, no force other than gravity acts on it (we shall ignore air resistance for now). The path, or trajectory, of the projectile is parabolic. ...
... the object in motion initially but, while it is moving through the air, no force other than gravity acts on it (we shall ignore air resistance for now). The path, or trajectory, of the projectile is parabolic. ...
Newton`s first law of motion
... speed of the parachutist is zero. However he will immediately be acted upon by his weight acting vertically downwards and since the external resultant force is not zero he will accelerate downwards. As the parachutist’s speed increases so does the air resistance. This opposes the downwards force of ...
... speed of the parachutist is zero. However he will immediately be acted upon by his weight acting vertically downwards and since the external resultant force is not zero he will accelerate downwards. As the parachutist’s speed increases so does the air resistance. This opposes the downwards force of ...
Sir Isaac Newton
... in particular, might it not reach all the way to the orbit of the Moon! Then, the orbit of the Moon about the Earth could be a consequence of the gravitational force, because the acceleration due to gravity could change the velocity of the Moon in just such a way that it followed an orbit around the ...
... in particular, might it not reach all the way to the orbit of the Moon! Then, the orbit of the Moon about the Earth could be a consequence of the gravitational force, because the acceleration due to gravity could change the velocity of the Moon in just such a way that it followed an orbit around the ...
Sir Isaac Newton
... in particular, might it not reach all the way to the orbit of the Moon! Then, the orbit of the Moon about the Earth could be a consequence of the gravitational force, because the acceleration due to gravity could change the velocity of the Moon in just such a way that it followed an orbit around the ...
... in particular, might it not reach all the way to the orbit of the Moon! Then, the orbit of the Moon about the Earth could be a consequence of the gravitational force, because the acceleration due to gravity could change the velocity of the Moon in just such a way that it followed an orbit around the ...
Centripetal Force - Northern Illinois University
... This experiment uses a vertical shaft that can freely rotate to spin a massive bob of mass m. The bob hangs by two strings from a horizontal bar with a counterweight on the other side. The counterweight helps the shaft rotate evenly. A spring can connect the bob to the shaft and provides a force to ...
... This experiment uses a vertical shaft that can freely rotate to spin a massive bob of mass m. The bob hangs by two strings from a horizontal bar with a counterweight on the other side. The counterweight helps the shaft rotate evenly. A spring can connect the bob to the shaft and provides a force to ...
Newton`s Laws
... 2. What equation summarizes Newton’s 2nd Law? Give the units used to measure each variable of the equation. ...
... 2. What equation summarizes Newton’s 2nd Law? Give the units used to measure each variable of the equation. ...