* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 13: Periodic Motion
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
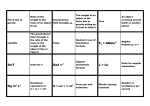
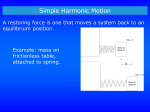
AP Physics: Mechanics Periodic Motion: Chapter 13 Objectives Students will learn that: o Periodic motion is motion that repeats itself in a definite cycle. It occurs whenever a body has a stable equilibrium position and a restoring force that acts when it is displaced from equilibrium. o Period is the time for one cycle. Frequency is the number of cycles per unit time. Angular frequency is 2𝜋 times the frequency. o If the net force is a restoring force that is directly proportional to the displacement, the motion is called simple harmonic motion (SHM). o The circle of reference construction uses a rotating vector called a phasor, having a length equal to the amplitude of the motion. o The angular frequency, frequency, and period in SHM do not depend on the amplitude, but only on the mass and force constant. o In SHM, the displacement, velocity, and acceleration are sinusoidal functions of time. o Energy is conserved in SHM. o In angular SHM, the frequency and angular frequency are related to the moment of inertia and the torsion constant. o A simple pendulum consists of a point mass at the end of a massless string of length. Its motion is approximately SMH for small amplitude. The angular frequency, frequency, and period depend only on gravity and length. o A physical pendulum is a body suspended from an axis of rotation a distance from its center of gravity. o When a damping force proportional to velocity is added to a simple harmonic oscillator, the motion is called a damped oscillation. o When a sinusoidally varying driving force is added to a damped harmonic oscillator, the resulting motion is called a force oscillation.. Homework: Read the Chapter PP 507-513 #’s 1,3,5,7,9,15,19,25,27,31,33,41,43,45,49,57,61,63,69,75,89,91 Take Home Quiz