WRL0638.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... The above definitions and postulates are all that is needed to define the subject of thermodynamics. Other functions can be defined in terms of the already defined quantities, and the derivation of relations and the discussion of thermal equilibrium in all of its different guises is mostly a matter ...
... The above definitions and postulates are all that is needed to define the subject of thermodynamics. Other functions can be defined in terms of the already defined quantities, and the derivation of relations and the discussion of thermal equilibrium in all of its different guises is mostly a matter ...
WRL1834.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... The above definitions and postulates are all that is needed to define the subject of thermodynamics. Other functions can be defined in terms of the already defined quantities, and the derivation of relations and the discussion of thermal equilibrium in all of its different guises is mostly a matter ...
... The above definitions and postulates are all that is needed to define the subject of thermodynamics. Other functions can be defined in terms of the already defined quantities, and the derivation of relations and the discussion of thermal equilibrium in all of its different guises is mostly a matter ...
The second law of thermodynamics
... We shell now replace the statistical weight Ω by a new quantity, the entropy, which will be defined by S ≡ kB ln Ω ...
... We shell now replace the statistical weight Ω by a new quantity, the entropy, which will be defined by S ≡ kB ln Ω ...
Chapter 2 Classical Thermodynamics: The Second Law 2.1 Heat
... This is a substantial chapter, containing many important results and many techniques. There are two common technical difficulties for many students at the beginning: proof of theorems and partial derivatives. We will emphasize the understanding and applications of the theorems and we will do many pr ...
... This is a substantial chapter, containing many important results and many techniques. There are two common technical difficulties for many students at the beginning: proof of theorems and partial derivatives. We will emphasize the understanding and applications of the theorems and we will do many pr ...
ENTROPY
... In the second place, and more important, no on knows what entropy really is, so in a debate you will always have the advantage.”” Note that compound probabilities are multiplicative, uncertainties are additive and so is entropy. For equally-probable microstates totalising a number Ω, their probabili ...
... In the second place, and more important, no on knows what entropy really is, so in a debate you will always have the advantage.”” Note that compound probabilities are multiplicative, uncertainties are additive and so is entropy. For equally-probable microstates totalising a number Ω, their probabili ...
Unit II - Chemical Thermodynamics
... Homogeneous system: A system is said to be “homogeneous” if it consists of only one phase and uniform thought. Ex. a solution of sugar in water. Heterogeneous system: When a system consists of two or more phases and is not uniform throughout it is called heterogeneous. Ex .Ice in water, chloroform i ...
... Homogeneous system: A system is said to be “homogeneous” if it consists of only one phase and uniform thought. Ex. a solution of sugar in water. Heterogeneous system: When a system consists of two or more phases and is not uniform throughout it is called heterogeneous. Ex .Ice in water, chloroform i ...
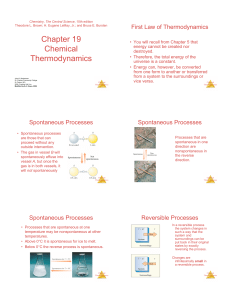
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... away from equil, sign of !G tells which way rxn goes Chemical ...
... away from equil, sign of !G tells which way rxn goes Chemical ...
heat engine
... A heat engine is any device that uses heat to perform work. It has three essential features. 1. Heat is supplied to the engine at a relatively high temperature from a place called the hot reservoir. 2. Part of the input heat is used to perform work by the working substance of the engine. 3. The rema ...
... A heat engine is any device that uses heat to perform work. It has three essential features. 1. Heat is supplied to the engine at a relatively high temperature from a place called the hot reservoir. 2. Part of the input heat is used to perform work by the working substance of the engine. 3. The rema ...
PPT
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
On Clausius, Boltzmann and Shannon Notions of Entropy
... Such meaning was inspired by an earlier formulation made by the French physician and mathematician Sasi Carnot (see [4]) who was known his broader formulation of the Second Law of Thermodynamics: entropy represents the energy no longer capable to perform work. In isolated systems it can only grow. S ...
... Such meaning was inspired by an earlier formulation made by the French physician and mathematician Sasi Carnot (see [4]) who was known his broader formulation of the Second Law of Thermodynamics: entropy represents the energy no longer capable to perform work. In isolated systems it can only grow. S ...
ESO201A: Thermodynamics
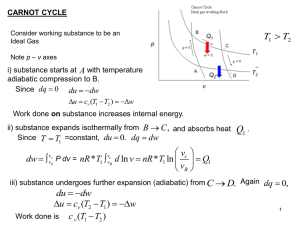
... reversible processes and their examples, internally reversible iso-thermal process, heat transfer processes, The Carnot’s heat engine cycle. Lecture #20 Carnot cycle implications, The Carnot principles, Thermodynamic temperature scale, Thermal efficiency of a reversible engine as a function of high ...
... reversible processes and their examples, internally reversible iso-thermal process, heat transfer processes, The Carnot’s heat engine cycle. Lecture #20 Carnot cycle implications, The Carnot principles, Thermodynamic temperature scale, Thermal efficiency of a reversible engine as a function of high ...