What is Thermodynamics?
... Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888): 2nd law of thermodynamics Heat can never pass from a colder to a warmer body without some change , connected with it, occurring at the same time ...
... Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888): 2nd law of thermodynamics Heat can never pass from a colder to a warmer body without some change , connected with it, occurring at the same time ...
about entropy in psoup
... The motion of each bug is pseudodeterministic. Due to the very large random, being driven by a pseudonumber of particles, statistical methods random number generator, and are used to discuss average behaviour moderated (biased) by the effects of the and/or probability distributions. Palmiter genes. ...
... The motion of each bug is pseudodeterministic. Due to the very large random, being driven by a pseudonumber of particles, statistical methods random number generator, and are used to discuss average behaviour moderated (biased) by the effects of the and/or probability distributions. Palmiter genes. ...
Thermodynamics for Systems Biology
... that is completely “thermalized”, i.e. as randomized as the temperature allows. Thermal energy at a high temperature is more ordered than thermal energy at a low temperature. In this connection, work can be viewed as heat from an infinite temperature system, i.e. not randomized at all but rather di ...
... that is completely “thermalized”, i.e. as randomized as the temperature allows. Thermal energy at a high temperature is more ordered than thermal energy at a low temperature. In this connection, work can be viewed as heat from an infinite temperature system, i.e. not randomized at all but rather di ...
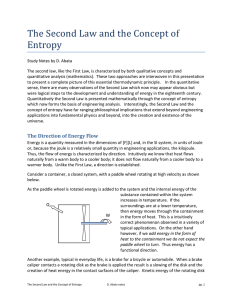
The Second Law and the Concept of Entropy
... irreversibility which will be illustrated with the mathematics of entropy. In the real world we are surrounded by the heat transfer process, hence we are surrounded by irreversibility which in the philosophical sense can be construed as synonymous with the passage of time, from the birth of the univ ...
... irreversibility which will be illustrated with the mathematics of entropy. In the real world we are surrounded by the heat transfer process, hence we are surrounded by irreversibility which in the philosophical sense can be construed as synonymous with the passage of time, from the birth of the univ ...
Carnot Cycle - University of Wyoming
... • The curve on the diagram is called the path taken between the initial and final states • The work done depends on the particular path – Same initial and final states, but different amounts of work are ...
... • The curve on the diagram is called the path taken between the initial and final states • The work done depends on the particular path – Same initial and final states, but different amounts of work are ...
File
... (b) Evaporation of water. (c) Distribution of solute throughout the solvent. (d) Expansion of gases. (e) Flow of water from a hill to the ground. (f) Mixing of gases. In all the above cases, the system reaches a state of greater disorder. Eventhough the energy of the system increases (endothermic) d ...
... (b) Evaporation of water. (c) Distribution of solute throughout the solvent. (d) Expansion of gases. (e) Flow of water from a hill to the ground. (f) Mixing of gases. In all the above cases, the system reaches a state of greater disorder. Eventhough the energy of the system increases (endothermic) d ...
Thermodynamics of ideal gases
... take place in an isolated system which is not allowed to exchange heat with or perform work on the environment. The First Law states that the energy is unchanged under any process in an isolated system. This implies that the energy of an open system can only change by exchange of heat or work with t ...
... take place in an isolated system which is not allowed to exchange heat with or perform work on the environment. The First Law states that the energy is unchanged under any process in an isolated system. This implies that the energy of an open system can only change by exchange of heat or work with t ...
Fundamentals of chemical thermodynamics and bioenergetics
... is located in a well-defined place and there is no spatial disorder either. In case of T = 0, the molecular motions in the substance are kept at a minimum and the number of microstates (W) is one (there is only one way to arrange the atoms or molecules to form a perfect crystal). Under these conditi ...
... is located in a well-defined place and there is no spatial disorder either. In case of T = 0, the molecular motions in the substance are kept at a minimum and the number of microstates (W) is one (there is only one way to arrange the atoms or molecules to form a perfect crystal). Under these conditi ...
1 Thermodynamics All biochemical and cellular processes obey the
... All biochemical and cellular processes obey the laws of chemistry and physics Biochemistry is not a special case. Therefore, in studying biochemistry, it is necessary to consider the relevant laws that control possible reactions. The three laws of thermodynamics First law: Energy is conserved The ov ...
... All biochemical and cellular processes obey the laws of chemistry and physics Biochemistry is not a special case. Therefore, in studying biochemistry, it is necessary to consider the relevant laws that control possible reactions. The three laws of thermodynamics First law: Energy is conserved The ov ...
Black Hole Entropy in String Theory.
... entropy formula is modified. If there is a Killing horizon, then one can associate an entropy, Wald ...
... entropy formula is modified. If there is a Killing horizon, then one can associate an entropy, Wald ...
Midterm Exam Problem 10 Example of using van der Waals
... For a Carnot cycle QH/QL = TH/TL so QH/TH − QL/TL = 0. Thus, if we approximate any reversible cycle (a) as an infinite sum of Carnot cycles as in (b), we see that the integral of dQ/T around a closed path is zero. This means that entropy is a state variable — like potential energy, the change in its ...
... For a Carnot cycle QH/QL = TH/TL so QH/TH − QL/TL = 0. Thus, if we approximate any reversible cycle (a) as an infinite sum of Carnot cycles as in (b), we see that the integral of dQ/T around a closed path is zero. This means that entropy is a state variable — like potential energy, the change in its ...
Thermodynamics
... Positive when system gains heat Negative when system loses heat W = net work done by ...
... Positive when system gains heat Negative when system loses heat W = net work done by ...
Thermodynamics
... A state variable describes the state of a system at time t, but it does not reveal how the system was put into that state. Examples of state variables: pressure, temperature, volume, number of moles, and internal energy. Thermal processes can change the state of a system. We assume that thermal proc ...
... A state variable describes the state of a system at time t, but it does not reveal how the system was put into that state. Examples of state variables: pressure, temperature, volume, number of moles, and internal energy. Thermal processes can change the state of a system. We assume that thermal proc ...
Lecture 12
... (1) The first inequality says that for a system at constant volume and constant internal energy (e.g., isothermal system), entropy increases in a spontaneous change (2) The second inequality says if S and V are constant, then internal energy must decrease with spontaneous change - system doesn’t spo ...
... (1) The first inequality says that for a system at constant volume and constant internal energy (e.g., isothermal system), entropy increases in a spontaneous change (2) The second inequality says if S and V are constant, then internal energy must decrease with spontaneous change - system doesn’t spo ...