Laser and nonlinear optics
... where tp is the pulse duration and ∆ν is the full width at half maximum. Nonlinear processes in the components of the resonator due to the high peak intensities of the laser pulses or insufficient modulation depth of the AOM such as dispersion can lead to deviations from this ideal value. For mode-l ...
... where tp is the pulse duration and ∆ν is the full width at half maximum. Nonlinear processes in the components of the resonator due to the high peak intensities of the laser pulses or insufficient modulation depth of the AOM such as dispersion can lead to deviations from this ideal value. For mode-l ...
Beam steering with spatial light modulators: Quantisation effects
... B. Hologram design So far, we have described the theoretical background for hologram design. From now on, we will develop the experimental details that need to be taken into consideration in hologram computation. For this purpose, we created a Matlab program. Due to the SLM non-flatness [4], a modif ...
... B. Hologram design So far, we have described the theoretical background for hologram design. From now on, we will develop the experimental details that need to be taken into consideration in hologram computation. For this purpose, we created a Matlab program. Due to the SLM non-flatness [4], a modif ...
Laser Cutting
... Of course this was all theoretical, it was not until the 1950s that the detail of how to go about light amplification were finally worked out. It would be the 1960s before the first laser oscillatiors were actually constructed. These devices could emit an intense beam of light made up of photons whi ...
... Of course this was all theoretical, it was not until the 1950s that the detail of how to go about light amplification were finally worked out. It would be the 1960s before the first laser oscillatiors were actually constructed. These devices could emit an intense beam of light made up of photons whi ...
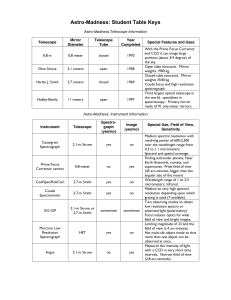
Astro-Madness: Student Table Keys
... Medium to very high spectral resolution depending upon which grating is used (7 available). Two observing modes to obtain low resolution spectra or polarized light (polarimetry). Focal reducer optics for wide field of view and bright images, Limiting magnitude of 23 and the field of view is 4 arc-mi ...
... Medium to very high spectral resolution depending upon which grating is used (7 available). Two observing modes to obtain low resolution spectra or polarized light (polarimetry). Focal reducer optics for wide field of view and bright images, Limiting magnitude of 23 and the field of view is 4 arc-mi ...
Laser Collimation of a Chromium Beam Using Doppler Force Wen
... The remarkable capabilities of laser cooling and trapping techniques for the precise handing of atoms has led to great advances in the field of atom optics. One of the most promising applications of finely controlled neutral atom beams is direct-write atom lithography of nanometer-scale features, wh ...
... The remarkable capabilities of laser cooling and trapping techniques for the precise handing of atoms has led to great advances in the field of atom optics. One of the most promising applications of finely controlled neutral atom beams is direct-write atom lithography of nanometer-scale features, wh ...
Semiconductor Laser Diodes
... to use compared to other types of lasers. • They can be used for many applications, and have the ability to be produced in a wide range of wavelengths and powers. • The most important electronic consideration is the fact that a precisely controlled current source is needed to regulate the amount of ...
... to use compared to other types of lasers. • They can be used for many applications, and have the ability to be produced in a wide range of wavelengths and powers. • The most important electronic consideration is the fact that a precisely controlled current source is needed to regulate the amount of ...
A Laser Module for 100Gbps Digital Coherent Optical Transmission System
... highly stable DFB (distributed feedback) LD. The light emitted from the front side (output side of the laser module) of the wavelength tunable LD passes through a lens where it is coupled to the optical fiber. The light emitted at the rear side (opposite side) enters the rear-side wavelength monitor ...
... highly stable DFB (distributed feedback) LD. The light emitted from the front side (output side of the laser module) of the wavelength tunable LD passes through a lens where it is coupled to the optical fiber. The light emitted at the rear side (opposite side) enters the rear-side wavelength monitor ...
Saturation
... through a gas with Maxwell-Boltzmann velocity distribution the laser frequency in the frame of the molecule is ' k v z With k v z fall within the linewidth ...
... through a gas with Maxwell-Boltzmann velocity distribution the laser frequency in the frame of the molecule is ' k v z With k v z fall within the linewidth ...
Optical Cavity for the Strontium Lattice Atomic Clock
... necessary to test the vacuum chamber viewports, which involved building a laser diode and an optical cavity. This paper will explore the theory behind both as well as their implementation. ...
... necessary to test the vacuum chamber viewports, which involved building a laser diode and an optical cavity. This paper will explore the theory behind both as well as their implementation. ...
optical design of an echelle grating based atomic emission
... The echelle grating used in the instrument has 79 lines/mm, a ruled area of 254 mm X 128 mm, and a blaze angle of 740. The entrance slit is a square aperture of 40 µm X 40 µm. Mirrors M1 and M2 are 250 mm and 175 mm focal length respectively with aluminium high reflection coatings. The Littrow prism ...
... The echelle grating used in the instrument has 79 lines/mm, a ruled area of 254 mm X 128 mm, and a blaze angle of 740. The entrance slit is a square aperture of 40 µm X 40 µm. Mirrors M1 and M2 are 250 mm and 175 mm focal length respectively with aluminium high reflection coatings. The Littrow prism ...