Dr Una Fairbrother
... amounts of other amino acids called fibroin b-Keratin molecules do not form a helix they lie on top of each other to give ridged sheets of linked amino acids, with glycine appearing on only one side of the sheets. The sheets then stack one on top of the other. This planar structure is felt when you ...
... amounts of other amino acids called fibroin b-Keratin molecules do not form a helix they lie on top of each other to give ridged sheets of linked amino acids, with glycine appearing on only one side of the sheets. The sheets then stack one on top of the other. This planar structure is felt when you ...
Reading Guide: Pratt and Cornely, Chapter 4, pp 87
... List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in h-bonding? 15. What is an irregular sec ...
... List a few interactions that contribute to or detract from polypeptide stability. 13. Describe the alpha helix structure. 14. Draw a parallel beta sheet between two oligonucleotides that are five alanine residues long. How is an antiparallel sheet different in h-bonding? 15. What is an irregular sec ...
View video content as a PDF
... An alpha helix can be folded by wrapping the toober around a finger. In the zinc finger sample protein, there is an alpha helix from amino acid 19 to amino acid 30. This entire area should be folded into an alpha helix. It is important to make extra sure that your alpha helices are always right hand ...
... An alpha helix can be folded by wrapping the toober around a finger. In the zinc finger sample protein, there is an alpha helix from amino acid 19 to amino acid 30. This entire area should be folded into an alpha helix. It is important to make extra sure that your alpha helices are always right hand ...
A.P.day52 proteins
... acids determine the tertiary structure which determines the function of the protein The order of amino acids are coded by the order of ...
... acids determine the tertiary structure which determines the function of the protein The order of amino acids are coded by the order of ...
Lecture 2 Thurs17 Oct
... enantiomeric For N = 2 there are 4 possible sterioisomers of which 2 are enatiomers and 2 are diastereomers ...
... enantiomeric For N = 2 there are 4 possible sterioisomers of which 2 are enatiomers and 2 are diastereomers ...
Unit1-KA4-Revision
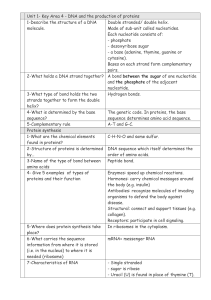
... - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of bond holds the two Hydrogen bonds. strands together to form the ...
... - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of bond holds the two Hydrogen bonds. strands together to form the ...
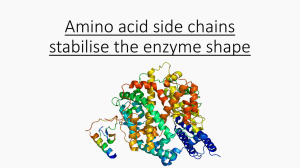
Amino acid side chains stabilise the enzyme shape Hydrogen bonds
... Many amino acids contain groups in the side chains that have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or nitrogen atom. Hydrogen bonding can occur between such groups. ...
... Many amino acids contain groups in the side chains that have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or nitrogen atom. Hydrogen bonding can occur between such groups. ...
Knuffke Prezi- Macromolecules
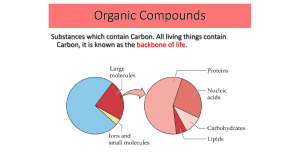
... Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. ...
... Organic Compounds Substances which contain Carbon. All living things contain Carbon, it is known as the backbone of life. ...
Slide 1
... (A) The carboxyl-terminal helix (red) is called the recognition helix because it participates in sequence-specific recognition of DNA. (B) This helix fits into the major groove of DNA, where it contacts the edges of the base pairs. From Molecular Biology of the Cell. 3rd ed. Alberts, Bruce; Bray, De ...
... (A) The carboxyl-terminal helix (red) is called the recognition helix because it participates in sequence-specific recognition of DNA. (B) This helix fits into the major groove of DNA, where it contacts the edges of the base pairs. From Molecular Biology of the Cell. 3rd ed. Alberts, Bruce; Bray, De ...
Proteins - Wesleyan College Faculty
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
Amino acids
... structure (simple, composite) form (fibrilar, globular) solubility (scleroproteins, albumins, histones, globulins) function (proteins of basic metabolism, specialized cells) ...
... structure (simple, composite) form (fibrilar, globular) solubility (scleroproteins, albumins, histones, globulins) function (proteins of basic metabolism, specialized cells) ...
Lecture 3
... Other factors resulting in helix deformation 1. Deformation is forced because of tertiary structure (crowding). 2. Strong H-bonding (e.g., between side chains). 3. Helix breakers inside; Pro will result in a kink for sure and Gly almost always but small polar amino acids such as Ser and Thr also c ...
... Other factors resulting in helix deformation 1. Deformation is forced because of tertiary structure (crowding). 2. Strong H-bonding (e.g., between side chains). 3. Helix breakers inside; Pro will result in a kink for sure and Gly almost always but small polar amino acids such as Ser and Thr also c ...
6. 3-D structure of proteins
... • The spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein is called its conformation. • Proteins in any of their functional folded conformations are called native proteins. • Stability can be defined as the tendency to ...
... • The spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein is called its conformation. • Proteins in any of their functional folded conformations are called native proteins. • Stability can be defined as the tendency to ...
Ch 4 Reading Guide
... 2. Give three reasons it is important to know the primary sequence of a protein. 3. Give a chemical explanation of why a peptide bond is planar. 4. Why are almost all peptide bonds in proteins trans rather than cis. 5. Regular, folded segments of amino acids near one another in linear sequence is ca ...
... 2. Give three reasons it is important to know the primary sequence of a protein. 3. Give a chemical explanation of why a peptide bond is planar. 4. Why are almost all peptide bonds in proteins trans rather than cis. 5. Regular, folded segments of amino acids near one another in linear sequence is ca ...