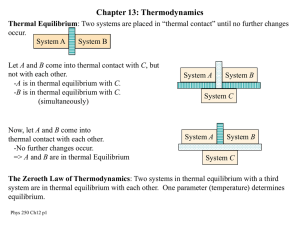
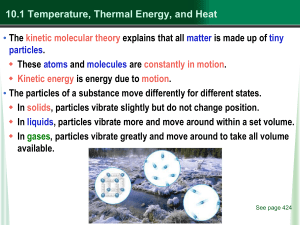
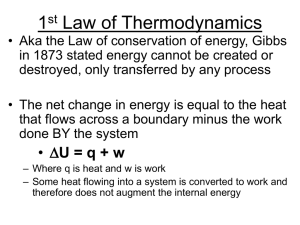
First Law of Thermodynamics
... •Is not a temperature •It is a pressure •Pressure above the liquid=pressure from particles leaving the surface ...
... •Is not a temperature •It is a pressure •Pressure above the liquid=pressure from particles leaving the surface ...
As a system asymptotically approaches absolute zero of
... and the entropy of the system asymptotically approaches a minimum value; also stated as: "the entropy of all systems and of all states of a system is smallest at absolute zero" or equivalently "it is impossible to reach the absolute zero of temperature by any finite number of processes." Absolute ze ...
... and the entropy of the system asymptotically approaches a minimum value; also stated as: "the entropy of all systems and of all states of a system is smallest at absolute zero" or equivalently "it is impossible to reach the absolute zero of temperature by any finite number of processes." Absolute ze ...
September 26, 2012
... Thermodynamic properties: composition, internal energy, volume, pressure, temperature, entropy, etc Properties: 1. Extensive a. Depends on size b. Larger system means larger value c. Volume is an example 2. Intensive a. Density is an example b. More important than extensive c. Pressure and temperatu ...
... Thermodynamic properties: composition, internal energy, volume, pressure, temperature, entropy, etc Properties: 1. Extensive a. Depends on size b. Larger system means larger value c. Volume is an example 2. Intensive a. Density is an example b. More important than extensive c. Pressure and temperatu ...
PS5, Thermo Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be
... 3. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although in many processes energy is transferred to the environment as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the work done by a heat engine ...
... 3. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although in many processes energy is transferred to the environment as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the work done by a heat engine ...
Homework 3 Solutions ()
... Plugging these into the three-dimensional heat equation shows that T does, in fact, satisfy this equation. (b) (0.5 point) Describe what happens to the temperature of the body after a long period of time. Over long periods of time, we can think of what happens as t → ∞. In this case, we know that co ...
... Plugging these into the three-dimensional heat equation shows that T does, in fact, satisfy this equation. (b) (0.5 point) Describe what happens to the temperature of the body after a long period of time. Over long periods of time, we can think of what happens as t → ∞. In this case, we know that co ...
ENT 211 Tutorial Week 1
... Thermodynamics deals with the amount of heat transfer as a system undergoes a process from one equilibrium state to another. Heat transfer, on the other hand, deals with the rate of heat transfer as well as the temperature distribution within the system at a specified time. ...
... Thermodynamics deals with the amount of heat transfer as a system undergoes a process from one equilibrium state to another. Heat transfer, on the other hand, deals with the rate of heat transfer as well as the temperature distribution within the system at a specified time. ...
Chemical Thermodynamics
... standard states and reactants in their standard states, it is a fixed quantity for a given reaction at a given temperature ΔG also depends on the composition of reaction mixture and varies and might even change sign as the reaction proceeds. ...
... standard states and reactants in their standard states, it is a fixed quantity for a given reaction at a given temperature ΔG also depends on the composition of reaction mixture and varies and might even change sign as the reaction proceeds. ...
Lecture 5 - Thermodynamics II
... • Besides knowing volume changes, need to figure out how S changes with T For internal energy of a thing: dU = dqtot – PdV; determining this at constant volume dU = CVdT where CV is the heat required to raise T by 1°C ...
... • Besides knowing volume changes, need to figure out how S changes with T For internal energy of a thing: dU = dqtot – PdV; determining this at constant volume dU = CVdT where CV is the heat required to raise T by 1°C ...