Using the “Clicker” - Boston University: Physics
... The number of moles is chosen so nR = 100 J/K. The following information is known about states 2 and 3. Pressure: P2 = P3 = 100 kPa Volume: V3 = 0.5 m3 What is the temperature of the system in state 3? ...
... The number of moles is chosen so nR = 100 J/K. The following information is known about states 2 and 3. Pressure: P2 = P3 = 100 kPa Volume: V3 = 0.5 m3 What is the temperature of the system in state 3? ...
Thermodynamics: Lecture 2
... Step 3: Involves isobaric cooling. Where only the volume of gas decreases as the vapor is cooled. ΔE3=q3 +W=CVp(T1-T2)-P(VT2-VT1) ; ΔH3=ΔE3+Δ(PV)=q3 This shows how an irreversible process can be broken down in terms of series of reversible processes and hence we can calculate associated changes in t ...
... Step 3: Involves isobaric cooling. Where only the volume of gas decreases as the vapor is cooled. ΔE3=q3 +W=CVp(T1-T2)-P(VT2-VT1) ; ΔH3=ΔE3+Δ(PV)=q3 This shows how an irreversible process can be broken down in terms of series of reversible processes and hence we can calculate associated changes in t ...
MME 2006 Metallurgical Thermodynamics
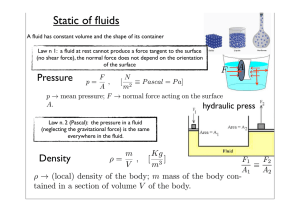
... diagrams are steep and closely spaced which means both volume expansion and isothermal compression coefficients of liquids are small A useful idealization known as incompressible fluid is employed in fluid mechanics for a sufficiently realistic model of liquid behavior The volume expansion and isoth ...
... diagrams are steep and closely spaced which means both volume expansion and isothermal compression coefficients of liquids are small A useful idealization known as incompressible fluid is employed in fluid mechanics for a sufficiently realistic model of liquid behavior The volume expansion and isoth ...
ENT 211 Tutorial Week 1
... Why is Heat Transfer a nonequilibrium phenomenon? Heat transfer is a non-equilibrium phenomena since in a system that is in equilibrium there can be no temperature differences and thus no heat flow. ...
... Why is Heat Transfer a nonequilibrium phenomenon? Heat transfer is a non-equilibrium phenomena since in a system that is in equilibrium there can be no temperature differences and thus no heat flow. ...
6-First Law
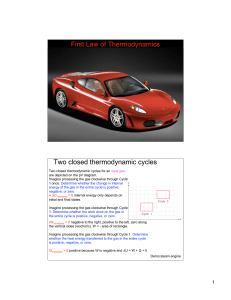
... Two closed thermodynamic cycles for an ideal gas are depicted on the pV diagram. Imagine processing the gas clockwise through Cycle 1 once. Determine whether the change in internal energy of the gas in the entire cycle is positive, negative, or zero. • ΔU1clockwise = 0 internal energy only depends o ...
... Two closed thermodynamic cycles for an ideal gas are depicted on the pV diagram. Imagine processing the gas clockwise through Cycle 1 once. Determine whether the change in internal energy of the gas in the entire cycle is positive, negative, or zero. • ΔU1clockwise = 0 internal energy only depends o ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... (a) The temperature of the gas doesn’t change. (b) Work is done on or by the gas. (c) No energy is transferred by heat to or from the gas. (d) The volume of the gas remains the same. (e) The pressure of the gas decreases uniformly. In an isobaric process on an ideal gas, pressure is constant while t ...
... (a) The temperature of the gas doesn’t change. (b) Work is done on or by the gas. (c) No energy is transferred by heat to or from the gas. (d) The volume of the gas remains the same. (e) The pressure of the gas decreases uniformly. In an isobaric process on an ideal gas, pressure is constant while t ...