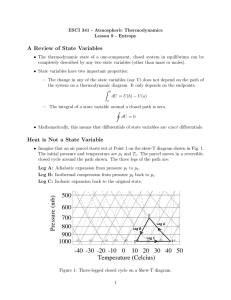
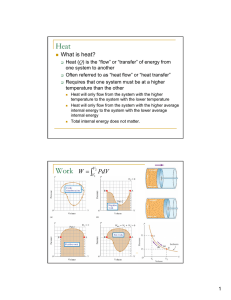
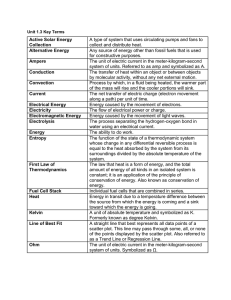
Chemical Thermodynamics
... Energy can not be created nor destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another or transferred from a system to surroundings (or vice versa) ...
... Energy can not be created nor destroyed, it can be converted from one form to another or transferred from a system to surroundings (or vice versa) ...
Joule-Thomson Expansion
... We are at the point where we can make our first analysis of an actual experiment.1 The experiment will be explained first. Then thermodynamics will be used to show that the experiment is isoenthalpic (meaning a constant enthalpy process). With this result, we can then explain the main result of the ...
... We are at the point where we can make our first analysis of an actual experiment.1 The experiment will be explained first. Then thermodynamics will be used to show that the experiment is isoenthalpic (meaning a constant enthalpy process). With this result, we can then explain the main result of the ...
T - Massey University
... The two forms of energy that influence this internal energy are heat, either transferred to the system from a source at higher temperature or lost to a sink at lower temperature and work, which can increase the internal energy if work is done on the system by its surroundings, or decrease the intern ...
... The two forms of energy that influence this internal energy are heat, either transferred to the system from a source at higher temperature or lost to a sink at lower temperature and work, which can increase the internal energy if work is done on the system by its surroundings, or decrease the intern ...