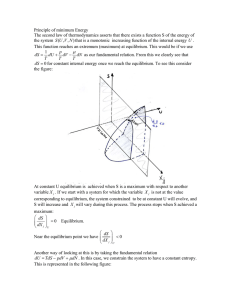
Chapter 1 Classical Thermodynamics: The First Law 1.1 Introduction
... through ∆T , Q is different. Thus C depends on method of heating. We usually discuss CP (constant pressure) and CV (constant volume) for a gas system. Heat capacity per unit mass (or per particle) is called specific heat. We will learn work W and heat Q are not state function. 11. Thermal isolation: ...
... through ∆T , Q is different. Thus C depends on method of heating. We usually discuss CP (constant pressure) and CV (constant volume) for a gas system. Heat capacity per unit mass (or per particle) is called specific heat. We will learn work W and heat Q are not state function. 11. Thermal isolation: ...
Tutorial 1 / SS 2013
... p is the pressure in kg/(m . s²), V the volume in m 3, n the number of moles, R is the gas constant with R = 8,314 J . mol-1 . K-1 and T the temperature in K (0 °C = 273.15 K). An ideal gas is approximated by a gas with a very low density. b) Work done by an ideal gas (expansion): W = ∫V i Vf –pdV, ...
... p is the pressure in kg/(m . s²), V the volume in m 3, n the number of moles, R is the gas constant with R = 8,314 J . mol-1 . K-1 and T the temperature in K (0 °C = 273.15 K). An ideal gas is approximated by a gas with a very low density. b) Work done by an ideal gas (expansion): W = ∫V i Vf –pdV, ...
Chapter 12 Slide
... An ideal gas aborbs 5000 J of energy while doing 2000 J of work on the environment during a constant pressure process. (a) Calculate the change in the internal energy of the gas. (b) If the internal energy drops by 4500 J and 7500 J is expelled from the system, find the change in volume , assuming a ...
... An ideal gas aborbs 5000 J of energy while doing 2000 J of work on the environment during a constant pressure process. (a) Calculate the change in the internal energy of the gas. (b) If the internal energy drops by 4500 J and 7500 J is expelled from the system, find the change in volume , assuming a ...