Nervous System – General - Austin Community College
... every cell in our body responds to stimuli by changing its metabolism in one way or another ...
... every cell in our body responds to stimuli by changing its metabolism in one way or another ...
02. Peripheral Nervous System
... nervous system outside of CNS. ► Nerves carry information between the organs and CNS (sensory and motor neurons). ► Includes afferent neurons and efferent neurons. ► Afferent – neurons that collect information and transmit it toward the CNS. ► Efferent – neurons that transmit information away from t ...
... nervous system outside of CNS. ► Nerves carry information between the organs and CNS (sensory and motor neurons). ► Includes afferent neurons and efferent neurons. ► Afferent – neurons that collect information and transmit it toward the CNS. ► Efferent – neurons that transmit information away from t ...
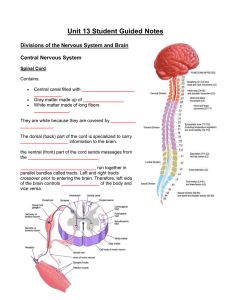
Unit 13 Student Guided Notes Divisions of the Nervous System and
... In the case where the hypothalamus detects that the effect of one of the hormones from the anterior pituitary is required, it releases a hormone-like substance called a releasing factor that travels through the very short blood vessel that is connected with the anterior pituitary. The effect of thi ...
... In the case where the hypothalamus detects that the effect of one of the hormones from the anterior pituitary is required, it releases a hormone-like substance called a releasing factor that travels through the very short blood vessel that is connected with the anterior pituitary. The effect of thi ...
SA2 REVISION WRK SHEET GRADE 5
... desertification 36) The pollutant responsible for hole in the ozone layer is __________ a) CO2 b) SO2 c) CO d) CFC 37) One of the best solutions to get rid of non-biodegradable wastes is ________ a) burning b) dumping c) burying d) recycling 38) Which of the following is biodegradable? ...
... desertification 36) The pollutant responsible for hole in the ozone layer is __________ a) CO2 b) SO2 c) CO d) CFC 37) One of the best solutions to get rid of non-biodegradable wastes is ________ a) burning b) dumping c) burying d) recycling 38) Which of the following is biodegradable? ...
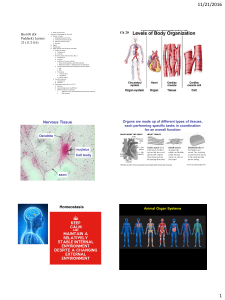
Part I: Levels of Biological Organization
... tissue. Brain tissue is a collection of cells, which because of their specialized structure are able to store and transmit information; a muscle cell could not perform the same function as a brain ...
... tissue. Brain tissue is a collection of cells, which because of their specialized structure are able to store and transmit information; a muscle cell could not perform the same function as a brain ...
Human Systems
... • Cells are specialized have specific structures and functions that allow them to perform chemical reactions inside our bodies ...
... • Cells are specialized have specific structures and functions that allow them to perform chemical reactions inside our bodies ...
Chapter 35 Directed Reading
... Impulses flow to and from the brain. It is made up of several main parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The ________________ is the largest and most prominent part of the brain. It is responsible for voluntary (________________) activities of the body. This is the sit ...
... Impulses flow to and from the brain. It is made up of several main parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem, thalamus, and hypothalamus. The ________________ is the largest and most prominent part of the brain. It is responsible for voluntary (________________) activities of the body. This is the sit ...
Nervous Tissue Homeostasis
... 13. What types of organisms undergo respiration simply by diffusion across their cell membranes or skin? 14. What types of organisms have gills? 15. Define the parts of the gill: gill arch, gill filaments, ...
... 13. What types of organisms undergo respiration simply by diffusion across their cell membranes or skin? 14. What types of organisms have gills? 15. Define the parts of the gill: gill arch, gill filaments, ...
A Trip Through The Human Body
... 18. What carries information throughout the body in the form of electrochemical signals called impulses? 19. What part of the nervous system has the responsibility for issuing nerve impulses and analyzing sensory data? What does it include? 20. What part of the nervous system has the responsibility ...
... 18. What carries information throughout the body in the form of electrochemical signals called impulses? 19. What part of the nervous system has the responsibility for issuing nerve impulses and analyzing sensory data? What does it include? 20. What part of the nervous system has the responsibility ...
Nervous System - Garnet Valley
... spinal cord to the muscles, skin, internal organs, and glands. ▪ 12 Nerves branch out from the brain ▪ 31 branch out from the spinal cord ...
... spinal cord to the muscles, skin, internal organs, and glands. ▪ 12 Nerves branch out from the brain ▪ 31 branch out from the spinal cord ...
Anatomy review
... 11) A nerve is made of a bundle of _____________________ 12)A sensory receptor turns a stimulus into ______________________ energy 13)Contrast sensory and motor neurons – check boxes Sensory neuron ...
... 11) A nerve is made of a bundle of _____________________ 12)A sensory receptor turns a stimulus into ______________________ energy 13)Contrast sensory and motor neurons – check boxes Sensory neuron ...
Respiratory system
... What does the nervous system respond to? • Stimuli • Neurons are able to respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses, and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells like muscle ...
... What does the nervous system respond to? • Stimuli • Neurons are able to respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses, and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells like muscle ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM IN HUMAN BEINGS
... 1) Sensory Nerves carry information from the sense organs and receptors to specific area of brain and spinal cord. Ex: sensory nerves of eye, ear, nose, tongue, skin etc 2) Motor nerves carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs. Stimulation of motor nerves make the muscles cont ...
... 1) Sensory Nerves carry information from the sense organs and receptors to specific area of brain and spinal cord. Ex: sensory nerves of eye, ear, nose, tongue, skin etc 2) Motor nerves carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs. Stimulation of motor nerves make the muscles cont ...
Function - Webster Elementary School
... Saturated Fats and / or lack of exercise. - Saturated Fats (plaque) build up and block the arteries that bring oxygen to the heart muscle (Coronary Arteries). - Lack of oxygen causes the heart muscle to die which really hurts a lot! - If enough of the heart muscle dies, the heart cannot function and ...
... Saturated Fats and / or lack of exercise. - Saturated Fats (plaque) build up and block the arteries that bring oxygen to the heart muscle (Coronary Arteries). - Lack of oxygen causes the heart muscle to die which really hurts a lot! - If enough of the heart muscle dies, the heart cannot function and ...
Central Nervous System {PowerPoint}
... masses of neurons accounts for the gray matter of the brain – Cerebral Cortex White Matter - Myelinated neurons gives neurons a white appearance – inner layer of cerebrum ...
... masses of neurons accounts for the gray matter of the brain – Cerebral Cortex White Matter - Myelinated neurons gives neurons a white appearance – inner layer of cerebrum ...
Nervous MusclesSkeleton
... electrical signals called impulses Cells that transmit these impulses are called neurons (basic units of nervous system) – 3 types of neurons 1. Sensory 2. Motor 3. Interneurons ...
... electrical signals called impulses Cells that transmit these impulses are called neurons (basic units of nervous system) – 3 types of neurons 1. Sensory 2. Motor 3. Interneurons ...
Maintaining the Inner Environment
... Systems are complementary. Both are active to some extent at the same time – not alternating. What happens during anger? ...
... Systems are complementary. Both are active to some extent at the same time – not alternating. What happens during anger? ...
Human (mammalian) Body Systems
... Human (mammalian) Body Systems Remember that all of your body systems are integrated and regulated by the neuroendocrine system (the coordination of the nervous and endocrine (hormones) systems. As time is limited, focus on the figures indicated. Digestive System ...
... Human (mammalian) Body Systems Remember that all of your body systems are integrated and regulated by the neuroendocrine system (the coordination of the nervous and endocrine (hormones) systems. As time is limited, focus on the figures indicated. Digestive System ...
spinal cord
... • Main communication link between brain and rest of body • 31 pair of spinal nerves branch out from spinal cord connecting brain to all of the diff. parts of body • Certain kinds of information, including some reflexes, are processed directly in the spinal cord ...
... • Main communication link between brain and rest of body • 31 pair of spinal nerves branch out from spinal cord connecting brain to all of the diff. parts of body • Certain kinds of information, including some reflexes, are processed directly in the spinal cord ...
Module 2 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... can also be divided into three categories. The central nervous system, or CNS, is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It is the center of your body and the center of control and coordination. The peripheral nervous system, or PNS, includes the nerves that reach the outer parts of your body. Finall ...
... can also be divided into three categories. The central nervous system, or CNS, is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It is the center of your body and the center of control and coordination. The peripheral nervous system, or PNS, includes the nerves that reach the outer parts of your body. Finall ...
Science Chapter 5 Study Sheet Name: My child studied for this test
... The respiratory system exchanges gases between air and blood. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and air sacs in the lungs. ...
... The respiratory system exchanges gases between air and blood. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and air sacs in the lungs. ...
Neuroscience

Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system. Traditionally, neuroscience has been seen as a branch of biology. However, it is currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, cognitive science, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics, medicine (including neurology), genetics, and allied disciplines including philosophy, physics, and psychology. It also exerts influence on other fields, such as neuroeducation, neuroethics, and neurolaw. The term neurobiology is usually used interchangeably with the term neuroscience, although the former refers specifically to the biology of the nervous system, whereas the latter refers to the entire science of the nervous system.The scope of neuroscience has broadened to include different approaches used to study the molecular, cellular, developmental, structural, functional, evolutionary, computational, and medical aspects of the nervous system. The techniques used by neuroscientists have also expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual nerve cells to imaging of sensory and motor tasks in the brain. Recent theoretical advances in neuroscience have also been aided by the study of neural networks.As a result of the increasing number of scientists who study the nervous system, several prominent neuroscience organizations have been formed to provide a forum to all neuroscientists and educators. For example, the International Brain Research Organization was founded in 1960, the International Society for Neurochemistry in 1963, the European Brain and Behaviour Society in 1968, and the Society for Neuroscience in 1969.